
The performance of gas turbine engines may be improved by increasing the tolerance of the turbine blades to hot gases emerging from the combustor. One approach to achieving high operating temperatures involves application of a thermal barrier coating (TBC) to the exterior surface of a blade, while passing cooling air through the blade. Typically, the blade is made from a high-temperature superalloy, such as Inconel
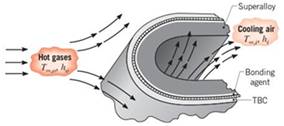
Consider conditions for which hot gases at
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 3 Solutions
Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer
- 40°C water with hwater = 800 W/m² K is flowing in a Pyrex tube. The inner and outer diameters of the tube are 25 mm and 35 mm. A thin metallic heater element bonded to the outer surface of the tube is being used to heat the water by transferring 600 W/m of thermal energy to the water flowing in the tube. The Pyrex tube and heater are covered with a 10-mm thick layer of foam insulation. The outer surface of the foam insulation is exposed to air at T = -5°C with hair = 12 W/m².K. The heater = air element must generate more than 600 W/m, because part of the heat being generated is lost to the air surrounding the foam insulation. Assume kp = 1.30 W/m K for Pyrex and k = 0.026 W/m K for the foam insulation. a) Find the temperature of the heater element needed to transfer 600 W/m of thermal energy to the water in the tube. b) Find the total rate at which the heater element must generate thermal energy. Water Pyrex tube, kp = 1.30 W/m.K = 40°C water hwater = 800 W/m².K Heater element Tair=…arrow_forwardPravinbhaiarrow_forwardQ1- An industrial freezer is design to operate with an internal air temperature of -20 °C when the external air temperature is 25 °C and the internal and external heat transfer coefficient are 12 W m?/K and 8 W m?/ K, respectively. The walls of the freezer are composite construction, comprising of an inner layer of plastic (k= 1 W/m K, and thickness of 3 mm), and an outer layer of stainless steel (k=16 W/m K, and thickness of 1 mm). Sandwiched between these two layers is a layer of insulation material with k=0.07 W/m K. Find the width of insulation that is required to reduce the convection heat loss to 15 W/m?. Support the solution by drawing. (25mark)arrow_forward
- answer provided is correctarrow_forwardA poor heat-conducting copper alloy (k = 45 BTU – ft/hr – ft² – °F) is drawn into 0.012-ft diameter wire for a critical aerospace application in an electronics enclosure. The conditions within the enclosure are maintained at 90°F by a forced air-cooling system. To keep the copper alloy below 270°F and to maximize heat transfer, the wire is to be covered with insulation (k = 0.03 BTU – ft/hr – ft² – °F ). The effective film coefficient for the insulation has been conservatively estimated as 2.0 BTU/hr – ft2 – °F. - - What insulation thickness should be used over the wire to maximize heat transfer? 2.arrow_forwardIndirect Cooling With Liquid Nitrogen. You are designing a system to cool an insulated silver plate of dimensions 2.00 cm × 2.00 cm × 0.60 cm. One end of a thermally insulated copper wire (diameter D = 2.70 mm and length L = 18.0 cm) is dipped into a vat of liquid nitrogen (T = 77.2 K), and the other end is attached to the bottom of the silver plate.(a) If the silver plate starts at room temperature (65.0 °F), what is the initial rate of heat flow between the plate and the liquid nitrogen reservoir?(b) Assuming the rate of heat flow calculated in part (a), estimate the temperature of the silver plate after 30.0 seconds.arrow_forward
- [2] An array of electronic chips is mounted within a sealed rectangular enclosure, and cooling is implemented by attaching an aluminum heat sink (k = 180 W/m K). The base of the heat sink has dimensions of w1 = W2 = 100 mm, while the 6 fins are of thickness t = 10 mm and pitch S = 18 mm. The fin length is Lr = 50 mm, and the base of the heat sink has a thickness of Lb = 10 mm. L -Chips Water u T Electronic package, P elec If cooling is implemented by water flow through the heat sink, with uo = 3 m/s and To = temperature Tb of the heat sink when power dissipation by the chips is Pelec = 1800 W? The average convection coefficient for surfaces of the fins and the exposed base may be estimated by assuming parallel flow over a flat plate. Properties of the water may be approximated as k = 0.62 W/m-K, p = 995 kg/m3, Cp = 4178 J/kg-K, v = 7.73 x 10-7 m2/s, and Pr = 5.2. 17°C, what is the base a.) Base temperature. А. 37.8°C B. 43.9°C С. 31.4°С D. 46.2°Carrow_forwardA bare fuel rod has a diameter of 0.373 in and length of 12 ft. The volumetric heat generation rate for this rod is q′′′ = 10,000 kW/ft3. The heat produced by the rod is removed by water used as the coolant, at 2250 psia and 575 F. Find the heat transfer coefficient between the bare fuel rod and the coolant.The fuel rod surface temperature is 675 Farrow_forwardIndirect Cooling With Liquid Nitrogen. You are designing a system to cool an insulated silver plate of dimensions 2.00 cm × 2.00 cm x 0.40 cm. One end of a thermally insulated copper wire (diameter D = 2.70 mm and length L = 12.0 cm) is dipped into a vat of liquid nitrogen (T = 77.2 K), and the other end is attached to the bottom of the silver plate. (a) If the silver plate starts at room temperature (73.0°F), what is the initial rate of heat flow between the plate and the liquid nitrogen reservoir? (b) Assuming the rate of heat flow calculated in part (a), estimate the temperature of the silver plate after 30.0 seconds.arrow_forward
- Consider two long, slender rods of the same diameter but different materials. One end of each rod is attached to a base surface maintained at 100 °C, while the surfaces of the rods are exposed to ambient air at 20 °C. By traversing the length of each rod with a thermocouple, it was observed that the temperatures of the rods were equal at the positions xд =0.15 m and x = 0.075 m, where x is measured from the base surface. If the thermal conductivity of rod A is known to be k₁ = 70 W/m*K, determine the value of kg for rod B. ASSUMPTIONS: (1) Steady-state, (2) One-dimensional conduction along rods, (3) Constant properties, (4) Negligible radiation, (5) Negligible contact resistance at base, (6) Infinitely long rods, (7) Rods are identical except for their thermal conductivity.arrow_forwardA composite plane wall consisting of materials, 1.5-in steel (k = 312 BTU-in/HR.ft2.0F) and 2-in aluminum (k = 1400 BTU-in/HR.ft2.0F), separates a hot gas at Ti = 2000F, hi = 2 BTU/HR.ft2.0F, from cold gas at To = 80 deg F, ho = 5. If the hot fluid is on the aluminum side, find: a) Transmittance, U; b) The heat through 100 sq. ft of the surface under steady state condition and c) The interface temperature at the junction of the metals.arrow_forwardDetermine the time needed to decrease the temperature of a solid cylinder from 40 C to 35 C if the ambient temperature is equal to 31 C. The cylinder has a length equals to 0.9 m and diameter equals to 100 mm. The heat convective coefficient is equal to 9 W/m^2.K. The cylinder has a conductivity equals to 2 W/m.K, a density equals to 1200 kg/m^3 and its Cp is equal to 4.700 kJ/kgK.arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





