
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
The structure of triphosphate of guanosine has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Composition of
Sugar: In both DNA and RNA, sugar portion is found. In DNA, the sugar is D-ribose, where at 2’hydroxyl group is absent and in RNA, the hydroxyl group is present at 2’.
Nitrogenous bases: Five types of nitrogenous bases (has unique one-letter code A, G, T, U, and C) are derived from two parent compounds called purine and pyrimidine. The purine derivatives are Adenine and Guanine are two fused nitrogen containing rings. The pyrimidine derivatives are Thymine, Cytosine, and Uracil are only one nitrogen containing six-membered ring. Adenine, Guanine, Thymine, and Cytosine are the nitrogenous bases present in DNA. Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine and Uracil are the nitrogenous bases present in RNA.
Nucleotide: (Nucleoside + phosphate)
Nucleotides are the building blocks of nuclei acids; monomers of DNA and RNA
Nucleoside and its naming: The combination of monosaccharide (sugar) and nitrogenous base is known as nucleoside. The nucleoside names are the nitrogenous base name modified with criteria. While naming nucleoside of purine derivatives the suffix ‘-osine’ is included and for pyrimidine derivatives the suffix ‘-idine’ is used. No prefix used for the nucleosides containing ribose and the prefix ‘deoxy-’ is used for deoxyribose.
Naming nucleotide: At the end of the nucleoside, phosphate group is added. For example, 5’-monophosphate means adding one phosphate group at 5’carbon in the sugar ring. Uridine monophosphate can be written as UMP.
Numbering the atoms in sugar and base rings:
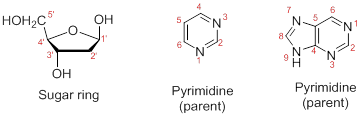
In order to distinguish the atoms in the sugar of a nucleoside and atoms of a base ring, numbers without prime is used for atoms in the base ring and numbers with prime used for the atoms in the sugar ring.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 26 Solutions
FUND.OF GEN CHEM CHAP 1-13 W/ACCESS
- Draw the product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. H H ⚫OH HO- -H H- -OH H- -OH CH2OH Ag*, NH4OH, H2O Draw Fischer Projectionarrow_forwardDraw the product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. H₂O -OH H ⚫OH HO H HO- CH2OH Cu2+ Draw Fischer Projectionarrow_forwardDraw the product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. H、 H -OH H ⚫OH H -OH CH2OH Fehlings' solution ⑤ Draw Fischer Projectionarrow_forward
- Draw the product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. HO C=0 H ⚫OH H ⚫OH HO- H HO H CH2OH Tollens' solution Draw Fischer Projectionarrow_forwardDraw the product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. H-C=O HO H HO H H- ⚫OH HO H CH2OH HNO3, H2O Draw Fischer Projectionarrow_forwardDraw the product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. HO HO- HO H HO ∙H HO CH2OH NaBH4, CH3OH Draw Fischer Projectionarrow_forward
- Draw the product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Но сво HO H HO H H OH H -OH CH2OH H2 Pd Draw Fischer Projectionarrow_forwardDraw the Haworth projection for Gulose-ẞ-1,6-sorbose and answer the following questions. (Gulose will be in the pyranose form and Sorbose will be in the furanose form) a. Label the reducing and nonreducing ends of the disaccharide b. Label the glycosidic bond c. Circle the anomeric carbons and label them as hemiacetals or acetals. d. Can this disaccharide undergo mutarotation?arrow_forwardDraw the product of the reaction below. Ignore inorganic byproducts. H OH HO HO HO ·H H OH H OH excess CH3CH2I KOHarrow_forward
- Draw the Haworth structures for the following: a. α-D-Gulopyranose b. ẞ-D-Sorbofuranose c. The two possible isomers of a-D-altrose (furanose and pyranose forms)arrow_forwardDraw the product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. HO H ⚫OH HO- ∙H H- -OH H ⚫OH CH2OH HNO3, H2Oarrow_forwardDraw the product of the reaction below. Ignore inorganic byproducts. HO CH2OH OH OH OH excess CHзI Ag2Oarrow_forward
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning





