
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
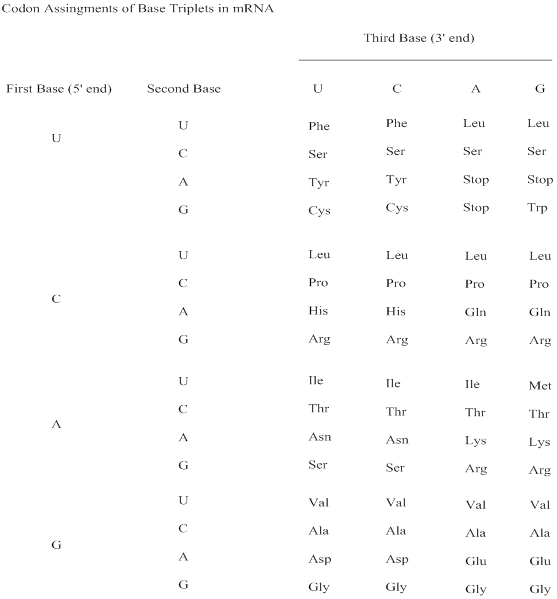
The amino acids those have most codons and least codons; reason for multiple codons for certain amino acids has to be interpreted.
Concept Introduction:
Codon: A sequence of three ribonucleotides in the mRNA chain that codes for a specific amino acid; also a three-
Genetic code: The sequence of nucleotides, coded in triplets (codons) in mRNA that determines the sequence of amino acids in protein synthesis.
Translation: A tRNA molecule is a single polynucleotide chain held together by regions of base pairing in a partially helical structure. An amino acid is bonded to its specific tRNA by an ester linkage. Connecting specific amino acid at end of the tRNA is known as charging tRNA. Once done, tRNA is ready to be used in the protein synthesis.
At the other end of the tRNA, three anticodons are present which are complementary to the codons present in mRNA. Once the anticodons pairs off with codons, the amino acid at terminal end of the tRNA is delivered and attached to the growing protein chain.
Illustrated relationships are:
DNA informational strand: 5’ ATG CCA GTA GGC CAC TTG TCA 3’
DNA Template strand: 3’ TAC GGT CAT CCG GTG AAC AGT 5’
mRNA: 5’ AUG CCA GUA GGC CAC UUG UCA 3’
protein: Met Pro Val Gly His Leu Ser
Notice: 5’ end of the mRNA strand codes for the N-terminal amino acid, whereas the 3’ end of the mRNA strand codes for the C-terminal amino acid. Proteins are always written N-terminal to C-terminal, reading left to right.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 26 Solutions
FUND.OF GEN CHEM CHAP 1-13 W/ACCESS
- In a diffraction experiment of a native crystal, intensity of reflection (-1 0 6) is equivalent to the intensity of reflection (1 0 -6). true or false?arrow_forwardin an x-ray diffraction experiment, moving the detector farther away from the crystal will allow collection of reflection of reflections with high Miller indices. true or false?arrow_forwardShow the mechanism for the acid-catalyzed formation of an [α-1,6] glycosidic linkagebetween two molecules of α-D-glucopyranose.arrow_forward
- Label the following polysaccharide derivatives as reducing or nonreducing. a. C. b. HO CH₂OH CH2OH OH OH OH OH OH HOCH₂ OH OH OH HOCH₂ HO HO HO OH OH ΙΟ CH₂OH OH OH "OH OHarrow_forwardFor a red blood cell (erythrocyte) undergoing active glycolysis, briefly explain how increases in concentration of the following factors are likely to affect glycolytic flux. a. ATP b. AMP c. F-1,6-BP d. F-2,6-BP e. Citrate f. Glucose-6-phosphatearrow_forwardThe ∆G°’ for hydrolysis of phosphoenol pyruvate is -62.2 kJ/mol. The standard freeenergy of ATP hydrolysis is -30.5 kJ/mol. A. What is the standard free energy and K eq of the spontaneous reaction betweenADP/ATP and phosphoenol pyruvate. B. Repeat A for F-1,6-BP (∆G°’=-16.7 kJ/mol) and 1,3-BPG (∆G°’=-49.6 kJ/mol)hydrolysis. C. If the ATP and ADP concentrations are 8mM and 1mM respectively, what would bethe ratio of pyruvate/phosphoenolpyruvate at equilibrium?arrow_forward
- Answerarrow_forward13. Which one is the major organic product of the following sequence of reactions? A OH (CH3)2CHCH2COOH SOCI2 CH3OH 1. CH3MgBr 2. H₂O, H+ B C D OH E OHarrow_forward14. Which one is the major organic product of the following sequence of reactions? (CH3)2CH-COCI CH3OH 1. DIBALH, -78°C 1. PhCH2MgBr ? 2. H2O, HCI 2. H2O, HCI OH OMe A Ph B Ph OH Ph C OMe Ph D E OH .Pharrow_forward
- 6. Which one is the major organic product obtained from the following reaction? CO₂Me 1. LiAlH4 2. H₂O CH₂OH CH₂OCH3 5555 HO A B HO C HO D CH₂OH E ?arrow_forward1. (10 points) Pulverized coal pellets, which may be ° approximated as carbon spheres of radius r = 1 mm, are burned in a pure oxygen atmosphere at 1450 K and 1 atm. Oxygen is transferred to the particle surface by diffusion, where it is consumed in the reaction C + O₂ →> CO₂. The reaction rate is first order and of the form No2 = k₁C₁₂(r), where k₁ = 0.1 m/s. Neglecting changes in r, determine the steady-state O₂ molar consumption rate in kmol/s. At 1450 K, the binary diffusion coefficient for O2 and CO2 is 1.71 x 10ª m²/s.arrow_forward2. (20 points) Consider combustion of hydrogen gas in a mixture of hydrogen and oxygen adjacent to the metal wall of a combustion chamber. Combustion occurs at constant temperature and pressure according to the chemical reaction 2H₂+ O₂→ 2H₂O. Measurements under steady-state conditions at 10 mm from the wall indicate that the molar concentrations of hydrogen, oxygen, and water vapor are 0.10, 0.10, and 0.20 kmol/m³, respectively. The generation rate of water vapor is 0.96x102 kmol/m³s throughout the region of interest. The binary diffusion coefficient for each of the species (H, O̟, and H₂O) in the remaining species is 0.6 X 10-5 m²/s. (a) Determine an expression for and make a qualitative plot of C as a function of distance from the wall. H2 (b) Determine the value of C2 at the wall. H2 (c) On the same coordinates used in part (a), sketch curves for the concentrations of oxygen and water vapor. This will require you to calculate Co, and C. 02 H20 (d) What is the molar flux of water…arrow_forward
 Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning





