
(a)
Interpretation:
The type of given carbonyl compound needs to be determined.
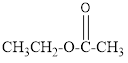
Concept introduction:
The functional group is the group present on the main carbon chain of an organic compound. It determines the chemical properties and the type of reactions an organic compound can show. The name of the group depends on the atoms present in the group for example an −OH group contains O and H atom thus, it is a hydroxyl group. The different
Name of some functional groups are: -OH: alcohol, -CHO:
Answer to Problem 14SSC
Ester.
Explanation of Solution
The given organic compound is as follows:
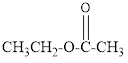
In the above organic compound, the general formula is R-COOR’ thus, it is an ester.
(b)
Interpretation:
The type of given carbonyl compound needs to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The functional group is the group present on the main carbon chain of an organic compound. It determines the chemical properties and the type of reactions an organic compound can show. The name of the group depends on the atoms present in the group for example an −OH group contains O and H atom thus, it is a hydroxyl group. The different functional groups are named according to IUPAC rule.
Name of some functional groups are: -OH: alcohol, -CHO: aldehyde, -COOH: carboxylic acid etc.
Answer to Problem 14SSC
Explanation of Solution
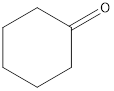
The given organic compound is as follows:
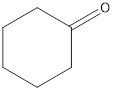
In the above organic compound, the functional group is −CO- which is a ketone group. Thus, it is a ketone.
(c)
Interpretation:
The type of given carbonyl compound needs to be determined.

Concept introduction:
The functional group is the group present on the main carbon chain of an organic compound. It determines the chemical properties and the type of reactions an organic compound can show. The name of the group depends on the atoms present in the group for example an −OH group contains O and H atom thus, it is a hydroxyl group. The different functional groups are named according to IUPAC rule.
Name of some functional groups are: -OH: alcohol, -CHO: aldehyde, -COOH: carboxylic acid etc.
Answer to Problem 14SSC
Amide.
Explanation of Solution
The given organic compound is as follows:

In the above organic compound, the general formula is RCONH2. Here, -CONH2 is an amide functional group thus, it is an amide.
(d)
Interpretation:
The type of given carbonyl compound needs to be determined.
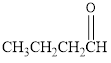
Concept introduction:
The functional group is the group present on the main carbon chain of an organic compound. It determines the chemical properties and the type of reactions an organic compound can show. The name of the group depends on the atoms present in the group for example an −OH group contains O and H atom thus, it is a hydroxyl group. The different functional groups are named according to IUPAC rule.
Name of some functional groups are: -OH: alcohol, -CHO: aldehyde, -COOH: carboxylic acid etc.
Answer to Problem 14SSC
Aldehyde.
Explanation of Solution
The given organic compound is as follows:
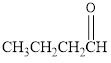
In the above organic compound, the general formula is R-CHO, here, -CHO is an aldehyde functional group thus, it is an aldehyde.
Chapter 22 Solutions
Chemistry: Matter and Change
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
- Using reaction free energy to predict equilibrium composition Consider the following equilibrium: 2NO(g) +Cl₂ (g) = 2NOC1 (g) AGº = -41. kJ Now suppose a reaction vessel is filled with 8.90 atm of chlorine (C12) and 5.71 atm of nitrosyl chloride (NOC1) at 1075. °C. Answer the following questions about this system: rise Under these conditions, will the pressure of NOCI tend to rise or fall? x10 fall Is it possible to reverse this tendency by adding NO? In other words, if you said the pressure of NOCI will tend to rise, can that be changed to a tendency to fall by adding NO? Similarly, if you said the pressure of NOCI will tend to fall, can that be changed to a tendency to rise by adding NO? yes no If you said the tendency can be reversed in the second question, calculate the minimum pressure of NO needed to reverse it. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. atm ☑ 18 Ararrow_forwardIdentifying the major species in weak acid or weak base equilibria The preparations of two aqueous solutions are described in the table below. For each solution, write the chemical formulas of the major species present at equilibrium. You can leave out water itself. Write the chemical formulas of the species that will act as acids in the 'acids' row, the formulas of the species that will act as bases in the 'bases' row, and the formulas of the species that will act as neither acids nor bases in the 'other' row. You will find it useful to keep in mind that HCN is a weak acid. acids: 0.29 mol of NaOH is added to 1.0 L of a 1.2M HCN solution. bases: ☑ other: 0.09 mol of HCl is added to acids: 1.0 L of a solution that is bases: 0.3M in both HCN and KCN. other: 0,0,... ? 00. 18 Ar 日arrow_forwardIdentifying the major species in weak acid or weak base equilibria The preparations of two aqueous solutions are described in the table below. For each solution, write the chemical formulas of the major species present at equilibrium. You can leave out water itself. Write the chemical formulas of the species that will act as acids in the 'acids' row, the formulas of the species that will act as bases in the 'bases' row, and the formulas of the species that will act as neither acids nor bases in the 'other' row. You will find it useful to keep in mind that HF is a weak acid. acids: 0.2 mol of KOH is added to 1.0 L of a 0.5 M HF solution. bases: Х other: ☐ acids: 0.10 mol of HI is added to 1.0 L of a solution that is 1.4M in both HF and NaF. bases: other: ☐ 0,0,... ด ? 18 Ararrow_forward
- Identifying the major species in weak acid or weak base equilibria The preparations of two aqueous solutions are described in the table below. For each solution, write the chemical formulas of the major species present at equilibrium. You can leave out water itself. Write the chemical formulas of the species that will act as acids in the 'acids' row, the formulas of the species that will act as bases in the 'bases' row, and the formulas of the species that will act as neither acids nor bases in the 'other' row. You will find it useful to keep in mind that NH3 is a weak base. acids: ☐ 1.8 mol of HCl is added to 1.0 L of a 1.0M NH3 bases: ☐ solution. other: ☐ 0.18 mol of HNO3 is added to 1.0 L of a solution that is 1.4M in both NH3 and NH₁Br. acids: bases: ☐ other: ☐ 0,0,... ? 000 18 Ar B 1arrow_forwardUsing reaction free energy to predict equilibrium composition Consider the following equilibrium: 2NH3 (g) = N2 (g) +3H₂ —N2 (g) AGº = 34. kJ Now suppose a reaction vessel is filled with 4.19 atm of ammonia (NH3) and 9.94 atm of nitrogen (N2) at 378. °C. Answer the following questions about this system: rise Under these conditions, will the pressure of NH 3 tend to rise or fall? ☐ x10 fall Х Is it possible to reverse this tendency by adding H₂? In other words, if you said the pressure of NH 3 will tend to rise, can that be changed to a tendency to fall by adding H₂? Similarly, if you said the pressure of NH3 will tend to fall, can that be changed to a tendency to rise by adding H₂? If you said the tendency can be reversed in the second question, calculate the minimum pressure of H₂ needed to reverse it. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. yes no atm 00. 18 Ar 무ㅎ ?arrow_forwardIdentifying the major species in weak acid or weak base equilibria The preparations of two aqueous solutions are described in the table below. For each solution, write the chemical formulas of the major species present at equilibrium. You can leave out water itself. Write the chemical formulas of the species that will act as acids in the 'acids' row, the formulas of the species that will act as bases in the 'bases' row, and the formulas of the species that will act as neither acids nor bases in the 'other' row. You will find it useful to keep in mind that HF is a weak acid. 2.2 mol of NaOH is added to 1.0 L of a 1.4M HF solution. acids: П bases: Х other: ☐ ப acids: 0.51 mol of KOH is added to 1.0 L of a solution that is bases: 1.3M in both HF and NaF. other: ☐ 00. 18 Ararrow_forward
- Using reaction free energy to predict equilibrium composition Consider the following equilibrium: N2O4 (g) 2NO2 (g) AG⁰ = 5.4 kJ Now suppose a reaction vessel is filled with 1.68 atm of dinitrogen tetroxide (N204) at 148. °C. Answer the following questions about this system: rise Under these conditions, will the pressure of N2O4 tend to rise or fall? x10 fall Is it possible to reverse this tendency by adding NO2? In other words, if you said the pressure of N2O4 will tend to rise, can that be changed to a tendency to fall by adding NO2? Similarly, if you said the pressure of N2O4 will tend to fall, can that be changed to a tendency to rise by adding NO2? If you said the tendency can be reversed in the second question, calculate the minimum pressure of NO 2 needed to reverse it. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. yes no 0.42 atm ☑ 5 0/5 ? مله Ararrow_forwardHomework 13 (Ch17) Question 4 of 4 (1 point) | Question Attempt: 2 of 2 ✓ 1 ✓ 2 = 3 4 Time Remaining: 4:25:54 Using the thermodynamic information in the ALEKS Data tab, calculate the standard reaction free energy of the following chemical reaction: 2CH3OH (g)+302 (g) → 2CO2 (g) + 4H₂O (g) Round your answer to zero decimal places. ☐ kJ x10 ☐ Subm Check 2020 Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Cearrow_forwardIdentifying the major species in weak acid or weak base equilibria Your answer is incorrect. • Row 2: Your answer is incorrect. • Row 3: Your answer is incorrect. • Row 6: Your answer is incorrect. 0/5 The preparations of two aqueous solutions are described in the table below. For each solution, write the chemical formulas of the major species present at equilibrium. You can leave out water itself. Write the chemical formulas of the species that will act as acids in the 'acids' row, the formulas of the species that will act as bases in the 'bases' row, and the formulas of the species that will act as neither acids nor bases in the 'other' row. You will find it useful to keep in mind that HF is a weak acid. acids: HF 0.1 mol of NaOH is added to 1.0 L of a 0.7M HF solution. bases: 0.13 mol of HCl is added to 1.0 L of a solution that is 1.0M in both HF and KF. Exponent other: F acids: HF bases: F other: K 1 0,0,... ? 000 18 Ararrow_forward
- Using reaction free energy to predict equilibrium composition Consider the following equilibrium: 2NOCI (g) 2NO (g) + Cl2 (g) AGº =41. kJ Now suppose a reaction vessel is filled with 4.50 atm of nitrosyl chloride (NOCI) and 6.38 atm of chlorine (C12) at 212. °C. Answer the following questions about this system: ? rise Under these conditions, will the pressure of NOCI tend to rise or fall? x10 fall Is it possible to reverse this tendency by adding NO? In other words, if you said the pressure of NOCI will tend to rise, can that be changed to a tendency to fall by adding NO? Similarly, if you said the pressure of NOCI will tend to fall, can that be changed to a tendency to rise by adding NO? yes no If you said the tendency can be reversed in the second question, calculate the minimum pressure of NO needed to reverse it. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. 0.035 atm ✓ G 00. 18 Ararrow_forwardHighlight each glycosidic bond in the molecule below. Then answer the questions in the table under the drawing area. HO- HO- -0 OH OH HO NG HO- HO- OH OH OH OH NG OHarrow_forward€ + Suppose the molecule in the drawing area below were reacted with H₂ over a platinum catalyst. Edit the molecule to show what would happen to it. That is, turn it into the product of the reaction. Also, write the name of the product molecule under the drawing area. Name: ☐ H C=0 X H- OH HO- H HO- -H CH₂OH ×arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





