
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The structure of organic compound with 4 carbon atoms and an ester group needs to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The organic compounds generally contain carbon atoms. The naming of organic compounds is done by considering three main terms which are prefix, suffix and the root name. The longest chain in the compound is first identified and named that will be the root name for the compound. For example, if there are 3 carbon atoms in the longest chain, the root name will be “prop”. To determine the suffix,
Explanation of Solution
According to the question, there are 4 carbon atoms in the main chain. Also, there is an ester group. The general formula of an ester is
Now, if there are 4 carbon atoms in the main chain, the structure of compound will be:
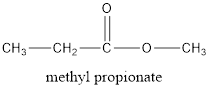
(b)
Interpretation:
The structure of organic compound with 4 carbon atoms and an aldehyde group needs to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The organic compounds generally contain carbon atoms. The naming of organic compounds is done by considering three main terms which are prefix, suffix and the root name. The longest chain in the compound is first identified and named that will be the root name for the compound. For example, if there are 3 carbon atoms in the longest chain, the root name will be “prop”. To determine the suffix, functional group should be identified. For example, alcohol group will have suffix −ol, aldehyde will have suffix −al. If there is no functional group the suffix will be −ane. In the last step, side groups are identified and named. Prefix is used to give number of side groups and substituent’s present on the main carbon chain.
Explanation of Solution
According to the question, there are 4 carbon atoms in the main chain. Also, there is an aldehyde group. The general formula of an aldehyde is
Now, if there are 4 carbon atoms in the main chain, the structure of compound will be:

(c)
Interpretation:
The structure of organic compound with 4 carbon atoms and an ether group needs to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The organic compounds generally contain carbon atoms. The naming of organic compounds is done by considering three main terms which are prefix, suffix and the root name. The longest chain in the compound is first identified and named that will be the root name for the compound. For example, if there are 3 carbon atoms in the longest chain, the root name will be “prop”. To determine the suffix, functional group should be identified. For example, alcohol group will have suffix −ol, aldehyde will have suffix −al. If there is no functional group the suffix will be −ane. In the last step, side groups are identified and named. Prefix is used to give number of side groups and substituent’s present on the main carbon chain.
Explanation of Solution
According to the question, there are 4 carbon atoms in the main chain. Also, there is an ether group. The general formula of ether is
Now, if there are 4 carbon atoms in the main chain, the structure of compound will be:
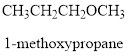
The other possible structure is as follows:
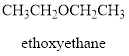
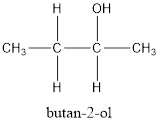
(d)
Interpretation:
The structure of organic compound with 4 carbon atoms and an alcohol group needs to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The organic compounds generally contain carbon atoms. The naming of organic compounds is done by considering three main terms which are prefix, suffix and the root name. The longest chain in the compound is first identified and named that will be the root name for the compound. For example, if there are 3 carbon atoms in the longest chain, the root name will be “prop”. To determine the suffix, functional group should be identified. For example, alcohol group will have suffix −ol, aldehyde will have suffix −al. If there is no functional group the suffix will be −ane. In the last step, side groups are identified and named. Prefix is used to give number of side groups and substituent’s present on the main carbon chain.
Explanation of Solution
According to the question, there are 4 carbon atoms in the main chain. Also, there is an alcohol group. The general formula of alcohol is
Now, if there are 4 carbon atoms in the main chain, the structure of compound will be:
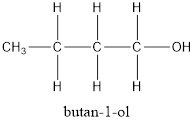 or
or
The other possible structure is as follows:
Chapter 22 Solutions
Chemistry: Matter and Change
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
- A block of zinc has an initial temperature of 94.2 degrees celcius and is immererd in 105 g of water at 21.90 degrees celcius. At thermal equilibrium, the final temperature is 25.20 degrees celcius. What is the mass of the zinc block? Cs(Zn) = 0.390 J/gxdegrees celcius Cs(H2O) = 4.18 J/gx degrees celcusarrow_forwardPotential Energy (kJ) 1. Consider these three reactions as the elementary steps in the mechanism for a chemical reaction. AH = -950 kJ AH = 575 kJ (i) Cl₂ (g) + Pt (s) 2C1 (g) + Pt (s) Ea = 1550 kJ (ii) Cl (g)+ CO (g) + Pt (s) → CICO (g) + Pt (s) (iii) Cl (g) + CICO (g) → Cl₂CO (g) Ea = 2240 kJ Ea = 2350 kJ AH = -825 kJ 2600 2400 2200 2000 1800 1600 1400 1200 1000 a. Draw the potential energy diagram for the reaction. Label the data points for clarity. The potential energy of the reactants is 600 kJ 800 600 400 200 0 -200- -400 -600- -800- Reaction Progressarrow_forwardCan u help me figure out the reaction mechanisms for these, idk where to even startarrow_forward
- Hi, I need your help with the drawing, please. I have attached the question along with my lab instructions. Please use the reaction from the lab only, as we are not allowed to use outside sources. Thank you!arrow_forwardHi, I need your help i dont know which one to draw please. I’ve attached the question along with my lab instructions. Please use the reaction from the lab only, as we are not allowed to use outside sources. Thank you!arrow_forward5. Write the formation reaction of the following complex compounds from the following reactants: 6. AgNO₃ + K₂CrO₂ + NH₄OH → 7. HgNO₃ + excess KI → 8. Al(NO₃)₃ + excess NaOH →arrow_forward
- Indicate whether the product formed in the reaction exhibits tautomerism. If so, draw the structure of the tautomers. CO₂C2H5 + CH3-NH-NH,arrow_forwardDraw the major product of this reaction N-(cyclohex-1-en-1-yl)-1-(pyrrolidino) reacts with CH2=CHCHO, heat, H3O+arrow_forwardDraw the starting material that would be needed to make this product through an intramolecular Dieckmann reactionarrow_forward
- Draw the major product of this reaction. Nitropropane reacts + pent-3-en-2-one reacts with NaOCH2CH3, CH3CHOHarrow_forwardIndicate whether the product formed in the reaction exhibits tautomerism. If so, draw the structure of the tautomers. OC2H5 + CoHs-NH-NH,arrow_forwardExplain how substitutions at the 5-position of barbituric acid increase the compound's lipophilicity.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





