
Concept explainers
Predict When sodium metal reacts with water, it produces sodium hydroxide, hydrogen gas, and heat. Write balanced chemical equations for 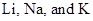 reacting with water. Use Figure 9.13 to predict the order of the amount ofheat released from least to most amount of heat released.
reacting with water. Use Figure 9.13 to predict the order of the amount ofheat released from least to most amount of heat released.
Interpretation:
The balanced chemical equations for reaction of Li, Na and K with water needs to be determined. The order of the amount of heat released from least to most needs to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The reactivity series of metals is as follows:
Lithium > Rubidium > Potassium > Calcium > Sodium > Magnesium > Aluminium > Manganese > Zinc > Iron > Nickel > Tin > Lead > Copper > Silver > Platinum > Gold
Answer to Problem 121A
Lithium reaction releases maximum amount of heat which is followed by the potassium reaction and lastly by the sodium reaction.
Following are the complete balanced reactions:
Explanation of Solution
The reactivity series of metals is as follows:
Lithium > Rubidium > Potassium > Calcium > Sodium > Magnesium > Aluminium > Manganese > Zinc > Iron > Nickel > Tin > Lead > Copper > Silver > Platinum > Gold
On the basis of the order of reactivity series of metals we can conclude that Lithium reaction releases maximum amount of heat which is followed by the potassium reaction and lastly by the sodium reaction.
Following are the complete balanced reactions:
Lithium reaction releases maximum amount of heat which is followed by the potassium reaction and lastly by the sodium reaction. This can be concluded on the basis of reactivity series of metals.
Following are the complete balanced reactions:
Chapter 9 Solutions
Chemistry: Matter and Change
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
Chemistry: The Central Science (14th Edition)
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
- In the electrode Pt, H2(1 atm) | H+(a=1), if the electrode balance potential is -0.118 V and the interface potential difference is +5 mV. The current voltage will be 0.005 - (-0.118) = 0.123 V ¿Correcto?arrow_forwardIn the electrode Pt, H2(1 atm) | H+(a=1) at 298K is 0.79 mA cm-2. If the balance potential of the electrode is -0.118 V and the potential difference of the interface is +5 mV. Determine its potential.arrow_forwardIn one electrode: Pt, H2(1 atm) | H+(a=1), the interchange current density at 298K is 0.79 mA·cm-2. If the voltage difference of the interface is +5 mV. What will be the correct intensity at pH = 2?. Maximum transfer voltage and beta = 0.5.arrow_forward
- In a Pt electrode, H2(1 atm) | H+(a=1), the interchange current density of an electrode is 0.79 mA cm-2. ¿Qué corriente flow across the electrode of área 5 cm2 when the difference in potential of the interface is +5 mV?.arrow_forwardIf the current voltage is n = 0.14 V, indicate which of the 2 voltage formulas of the ley of Tafel must be applied i a a) == exp (1-B). xp[(1 - ß³): Fn Fn a b) == exp B RT RTarrow_forwardIf the current voltage is n = 0.14 V. Indicate which of the 2 formulas must be applied a) = a T = i exp[(1 - p) F Fn Fn b) i==exp B RTarrow_forward
- Topic: Photochemistry and Photophysics of Supramoleculesarrow_forwardTwo cations that exchange an electron in an interface, the exchange density is worth 1.39 mA/cm2 and the current density is worth 15 mA/cm2 at 25°C. If the overvoltage is 0.14 V, calculate the reaction rate and symmetry factor. Data: R = 8,314 J mol-1 k-1: F = 96500 Carrow_forwardWith the help of the Tafel line, it is estimated that the interchange density of the VO2+/VO2+ system on the carbon paper has a value of 3 mA cm-2. Calculate a) the current density if the voltage has a value of 1.6 mV and the temperature is 25°C. b) the beta value of the anódico process if the Tafel pendulum is 0.6 V at 25°C. Data: R = 8.314 JK-1mol-1, y F = 96485 C mol-1.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





