
Interpretation:
Formula for ionic compound formed by magnesium and chloride needs to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Ionic compounds are formed as the result of formation of positive as well as negative ions. Electrons are basically transformed from one atom to other for formation of rare gas electron structure for each ion.
The atom that forms a positive ion will loses electrons to the atom that basically gains electrons for formation of a negative ion.
Answer to Problem 20PP
Formula is
Explanation of Solution
Formula for the ionic compounds formed by magnesium and chloride is
The charge on Mg ion is +2 and that on Cl ion is -1 thus, to from neutral compound, 1 mol of Mg ion should react with 2 mol of Cl ion.
Chemical equation is represented as follows:
Here, 2 electrons from Mg are transferred to 2 Cl atoms (1 electron each).
The electronic configuration can be represented as follows:
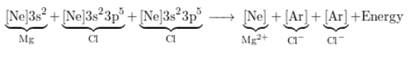
Therefore,
Chapter 7 Solutions
Glencoe Chemistry: Matter and Change, Student Edition
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
- (15 pts) Consider the molecule B2H6. Generate a molecular orbital diagram but this time using a different approach that draws on your knowledge and ability to put concepts together. First use VSEPR or some other method to make sure you know the ground state structure of the molecule. Next, generate an MO diagram for BH2. Sketch the highest occupied and lowest unoccupied MOs of the BH2 fragment. These are called frontier orbitals. Now use these frontier orbitals as your basis set for producing LGO's for B2H6. Since the BH2 frontier orbitals become the LGOS, you will have to think about what is in the middle of the molecule and treat its basis as well. Do you arrive at the same qualitative MO diagram as is discussed in the book? Sketch the new highest occupied and lowest unoccupied MOs for the molecule (B2H6).arrow_forwardQ8: Propose an efficient synthesis of cyclopentene from cyclopentane.arrow_forwardQ7: Use compound A-D, design two different ways to synthesize E. Which way is preferred? Please explain. CH3I ONa NaOCH 3 A B C D E OCH3arrow_forward
- Predict major product(s) for the following reactions. Note the mechanism(s) of the reactions (SN1, E1, SN2 or E2).arrow_forward(10 pts) The density of metallic copper is 8.92 g cm³. The structure of this metal is cubic close-packed. What is the atomic radius of copper in copper metal?arrow_forwardPredict major product(s) for the following reactions. Note the mechanism(s) of the reactions (SN1, E1, SN2 or E2).arrow_forward
- Predict major product(s) for the following reactions. Note the mechanism(s) of the reactions (SN1, E1, SN2 or E2).arrow_forwardQ3: Rank the following compounds in increasing reactivity of E1 and E2 eliminations, respectively. Br ca. go do A CI CI B C CI Darrow_forwardQ5: Predict major product(s) for the following reactions. Note the mechanism(s) of the reactions (SN1, E1, SN2 or E2). H₂O דיי "Br KN3 CH3CH2OH NaNH2 NH3 Page 3 of 6 Chem 0310 Organic Chemistry 1 HW Problem Sets CI Br excess NaOCH 3 CH3OH Br KOC(CH3)3 DuckDuckGarrow_forward
- Q4: Circle the substrate that gives a single alkene product in a E2 elimination. CI CI Br Brarrow_forwardPlease calculate the chemical shift of each protonsarrow_forwardQ1: Answer the questions for the reaction below: ..!! Br OH a) Predict the product(s) of the reaction. b) Is the substrate optically active? Are the product(s) optically active as a mix? c) Draw the curved arrow mechanism for the reaction. d) What happens to the SN1 reaction rate in each of these instances: 1. Change the substrate to Br 'CI 2. Change the substrate to 3. Change the solvent from 100% CH3CH2OH to 10% CH3CH2OH + 90% DMF 4. Increase the substrate concentration by 3-fold.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





