
(a)
Interpretation:
The subscripts most likely to be used if ionic compound is formed between alkali metal and halogen.
Concept introduction:
The naming of ionic compound is such that the cation comes first and anion comes next. The subscripts are numeric indicating number of atoms that are involved in bonding. To get electrically neutral compound, there is balancing of the polyatomic ions that forms ionic bonds.
Answer to Problem 39SSC
The subscript to be used if ionic compound is formed between alkali metal and halogen is 1, 1.
Explanation of Solution
The binary ionic compound is written with the metal ion first and then the nonmetal next. The charge of the metal ion and non metal ion is balanced by cancelling out each other depending on the number of ions of each.
The alkali metal belongs to Group 1. It has electronic configuration as
The halogens belong of Group 7. It has electronic configuration as
Combining alkali metal ion and halogen ion, it will be written as

Therefore, the subscripts for this ionic compound is 1, 1
(b)
Interpretation:
The subscripts most likely to be used if ionic compound is formed between alkali metal and non metal from group 16.
Concept introduction:
The naming of ionic compound is such that the cation comes first and anion comes next. The subscripts are numeric indicating number of atoms that are involved in bonding. To get electrically neutral compound, there is balancing of the polyatomic ions that forms ionic bonds.
(b)
Answer to Problem 39SSC
The subscript to be used if ionic compound is formed between alkali metal and non metal from group 16 is 2, 1
Explanation of Solution
The binary ionic compound is written with the metal ion first and then the nonmetal next. The charge of the metal ion and non metal ion is balanced by cancelling out each other depending on the number of ions of each.
The alkali metal belongs to Group 1. It has electronic configuration as
The elements of Group 16 have electronic configuration as
Combining alkali metal ion and non metal ion of group 16, it will be written as

Therefore, the subscripts for this ionic compound is 2, 1
(c)
Interpretation:
The subscripts most likely to be used if ionic compound is formed between alkaline earth metal and halogen
Concept introduction:
The naming of ionic compound is such that the cation comes first and anion comes next. The subscripts are numeric indicating number of atoms that are involved in bonding. To get electrically neutral compound, there is balancing of the polyatomic ions that forms ionic bonds.
(c)
Answer to Problem 39SSC
The subscript to be used if ionic compound is formed between alkaline earth metal and halogen
is 1, 2.
Explanation of Solution
The binary ionic compound is written with the metal ion first and then the nonmetal next. The charge of the metal ion and non metal ion is balanced by cancelling out each other depending on the number of ions of each.
The alkaline earth metal belongs to Group 2. It has electronic configuration as
The halogens belong of Group 7. It has electronic configuration as
Combining alkali metal ion and non metal ion of group 16, it will be written as
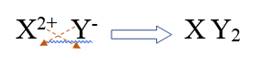
Therefore, the subscripts for this ionic compound is 1, 2
(d)
Interpretation:
The subscripts most likely to be used if ionic compound is formed between alkaline earth metal and non metal from group 16.
Concept introduction:
The naming of ionic compound is such that the cation comes first and anion comes next. The subscripts are numeric indicating number of atoms that are involved in bonding. To get electrically neutral compound, there is balancing of the polyatomic ions that forms ionic bonds.
(d)
Answer to Problem 39SSC
The subscript to be used if ionic compound is formed between alkaline earth metal and non metal form group 16 is 1, 1.
Explanation of Solution
The binary ionic compound is written with the metal ion first and then the nonmetal next. The charge of the metal ion and non metal ion is balanced by cancelling out each other depending on the number of ions of each.
The alkaline earth metal belongs to Group 2. It has electronic configuration as
The elements of Group 16 have electronic configuration as
Combining alkaline earth metal ion and non metal ion of group 16, it will be written as
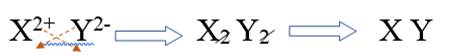
Therefore, the subscripts for this ionic compound is 1, 1
Chapter 7 Solutions
Glencoe Chemistry: Matter and Change, Student Edition
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Chemistry: A Molecular Approach (4th Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
Chemistry: The Central Science (14th Edition)
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
- 3. SYNTHESIS. Propose a sequence of synthetic steps (FGI) that convert the starting material (SM) into the Target molecule. For each FGI in your proposed synthesis, specify the reagents / conditions, and draw the product(s) of that FGI. DO NOT INCLUDE the FGI mxn in the answer you submit. If an FGI requires two reagent sets, specify the order in which the reagent sets are added, e.g., i) Hg(OAc)2 / H₂O; ii) NaBH4/MeOH. Indicate the stereochemistry (if any) of the products of each FGI. FGI 1. Me Starting Material Source of all carbons in the Target molecule (can use multiple copies) Me Me Target molecule + enantiomerarrow_forwardcurved arrows are used to illustate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction mechanism stepsarrow_forwardIf is was a very hot day, what would the aldol condensation product be? *see imagearrow_forward
- Please help me with number 1-3. Thank you so much.arrow_forwardDraw the major product of this reaction ingnore the inorganic byproducts. 1. NaOCH2CH3 at 25 C 2. PhCH2Br (1 eq)arrow_forwardAt 90ºC the vapor pressure of ortho-xylene is 20 kPa and that of meta-xylene is 18 kPa. What is the composition of the vapor in equilibrium with a mixture in which the mole fraction of o-xylene is 0.60?arrow_forward
- Draw the products of this reduction of a ketone with sodium borohydride. Use a dash or wedge bond to indicate the stereochemistry of substituents on asymmetric centers, where applicableIgnore any inorganic byproducts. 1) NaBH4 2) HCI/H2O Select to Drawarrow_forwardWhy do you think people who live at high altitudes are advised to add salt to water when boiling food like pasta? What mole fraction of NaCl is needed to raise the boiling point of H2O by 3˚C? Does the amount of salt added to water (typically about one teaspoon to four quarts of water) substantially change the boiling point? (Kb (H2O) = 0.51˚C/molal.)arrow_forwardpls help asaparrow_forward
- pls help asaparrow_forward9. Consider the following galvanic cell: Fe (s) | Fe(NO3)2 (aq) || Sn(NO3)2 (aq) | Sn (s) a. Write an equation for the half reactions occurring at the anode and cathode. b. Calculate the standard cell potential Show all of your work. c. Draw and label the galvanic cell, including the anode and cathode, direction of electron flow, and direction of ion migration.arrow_forwardpls help asaparrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





