
Interpretation:
The formation of ionic compound from elements Strontium and fluorine needs to be explained.
Concept introduction:
Chemical compounds are formed when the atoms, ions or molecules of two substances are attracted towards each other forming a
Answer to Problem 9PP
1 Strontium will lose 2 electrons which is gained by 2 of Fluorine atoms to form ionic compound,
Explanation of Solution
The formation of Strontium Fluoride is when Strontium atoms interact with fluorine atom.
The electronic configuration of Strontium is
Strontium atom has two outermost electron which can be lost to become a positive ion.
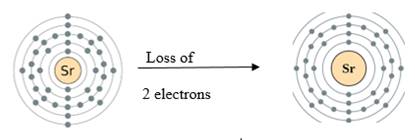
Figure 1
The electronic configuration of fluorine is
Fluorine atom has 1 half filled shells of p orbital. To fill up the half filled shell, it can take up 1 electron to become a fluoride anion.
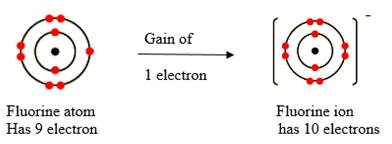
Figure 2
The 2 electrons lost by Strontium can be taken up by 2 of Fluorine atoms and form ionic compound. The Strontium is positively charged and Fluorine ion is negatively charged which gets attracted to form ionic compound.
Hence, we can say that one Strontium atom bonds with 2 Fluorine atoms to form ionic compound. The 2 electrons of Strontium gets gained by Fluorine to get an octet structure and form ionic compound,
1 Strontium will lose 2 electrons which is gained by 2 of Fluorine atoms to form ionic compound
Chapter 7 Solutions
Glencoe Chemistry: Matter and Change, Student Edition
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System (5th Edition)
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
Chemistry: The Central Science (14th Edition)
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
- Can u help me figure out the reaction mechanisms for these, idk where to even startarrow_forwardHi, I need your help with the drawing, please. I have attached the question along with my lab instructions. Please use the reaction from the lab only, as we are not allowed to use outside sources. Thank you!arrow_forwardHi, I need your help i dont know which one to draw please. I’ve attached the question along with my lab instructions. Please use the reaction from the lab only, as we are not allowed to use outside sources. Thank you!arrow_forward
- 5. Write the formation reaction of the following complex compounds from the following reactants: 6. AgNO₃ + K₂CrO₂ + NH₄OH → 7. HgNO₃ + excess KI → 8. Al(NO₃)₃ + excess NaOH →arrow_forwardIndicate whether the product formed in the reaction exhibits tautomerism. If so, draw the structure of the tautomers. CO₂C2H5 + CH3-NH-NH,arrow_forwardDraw the major product of this reaction N-(cyclohex-1-en-1-yl)-1-(pyrrolidino) reacts with CH2=CHCHO, heat, H3O+arrow_forward
- Draw the starting material that would be needed to make this product through an intramolecular Dieckmann reactionarrow_forwardDraw the major product of this reaction. Nitropropane reacts + pent-3-en-2-one reacts with NaOCH2CH3, CH3CHOHarrow_forwardIndicate whether the product formed in the reaction exhibits tautomerism. If so, draw the structure of the tautomers. OC2H5 + CoHs-NH-NH,arrow_forward
- Explain how substitutions at the 5-position of barbituric acid increase the compound's lipophilicity.arrow_forwardExplain how substitutions at the 5-position of phenobarbital increase the compound's lipophilicity.arrow_forwardName an interesting derivative of barbituric acid, describing its structure.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





