
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781118230725
Author: David Halliday, Robert Resnick, Jearl Walker
Publisher: Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 6, Problem 73P
In Fig. 6-54, the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and inclined plane is 0.20, and angle θ is 60°. What are the (a) magnitude a and (b) direction (up or down the plane) of the block’s acceleration if the block is sliding down the plane? What are (c) a and (d) the direction if the block is sent sliding up the plane?
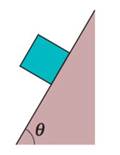
Figure 6-54 Problem 73.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
For each of the actions depicted below, a magnet and/or metal loop moves with velocity v→ (v→ is constant and has the same magnitude in all parts). Determine whether a current is induced in the metal loop. If so, indicate the direction of the current in the loop, either clockwise or counterclockwise when seen from the right of the loop. The axis of the magnet is lined up with the center of the loop. For the action depicted in (Figure 5), indicate the direction of the induced current in the loop (clockwise, counterclockwise or zero, when seen from the right of the loop). I know that the current is clockwise, I just dont understand why. Please fully explain why it's clockwise, Thank you
A planar double pendulum consists of two point masses \[m_1 = 1.00~\mathrm{kg}, \qquad m_2 = 1.00~\mathrm{kg}\]connected by massless, rigid rods of lengths \[L_1 = 1.00~\mathrm{m}, \qquad L_2 = 1.20~\mathrm{m}.\]The upper rod is hinged to a fixed pivot; gravity acts vertically downward with\[g = 9.81~\mathrm{m\,s^{-2}}.\]Define the generalized coordinates \(\theta_1,\theta_2\) as the angles each rod makes with thedownward vertical (positive anticlockwise, measured in radians unless stated otherwise).At \(t=0\) the system is released from rest with \[\theta_1(0)=120^{\circ}, \qquad\theta_2(0)=-10^{\circ}, \qquad\dot{\theta}_1(0)=\dot{\theta}_2(0)=0 .\]Using the exact nonlinear equations of motion (no small-angle or planar-pendulumapproximations) and assuming the rods never stretch or slip, determine the angle\(\theta_2\) at the instant\[t = 10.0~\mathrm{s}.\]Give the result in degrees, in the interval \((-180^{\circ},180^{\circ}]\).
What are the expected readings of the ammeter and voltmeter for the circuit in the figure below? (R = 5.60 Ω, ΔV = 6.30 V)
ammeter
I =
Chapter 6 Solutions
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
Ch. 6 - In Fig. 6-12, if the box is stationary and the...Ch. 6 - Prob. 2QCh. 6 - In Fig. 6-13, horizontal force F1 of magnitude 10...Ch. 6 - In three experiments, three different horizontal...Ch. 6 - If you press an apple crate against a wall so hard...Ch. 6 - In Fig. 6-14, a block of mass m is held stationary...Ch. 6 - Reconsider Question 6 but with the force F now...Ch. 6 - In Fig. 6-15, a horizontal force of 100 N is to be...Ch. 6 - Prob. 9QCh. 6 - Prob. 10Q
Ch. 6 - A person riding a Ferris wheel moves through...Ch. 6 - During a routine flight in 1956, test pilot Tom...Ch. 6 - A box is on a ramp that is at angle to the...Ch. 6 - The floor of a railroad flatcar is loaded with...Ch. 6 - In a pickup game of dorm shuffleboard, students...Ch. 6 - SSM WWW A bedroom bureau with a mass of 45 kg,...Ch. 6 - A slide-loving pig slides down a certain 35 slide...Ch. 6 - GO A 2.5 kg block is initially at rest on a...Ch. 6 - A baseball player with mass m 79 kg, sliding into...Ch. 6 - SSM ILW A person pushes horizontally with a force...Ch. 6 - The mysterious sliding stones. Along the remote...Ch. 6 - GO A 3.5 kg block is pushed along a horizontal...Ch. 6 - Figure 6-20 shows an initially stationary block of...Ch. 6 - SSM A 68 kg crate is dragged across a floor by...Ch. 6 - In about 1915, Henry Sincosky of Philadelphia...Ch. 6 - A worker pushes horizontally on a 35 kg crate with...Ch. 6 - Figure 6-22 shows the cross section of a road cut...Ch. 6 - The coefficient of static friction between Teflon...Ch. 6 - A loaded penguin sled weighing 80 N rests on a...Ch. 6 - In Fig. 6-24, a force P acts on a block weighing...Ch. 6 - GO You testify as an expert witness in a case...Ch. 6 - A 12 N horizontal force F pushes a block weighing...Ch. 6 - GO In Fig. 6-27, a box of Cheerios mass mC = 1.0...Ch. 6 - An initially stationary box of sand is to be...Ch. 6 - GO In Fig. 6-23, a sled is held on an inclined...Ch. 6 - When the three blocks in Fig. 6-29 are released...Ch. 6 - A 4.10 kg block is pushed along a floor by a...Ch. 6 - SSM WWW Block B in Fig. 6-31 weighs 711 N. The...Ch. 6 - GO Figure 6-32 shows three crates being pushed...Ch. 6 - GO Body A in Fig. 6-33 weighs 102 N, and body B...Ch. 6 - In Fig. 6-33, two blocks are connected over a...Ch. 6 - GO In Fig. 6-34, blocks A and B have weights of 44...Ch. 6 - A toy chest and its contents have a combined...Ch. 6 - SSM Two blocks, of weights 3.6 N and 7.2 N, are...Ch. 6 - GO A block is pushed across a floor by a constant...Ch. 6 - SSM A 1000 kg boat is traveling at 90 km/h when...Ch. 6 - GO In Fig. 6-37, a slab of mass m1= 40 kg rests on...Ch. 6 - ILW The two blocks m = 16 kg and M = 88 kg in Fig....Ch. 6 - The terminal speed of a sky diver is 160 km/h in...Ch. 6 - Continuation of Problem 8. Now assume that Eq....Ch. 6 - Assume Eq. 6-14 gives the drag force on a pilot...Ch. 6 - Calculate the ratio of the drag force on a jet...Ch. 6 - In downhill speed skiing a skier is retarded by...Ch. 6 - A cat dozes on a stationary merry-go-round in an...Ch. 6 - Suppose the coefficient of static friction between...Ch. 6 - ILW What is the smallest radius of an unbanked...Ch. 6 - During an Olympic bobsled run, the Jamaican team...Ch. 6 - SSM ILW A student of weight 667 N rides a steadily...Ch. 6 - A police officer in hot pursuit drives her car...Ch. 6 - A circular-motion addict of mass 80 kg rides a...Ch. 6 - A roller-coaster car at an amusement park has a...Ch. 6 - GO In Fig. 6-39, a car is driven at constant speed...Ch. 6 - An 85.0 kg passenger is made to move along a...Ch. 6 - SSM WWW An airplane is flying in a horizontal...Ch. 6 - An amusement park ride consists of a car moving in...Ch. 6 - An old streetcar rounds a flat corner of radius...Ch. 6 - In designing circular rides for amusement parks,...Ch. 6 - A bolt is threaded onto one end of a thin...Ch. 6 - GO A banked circular highway curve is designed for...Ch. 6 - GO A puck of mass m = 1.50 kg slides in a circle...Ch. 6 - Brake or turn? Figure 6- 44 depicts an overhead...Ch. 6 - SSM ILW In Fig. 6-45, a 1.34 kg ball is connected...Ch. 6 - GO In Fig. 6-46, a box of ant aunts total mass m1...Ch. 6 - SSM A block of mass mt = 4.0 kg is put on top of a...Ch. 6 - A 5.00 kg stone is rubbed across the horizontal...Ch. 6 - In Fig. 6-49, a 49 kg rock climber is climbing a...Ch. 6 - A high-speed railway car goes around a flat,...Ch. 6 - Continuation of Problems 8 and 37. Another...Ch. 6 - GO In Fig. 6-50, block 1 of mass m1 = 2.0 kg and...Ch. 6 - In Fig. 6-51, a crate slides down an inclined...Ch. 6 - Engineering a highway curve. If a car goes through...Ch. 6 - A student, crazed by final exams, uses a force P...Ch. 6 - GO Figure 6-53 shows a conical pendulum, in which...Ch. 6 - An 8.00 kg block of steel is at rest on a...Ch. 6 - A box of canned goods slides down a ramp from...Ch. 6 - In Fig. 6-54, the coefficient of kinetic friction...Ch. 6 - A 110 g hockey puck sent sliding over ice is...Ch. 6 - A locomotive accelerates a 25-car train along a...Ch. 6 - A house is built on the top of a hill with a...Ch. 6 - What is the terminal speed of a 6.00 kg spherical...Ch. 6 - A student wants to determine the coefficients of...Ch. 6 - SSM Block A in Fig. 6-56 has mass mA = 4.0 kg, and...Ch. 6 - Calculate the magnitude of the drag force on a...Ch. 6 - SSM A bicyclist travels in a circle of radius 25.0...Ch. 6 - In Fig. 6-57, a stuntman drives a car without...Ch. 6 - You must push a crate across a floor to a docking...Ch. 6 - In Fig. 6-58, force F is applied to a crate of...Ch. 6 - In the early afternoon, a car is parked on a...Ch. 6 - A sling-thrower puts a stone 0.250 kg in the...Ch. 6 - SSM A car weighing 10.7 kN and traveling at 13.4...Ch. 6 - In Fig. 6-59, block 1 of mass m1 = 2.0 kg and...Ch. 6 - SSM A filing cabinet weighing 556 N rests on the...Ch. 6 - In Fig. 6-60, a block weighing 22 N is held at...Ch. 6 - Prob. 91PCh. 6 - A circular curve of highway is designed for...Ch. 6 - A 1.5 kg box is initially at rest on a horizontal...Ch. 6 - A child weighing 140 N sits at rest at the top of...Ch. 6 - In Fig. 6-61 a fastidious worker pushes directly...Ch. 6 - A child places a picnic basket on the outer rim of...Ch. 6 - SSM A warehouse worker exerts a constant...Ch. 6 - In Fig. 6-62, a 5.0 kg block is sent sliding up a...Ch. 6 - An 11 kg block of steel is at rest on a horizontal...Ch. 6 - A ski that is placed on snow will stick to the...Ch. 6 - Playing near a road construction site, a child...Ch. 6 - A 100 N force, directed at an angle above a...Ch. 6 - A certain string can withstand a maximum tension...Ch. 6 - A four-person bobsled total mass = 630 kg comes...Ch. 6 - As a 40 N block slides down a plane that is...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
MAKE CONNECTIONS Review the description of meiosis (see Figure 10.8) and Mendels laws of segregation and indepe...
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
SCIENTIFIC INQUIRY You are handed a mystery pea plant with tall stems and axial flowers and asked to determine ...
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
43. What is the angular momentum vector of the 2.0 kg, 4.0-cm-diameter rotating disk in FIGURE EX12.43?
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
Name the bones that form the lower limb, from proximal to distal.
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
Choose the best answer to etch of the following. Explain your reasoning. Which of these stars is the most massi...
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
In pea plants, plant height, seed shape, and seed color are governed by three independently assorting genes. Th...
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- simple diagram to illustrate the setup for each law- coulombs law and biot savart lawarrow_forwardA circular coil with 100 turns and a radius of 0.05 m is placed in a magnetic field that changes at auniform rate from 0.2 T to 0.8 T in 0.1 seconds. The plane of the coil is perpendicular to the field.• Calculate the induced electric field in the coil.• Calculate the current density in the coil given its conductivity σ.arrow_forwardAn L-C circuit has an inductance of 0.410 H and a capacitance of 0.250 nF . During the current oscillations, the maximum current in the inductor is 1.80 A . What is the maximum energy Emax stored in the capacitor at any time during the current oscillations? How many times per second does the capacitor contain the amount of energy found in part A? Please show all steps.arrow_forward
- A long, straight wire carries a current of 10 A along what we’ll define to the be x-axis. A square loopin the x-y plane with side length 0.1 m is placed near the wire such that its closest side is parallel tothe wire and 0.05 m away.• Calculate the magnetic flux through the loop using Ampere’s law.arrow_forwardDescribe the motion of a charged particle entering a uniform magnetic field at an angle to the fieldlines. Include a diagram showing the velocity vector, magnetic field lines, and the path of the particle.arrow_forwardDiscuss the differences between the Biot-Savart law and Coulomb’s law in terms of their applicationsand the physical quantities they describe.arrow_forward
- Explain why Ampere’s law can be used to find the magnetic field inside a solenoid but not outside.arrow_forward3. An Atwood machine consists of two masses, mA and m B, which are connected by an inelastic cord of negligible mass that passes over a pulley. If the pulley has radius RO and moment of inertia I about its axle, determine the acceleration of the masses mA and m B, and compare to the situation where the moment of inertia of the pulley is ignored. Ignore friction at the axle O. Use angular momentum and torque in this solutionarrow_forwardA 0.850-m-long metal bar is pulled to the right at a steady 5.0 m/s perpendicular to a uniform, 0.650-T magnetic field. The bar rides on parallel metal rails connected through a 25-Ω, resistor (Figure 1), so the apparatus makes a complete circuit. Ignore the resistance of the bar and the rails. Please explain how to find the direction of the induced current.arrow_forward
- For each of the actions depicted, determine the direction (right, left, or zero) of the current induced to flow through the resistor in the circuit containing the secondary coil. The coils are wrapped around a plastic core. Immediately after the switch is closed, as shown in the figure, (Figure 1) in which direction does the current flow through the resistor? If the switch is then opened, as shown in the figure, in which direction does the current flow through the resistor? I have the answers to the question, but would like to understand the logic behind the answers. Please show steps.arrow_forwardWhen violet light of wavelength 415 nm falls on a single slit, it creates a central diffraction peak that is 8.60 cm wide on a screen that is 2.80 m away. Part A How wide is the slit? ΟΙ ΑΣΦ ? D= 2.7.10-8 Submit Previous Answers Request Answer × Incorrect; Try Again; 8 attempts remaining marrow_forwardTwo complex values are z1=8 + 8i, z2=15 + 7 i. z1∗ and z2∗ are the complex conjugate values. Any complex value can be expessed in the form of a+bi=reiθ. Find θ for (z1-z∗2)/z1+z2∗. Find r and θ for (z1−z2∗)z1z2∗ Please show all stepsarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:9780534408961
Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Conservative and Non Conservative Forces; Author: AK LECTURES;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vFVCluvSrFc;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY