
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781118230725
Author: David Halliday, Robert Resnick, Jearl Walker
Publisher: Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 6, Problem 25P
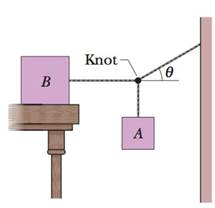
SSM WWW Block B in Fig. 6-31 weighs 711 N. The coefficient of static friction between block and table is 0.25; angle θ is 30°; assume that the cord between B and the knot is horizontal. Find the maximum weight of block A for which the system will be stationary.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Is work function of a metals surface related to surface energy and surface tension? What is the need to the work function component in the math of tension of metal surfaces that cannot be provided by existing equations of surface energy and surface tension? What are the key differences in each parameter and variables that allow for a differentiation of each function? What has a more significant meaning work function, surface tension or surface energy? Are there real differences and meaning? Please clarify and if possible provide examples . Does surface tension dependant on thickness of a metal or type of metal surface all having the same thickness? Clearly temperature has a profound change on surface tension what other variables besides temperature are key to surface tension. What if any is there a connection between crystal structure of the element and surface energy and tension? This is NOT a Assignment Question!!!
The cylindrical beam of a 12.7-mW laser is 0.920 cm in diameter. What is the rms value of the electric field?
V/m
Consider a rubber rod that has been rubbed with fur to give the rod a net negative charge, and a glass rod that has been rubbed with silk to give it a net positive charge. After being charged by contact by the fur and silk...?
a. Both rods have less mass
b. the rubber rod has more mass and the glass rod has less mass
c. both rods have more mass
d. the masses of both rods are unchanged
e. the rubber rod has less mass and the glass rod has mroe mass
Chapter 6 Solutions
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
Ch. 6 - In Fig. 6-12, if the box is stationary and the...Ch. 6 - Prob. 2QCh. 6 - In Fig. 6-13, horizontal force F1 of magnitude 10...Ch. 6 - In three experiments, three different horizontal...Ch. 6 - If you press an apple crate against a wall so hard...Ch. 6 - In Fig. 6-14, a block of mass m is held stationary...Ch. 6 - Reconsider Question 6 but with the force F now...Ch. 6 - In Fig. 6-15, a horizontal force of 100 N is to be...Ch. 6 - Prob. 9QCh. 6 - Prob. 10Q
Ch. 6 - A person riding a Ferris wheel moves through...Ch. 6 - During a routine flight in 1956, test pilot Tom...Ch. 6 - A box is on a ramp that is at angle to the...Ch. 6 - The floor of a railroad flatcar is loaded with...Ch. 6 - In a pickup game of dorm shuffleboard, students...Ch. 6 - SSM WWW A bedroom bureau with a mass of 45 kg,...Ch. 6 - A slide-loving pig slides down a certain 35 slide...Ch. 6 - GO A 2.5 kg block is initially at rest on a...Ch. 6 - A baseball player with mass m 79 kg, sliding into...Ch. 6 - SSM ILW A person pushes horizontally with a force...Ch. 6 - The mysterious sliding stones. Along the remote...Ch. 6 - GO A 3.5 kg block is pushed along a horizontal...Ch. 6 - Figure 6-20 shows an initially stationary block of...Ch. 6 - SSM A 68 kg crate is dragged across a floor by...Ch. 6 - In about 1915, Henry Sincosky of Philadelphia...Ch. 6 - A worker pushes horizontally on a 35 kg crate with...Ch. 6 - Figure 6-22 shows the cross section of a road cut...Ch. 6 - The coefficient of static friction between Teflon...Ch. 6 - A loaded penguin sled weighing 80 N rests on a...Ch. 6 - In Fig. 6-24, a force P acts on a block weighing...Ch. 6 - GO You testify as an expert witness in a case...Ch. 6 - A 12 N horizontal force F pushes a block weighing...Ch. 6 - GO In Fig. 6-27, a box of Cheerios mass mC = 1.0...Ch. 6 - An initially stationary box of sand is to be...Ch. 6 - GO In Fig. 6-23, a sled is held on an inclined...Ch. 6 - When the three blocks in Fig. 6-29 are released...Ch. 6 - A 4.10 kg block is pushed along a floor by a...Ch. 6 - SSM WWW Block B in Fig. 6-31 weighs 711 N. The...Ch. 6 - GO Figure 6-32 shows three crates being pushed...Ch. 6 - GO Body A in Fig. 6-33 weighs 102 N, and body B...Ch. 6 - In Fig. 6-33, two blocks are connected over a...Ch. 6 - GO In Fig. 6-34, blocks A and B have weights of 44...Ch. 6 - A toy chest and its contents have a combined...Ch. 6 - SSM Two blocks, of weights 3.6 N and 7.2 N, are...Ch. 6 - GO A block is pushed across a floor by a constant...Ch. 6 - SSM A 1000 kg boat is traveling at 90 km/h when...Ch. 6 - GO In Fig. 6-37, a slab of mass m1= 40 kg rests on...Ch. 6 - ILW The two blocks m = 16 kg and M = 88 kg in Fig....Ch. 6 - The terminal speed of a sky diver is 160 km/h in...Ch. 6 - Continuation of Problem 8. Now assume that Eq....Ch. 6 - Assume Eq. 6-14 gives the drag force on a pilot...Ch. 6 - Calculate the ratio of the drag force on a jet...Ch. 6 - In downhill speed skiing a skier is retarded by...Ch. 6 - A cat dozes on a stationary merry-go-round in an...Ch. 6 - Suppose the coefficient of static friction between...Ch. 6 - ILW What is the smallest radius of an unbanked...Ch. 6 - During an Olympic bobsled run, the Jamaican team...Ch. 6 - SSM ILW A student of weight 667 N rides a steadily...Ch. 6 - A police officer in hot pursuit drives her car...Ch. 6 - A circular-motion addict of mass 80 kg rides a...Ch. 6 - A roller-coaster car at an amusement park has a...Ch. 6 - GO In Fig. 6-39, a car is driven at constant speed...Ch. 6 - An 85.0 kg passenger is made to move along a...Ch. 6 - SSM WWW An airplane is flying in a horizontal...Ch. 6 - An amusement park ride consists of a car moving in...Ch. 6 - An old streetcar rounds a flat corner of radius...Ch. 6 - In designing circular rides for amusement parks,...Ch. 6 - A bolt is threaded onto one end of a thin...Ch. 6 - GO A banked circular highway curve is designed for...Ch. 6 - GO A puck of mass m = 1.50 kg slides in a circle...Ch. 6 - Brake or turn? Figure 6- 44 depicts an overhead...Ch. 6 - SSM ILW In Fig. 6-45, a 1.34 kg ball is connected...Ch. 6 - GO In Fig. 6-46, a box of ant aunts total mass m1...Ch. 6 - SSM A block of mass mt = 4.0 kg is put on top of a...Ch. 6 - A 5.00 kg stone is rubbed across the horizontal...Ch. 6 - In Fig. 6-49, a 49 kg rock climber is climbing a...Ch. 6 - A high-speed railway car goes around a flat,...Ch. 6 - Continuation of Problems 8 and 37. Another...Ch. 6 - GO In Fig. 6-50, block 1 of mass m1 = 2.0 kg and...Ch. 6 - In Fig. 6-51, a crate slides down an inclined...Ch. 6 - Engineering a highway curve. If a car goes through...Ch. 6 - A student, crazed by final exams, uses a force P...Ch. 6 - GO Figure 6-53 shows a conical pendulum, in which...Ch. 6 - An 8.00 kg block of steel is at rest on a...Ch. 6 - A box of canned goods slides down a ramp from...Ch. 6 - In Fig. 6-54, the coefficient of kinetic friction...Ch. 6 - A 110 g hockey puck sent sliding over ice is...Ch. 6 - A locomotive accelerates a 25-car train along a...Ch. 6 - A house is built on the top of a hill with a...Ch. 6 - What is the terminal speed of a 6.00 kg spherical...Ch. 6 - A student wants to determine the coefficients of...Ch. 6 - SSM Block A in Fig. 6-56 has mass mA = 4.0 kg, and...Ch. 6 - Calculate the magnitude of the drag force on a...Ch. 6 - SSM A bicyclist travels in a circle of radius 25.0...Ch. 6 - In Fig. 6-57, a stuntman drives a car without...Ch. 6 - You must push a crate across a floor to a docking...Ch. 6 - In Fig. 6-58, force F is applied to a crate of...Ch. 6 - In the early afternoon, a car is parked on a...Ch. 6 - A sling-thrower puts a stone 0.250 kg in the...Ch. 6 - SSM A car weighing 10.7 kN and traveling at 13.4...Ch. 6 - In Fig. 6-59, block 1 of mass m1 = 2.0 kg and...Ch. 6 - SSM A filing cabinet weighing 556 N rests on the...Ch. 6 - In Fig. 6-60, a block weighing 22 N is held at...Ch. 6 - Prob. 91PCh. 6 - A circular curve of highway is designed for...Ch. 6 - A 1.5 kg box is initially at rest on a horizontal...Ch. 6 - A child weighing 140 N sits at rest at the top of...Ch. 6 - In Fig. 6-61 a fastidious worker pushes directly...Ch. 6 - A child places a picnic basket on the outer rim of...Ch. 6 - SSM A warehouse worker exerts a constant...Ch. 6 - In Fig. 6-62, a 5.0 kg block is sent sliding up a...Ch. 6 - An 11 kg block of steel is at rest on a horizontal...Ch. 6 - A ski that is placed on snow will stick to the...Ch. 6 - Playing near a road construction site, a child...Ch. 6 - A 100 N force, directed at an angle above a...Ch. 6 - A certain string can withstand a maximum tension...Ch. 6 - A four-person bobsled total mass = 630 kg comes...Ch. 6 - As a 40 N block slides down a plane that is...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Several depositional features near Drakes Estero are related to the movement of sediment by longshore currents....
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
How is the female pelvis adapted for pregnancy and childbirth?
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
11. Birds and mammals are both endothermic, and both have four-chambered hearts. Most reptiles are ectothermic ...
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
41. A 15-m-long garden hose has an inner diameter of 2.5 cm. One end is connected to a spigot; 20°C water flows...
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
WRITE ABOUT A THEME: ENERGY In a short essay (about 100150 words), discuss how prokaryotes and other members of...
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Which culture uses NAD+? Use the following choices to answer questions. a. E. coli growing in glucose broth at ...
Microbiology: An Introduction
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 8. With the aid of a diagram draw the following electric circuit and use the resistor as the load, (a) Closed circuit (b) Open circuitarrow_forwardLab 8 Part 3 PHET Wave Interface simulation. I am having trouble with this part of the lab.arrow_forwardMick and Rick are twins born on Earth in the year 2175. Rick grows up to be an Earth-bound robotics technician while Mick becomes an intergalactic astronaut. Mick leaves the Earth on his first space mission in the year 2200 and travels, according to his clock, for 10 years at a speed of 0.75c. Unfortunately, at this point in his journey, the structure of his ship undergoes mechanical breakdown and the ship explodes. How old is Rick when his brother dies?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:9780534408961
Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:OpenStax College

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Conservative and Non Conservative Forces; Author: AK LECTURES;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vFVCluvSrFc;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY