
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
10th Edition
ISBN: 9780134319650
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 3.4, Problem 3.7P
The rigid beam is supported by a pin at C and an A-36 steel guy wire AB. If the wire has a diameter of 0.2 in., determine how much it stretches when a distributed load of w = 100 lb/ft acts on the beam. The material remains elastic.
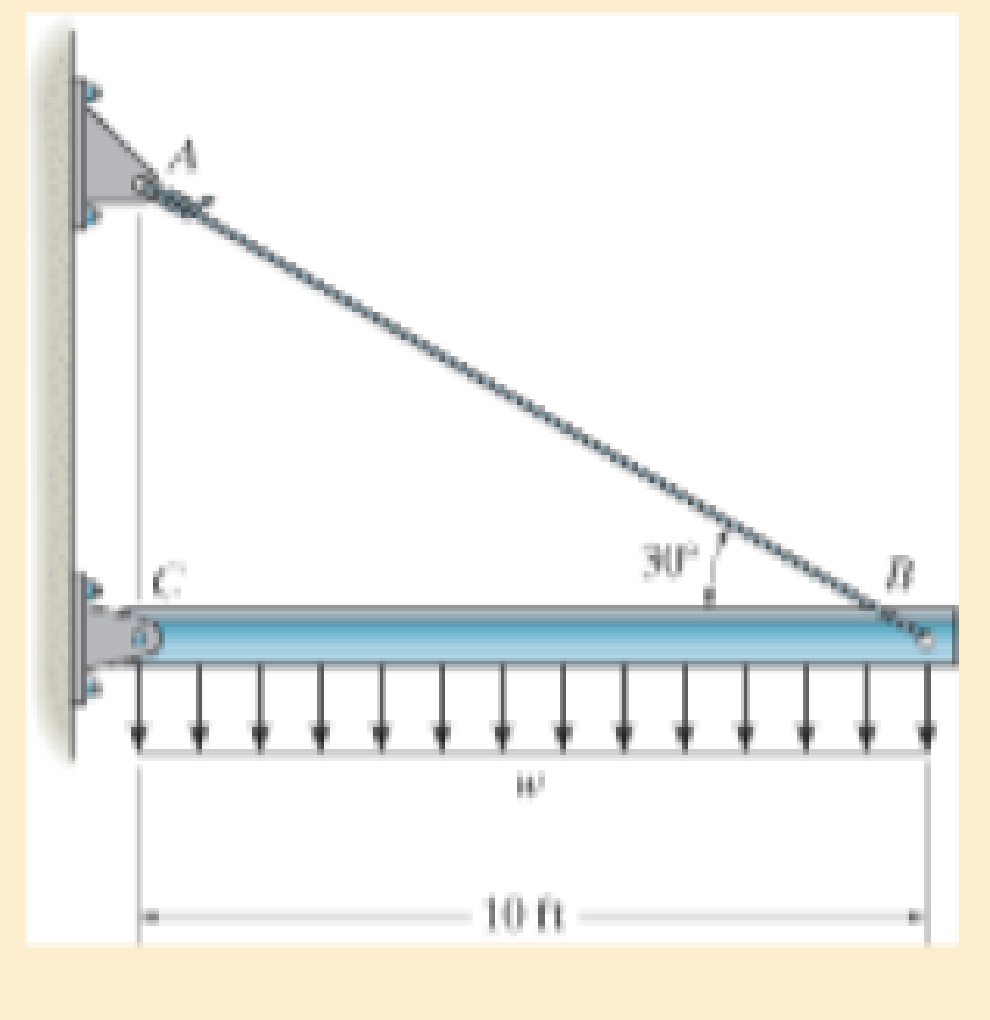
Probs. 3–7/8
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Problem 3.21P: Air at 100F(38C) db,65F(18C) wb, and sea-level pressure is humidified adiabatically with steam. The steam supplied contains 20 percent moisture(quality of 0.80) at 14.7psia(101.3kpa). The air is humidified to 60 percent relative humidity. Find the dry bulb temperature of the humidified air using (a)chart 1a or 1b and (b) the program PSYCH.
PUNTO 4.
calculate their DoF using Gruebler's formula.
PUNTO 5.
Ground
PUNTO 2.
PUNTO 3.
calculate their DoF using Gruebler's formula.
III
IA
Chapter 3 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Ch. 3.4 - Define a homogeneous material.Ch. 3.4 - Indicate the points on the stress-strain diagram...Ch. 3.4 - Define the modulus of elasticity E.Ch. 3.4 - At room temperature, mild steel is a ductile...Ch. 3.4 - Engineering stress and strain are calculated using...Ch. 3.4 - As the temperature increases the modulus of...Ch. 3.4 - A 100-mm-long rod has a diameter of 15 mm. If an...Ch. 3.4 - A bar has a length of 8 in. and cross-sectional...Ch. 3.4 - A 10-mm-diameter rod has a modulus of elasticity...Ch. 3.4 - The material for the 50-mm-long specimen has the...
Ch. 3.4 - The material for the 50-mm-long specimen has the...Ch. 3.4 - If the elongation of wire BC is 0.2 mm after the...Ch. 3.4 - A tension test was performed on a steel specimen...Ch. 3.4 - Data taken from a stress-strain test for a ceramic...Ch. 3.4 - Data taken from a stress-strain test for a ceramic...Ch. 3.4 - The stress-strain diagram for a steel alloy having...Ch. 3.4 - The stress-strain diagram for a steel alloy having...Ch. 3.4 - The stress-strain diagram for a steel alloy having...Ch. 3.4 - The rigid beam is supported by a pin at C and an...Ch. 3.4 - The rigid beam is supported by a pin at C and an...Ch. 3.4 - Acetal plastic has a stress-strain diagram as...Ch. 3.4 - The stress-strain diagram for an aluminum alloy...Ch. 3.4 - The stress-strain diagram for an aluminum alloy...Ch. 3.4 - The stress-strain diagram for an aluminum alloy...Ch. 3.4 - A bar having a length of 5 in. and cross-sectional...Ch. 3.4 - The rigid pipe is supported by a pin at A and an...Ch. 3.4 - The rigid pipe is supported by a pin at A and an...Ch. 3.4 - Direct tension indicators are sometimes used...Ch. 3.4 - The rigid beam is supported by a pin at C and an...Ch. 3.4 - The rigid beam is supported by a pin at C and an...Ch. 3.4 - The stress-strain diagram for a bone is shown, and...Ch. 3.4 - The stress-strain diagram for a bone is shown and...Ch. 3.4 - The two bars are made of a material that has the...Ch. 3.4 - The two bars are made of a material that has the...Ch. 3.4 - The pole is supported by a pin at C and an A-36...Ch. 3.4 - The bar DA is rigid and is originally held in the...Ch. 3.7 - A 100-mm-long rod has a diameter of 15 mm. If an...Ch. 3.7 - A solid circular rod that is 600 mm long and 20 mm...Ch. 3.7 - A 20-mm-wide block is firmly bonded to rigid...Ch. 3.7 - A 20-mm-wide block is bonded to rigid plates at...Ch. 3.7 - The acrylic plastic rod is 200 mm long and 15 mm...Ch. 3.7 - The plug has a diameter of 30 mm and fits within a...Ch. 3.7 - The elastic portion of the stress-strain diagram...Ch. 3.7 - The elastic portion of the stress-strain diagram...Ch. 3.7 - The brake pads for a bicycle tire are made of...Ch. 3.7 - The lap joint is connected together using a 1.25...Ch. 3.7 - The lap joint is connected together using a 1.25...Ch. 3.7 - The rubber block is subjected to an elongation of...Ch. 3.7 - The shear stress-strain diagram for an alloy is...Ch. 3.7 - A shear spring is made from two blocks of rubber,...Ch. 3 - The elastic portion of the tension stress-strain...Ch. 3 - The elastic portion of the tension stress-strain...Ch. 3 - The rigid beam rests in the horizontal position on...Ch. 3 - The wires each have a diameter of 12 in., length...Ch. 3 - The wires each have a diameter of 12 in., length...Ch. 3 - diameter steel bolts. If the clamping force in...Ch. 3 - The stress-strain diagram for polyethylene, which...Ch. 3 - The pipe with two rigid caps attached to its ends...Ch. 3 - The 8-mm-diameter bolt is made of an aluminum...Ch. 3 - An acetal polymer block is fixed to the rigid...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- calculate their DoF using Gruebler's formula. PUNTO 6. PUNTO 7. (Ctrl)arrow_forwardA pump delivering 230 lps of water at 30C has a 300-mm diameter suction pipe and a 254-mm diameter discharge pipe as shown in the figure. The suction pipe is 3.5 m long and the discharge pipe is 23 m long, both pipe's materials are cast iron. The water is delivered 16m above the intake water level. Considering head losses in fittings, valves, and major head loss. a) Find the total dynamic head which the pump must supply. b)It the pump mechanical efficiency is 68%, and the motor efficiency is 90%, determine the power rating of the motor in hp.given that: summation of K gate valve = 0.25check valve=390 degree elbow= 0.75foot valve= 0.78arrow_forwardA pump delivering 230 lps of water at 30C has a 300-mm diameter suction pipe and a 254-mm diameter discharge pipe as shown in the figure. The suction pipe is 3.5 m long and the discharge pipe is 23 m long, both pipe's materials are cast iron. The water is delivered 16m above the intake water level. Considering head losses in fittings, valves, and major head loss. a) Find the total dynamic head which the pump must supply. b)It the pump mechanical efficiency is 68%, and the motor efficiency is 90%, determine the power rating of the motor in hp.arrow_forward
- The tensile 0.2 percent offset yield strength of AISI 1137 cold-drawn steel bars up to 1 inch in diameter from 2 mills and 25 heats is reported as follows: Sy 93 95 101 f 97 99 107 109 111 19 25 38 17 12 10 5 4 103 105 4 2 where Sy is the class midpoint in kpsi and fis the number in each class. Presuming the distribution is normal, determine the yield strength exceeded by 99.0% of the population. The yield strength exceeded by 99.0% of the population is kpsi.arrow_forwardSolve this problem and show all of the workarrow_forwardI tried to go through this problem but I don't know what I'm doing wrong can you help me?arrow_forward
- Generate the kinematic diagram of the following mechanisms using the given symbols. Then, draw their graphs and calculate their degrees of freedom (DoF) using Gruebler's formula. PUNTO 2. PUNTO 3. !!!arrow_forwardCreate a schematic representation of the following mechanisms using the given symbols and draw their graphs. Then, calculate their degrees of freedom (DoF) using Gruebler's formula. PUNTO 6. PUNTO 7.arrow_forwardhow the kinematic diagram of the following mechanisms would be represented using the given symbols? PUNTO 0. PUNTO 1. °arrow_forward
- Create a schematic representation of the following mechanisms using the given symbols and draw their graphs. Then, calculate their degrees of freedom (DOF) using Gruebler's formula. PUNTO 4. PUNTO 5. (0) Groundarrow_forwardDraw the graph of ALL the mechanisms and calculate their DoF using Gruebler's formula. PUNTO 0. PUNTO 1.arrow_forwardAn adjustable support. Construction designed to carry vertical load and is adjusted by moving the blue attachment vertically. The link is articulated at both ends (free to rotate) and can therefore only transmit power axially. Analytically calculate the force to which the link is subjected? Calculate analytically rated voltage in the middle of the link.? F=20kN Alpha 30 deg Rel 225 Mpans:5arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Mechanics of Materials Lecture: Beam Design; Author: UWMC Engineering;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-wVs5pvQPm4;License: Standard Youtube License