
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
10th Edition
ISBN: 9780134319650
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 3.4, Problem 3.12FP
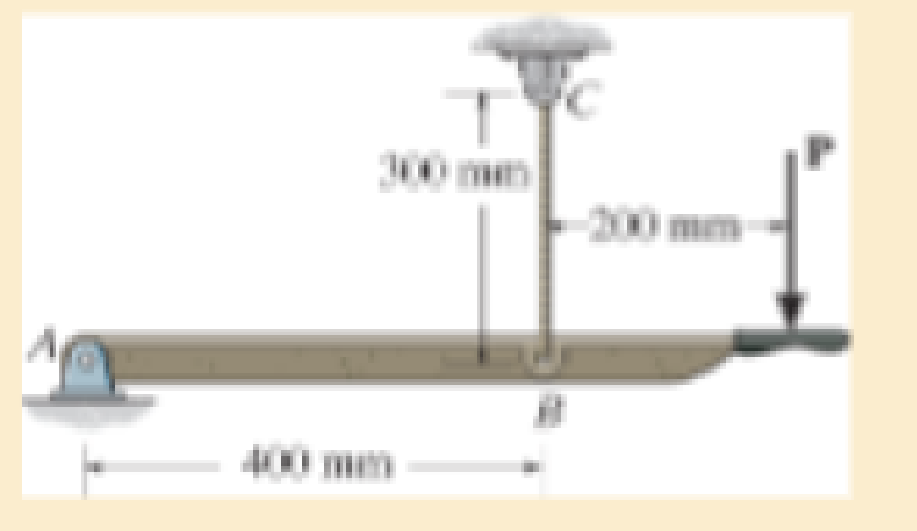
If the elongation of wire BC is 0.2 mm after the force P is applied, determine the magnitude of P. The wire is A-36 steel and has a diameter of 3 mm.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Find the resultant force vector from adding F1, F2 and F3, where … F1 = {-8i+10j-32k} N F2 is 40 N in magnitude with coordinate direction angles α, β, and γ, of 45, 120 and 60 degrees, respectively and F3 is 22 N in magnitude with transverse and azimuth angles of 65 and 40 degrees, respectively Express your final answer as a Cartesian vector as well as a magnitude with angles.
A 2-kW resistance heater wire with thermal conductivity of k=20 W/mK, a diameter of D=4mm, and a length of L=0.9m is used to boil water. If the outer surface temp of the resistance wire is Ts=110 degrees C, determine the temp at the center of the wire.
A flat-plate solar collector is used to heat water by having water flow through tubes attached at the back of the thin solar absorber plate. The absorber plate has emmisssivity and an absorptivity of 0.9. The top surface where x=0 temp of the absorber is T0=35 degrees C, and solar radiation is incident on the basorber at 500 W/m^2 with a surrounding temp of 0 degrees C. The convection heat transfer coefficient at the absorber surface is 5 W/m^2 K, while the ambient temp is 25 degrees C. Show that the variation of the temp in the basorber plate can be expressed as T(x)=-(q0/k)x+T0, and determine net heat flux, q, absorbed by solar collector.
Chapter 3 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Ch. 3.4 - Define a homogeneous material.Ch. 3.4 - Indicate the points on the stress-strain diagram...Ch. 3.4 - Define the modulus of elasticity E.Ch. 3.4 - At room temperature, mild steel is a ductile...Ch. 3.4 - Engineering stress and strain are calculated using...Ch. 3.4 - As the temperature increases the modulus of...Ch. 3.4 - A 100-mm-long rod has a diameter of 15 mm. If an...Ch. 3.4 - A bar has a length of 8 in. and cross-sectional...Ch. 3.4 - A 10-mm-diameter rod has a modulus of elasticity...Ch. 3.4 - The material for the 50-mm-long specimen has the...
Ch. 3.4 - The material for the 50-mm-long specimen has the...Ch. 3.4 - If the elongation of wire BC is 0.2 mm after the...Ch. 3.4 - A tension test was performed on a steel specimen...Ch. 3.4 - Data taken from a stress-strain test for a ceramic...Ch. 3.4 - Data taken from a stress-strain test for a ceramic...Ch. 3.4 - The stress-strain diagram for a steel alloy having...Ch. 3.4 - The stress-strain diagram for a steel alloy having...Ch. 3.4 - The stress-strain diagram for a steel alloy having...Ch. 3.4 - The rigid beam is supported by a pin at C and an...Ch. 3.4 - The rigid beam is supported by a pin at C and an...Ch. 3.4 - Acetal plastic has a stress-strain diagram as...Ch. 3.4 - The stress-strain diagram for an aluminum alloy...Ch. 3.4 - The stress-strain diagram for an aluminum alloy...Ch. 3.4 - The stress-strain diagram for an aluminum alloy...Ch. 3.4 - A bar having a length of 5 in. and cross-sectional...Ch. 3.4 - The rigid pipe is supported by a pin at A and an...Ch. 3.4 - The rigid pipe is supported by a pin at A and an...Ch. 3.4 - Direct tension indicators are sometimes used...Ch. 3.4 - The rigid beam is supported by a pin at C and an...Ch. 3.4 - The rigid beam is supported by a pin at C and an...Ch. 3.4 - The stress-strain diagram for a bone is shown, and...Ch. 3.4 - The stress-strain diagram for a bone is shown and...Ch. 3.4 - The two bars are made of a material that has the...Ch. 3.4 - The two bars are made of a material that has the...Ch. 3.4 - The pole is supported by a pin at C and an A-36...Ch. 3.4 - The bar DA is rigid and is originally held in the...Ch. 3.7 - A 100-mm-long rod has a diameter of 15 mm. If an...Ch. 3.7 - A solid circular rod that is 600 mm long and 20 mm...Ch. 3.7 - A 20-mm-wide block is firmly bonded to rigid...Ch. 3.7 - A 20-mm-wide block is bonded to rigid plates at...Ch. 3.7 - The acrylic plastic rod is 200 mm long and 15 mm...Ch. 3.7 - The plug has a diameter of 30 mm and fits within a...Ch. 3.7 - The elastic portion of the stress-strain diagram...Ch. 3.7 - The elastic portion of the stress-strain diagram...Ch. 3.7 - The brake pads for a bicycle tire are made of...Ch. 3.7 - The lap joint is connected together using a 1.25...Ch. 3.7 - The lap joint is connected together using a 1.25...Ch. 3.7 - The rubber block is subjected to an elongation of...Ch. 3.7 - The shear stress-strain diagram for an alloy is...Ch. 3.7 - A shear spring is made from two blocks of rubber,...Ch. 3 - The elastic portion of the tension stress-strain...Ch. 3 - The elastic portion of the tension stress-strain...Ch. 3 - The rigid beam rests in the horizontal position on...Ch. 3 - The wires each have a diameter of 12 in., length...Ch. 3 - The wires each have a diameter of 12 in., length...Ch. 3 - diameter steel bolts. If the clamping force in...Ch. 3 - The stress-strain diagram for polyethylene, which...Ch. 3 - The pipe with two rigid caps attached to its ends...Ch. 3 - The 8-mm-diameter bolt is made of an aluminum...Ch. 3 - An acetal polymer block is fixed to the rigid...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Using properties of a saturated water, explain how you would determine the mole fraction of water vapor at the surface of a lake when the temp of the lake surface and the atmospheric pressure are specified.arrow_forwardConsider a glass of water in a room at 15 degrees C and 97 kPa. If the relative humidity in the room is 100 percent and the water and the air are in thermal and phase equilibrium, determine the mole fraction of the water vapor in the air and the mole fraction of air in the water.arrow_forwardStaring with an energy balance on a cylindirical shell volume element, derive the steady one dimensional heat conduction equation for a long cylinder with constant thermal conductivity in which heat is generated at a rate of egen.arrow_forward
- Consider a round potato being baked in an oven. Would you model the heat transfer to the potato as one, two, or three dimensional? Would the heat transfer be steady or transient? Also, which coordinate system would you use to solve this problem, and where would you place the origin? Explain.arrow_forward0 = 6 a = 25 t = 3 Y b = 30 xarrow_forwardSolve this problem and show all of the workarrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardreading is 0.4 mas SHOWN. Assume h₁ = 0.4 m, h₂ = 0.5 m. (a) Do you know the specific weight of mercury? (b) Do you know the specific weight of gasoline? (c) Do you know the specific weight of oil? (a) YHg = 133,000 (b) Ygas = 6867 (c) Yoil = 8829 eTextbook and Media Part 2 N/m³ N/m³ N/m³ A+ Gasoline t +B Oil -Mercury Attempts: unlimited Did you calculate the pressure difference between two locations using the correct specific weight? Did you assume that the pressures in fluid are the same in a horizontal plane even though they are in different tubes? Are the calculated pressures in a column of fluid always higher at lower elevations? Did you account for the fact that the two horizontal tubes of the U-tube are above the ground? Concepts: The pressure in a fluid is a function of the specific weight of the fluid and the height relative to a reference. Pressure is constant in a horizontal plane of a continuous mass of fluid. (a) What is the initial pressure difference? (PA-PB) (b) What is…arrow_forwardFind the solution of the following Differential Equations 1) "-4y+3y=0 3) "+16y=0 2) y"-16y=0 4) y"-y-6y=0 5) y"+2y=0 7) y"+y=0, (#0) 9) y"-y=0, y(0) = 6, y'(0) = -4 11) y"-4y+3y=0, y(0)=-1, 13) y'(0) = -5 "+2y+2y=0 15) y"-9y=0 17) y"-4y=0 6) y"-2y+2y=0 8) "+4y+5y=0 10) y"-9y=0, y(0) = 2, y'(0) = 0 12) y"-3y+2y= 0, y(0)=-1, y'(0) = 0 14) 4y+4y+y=0 16) "+6y+12y=0 18) 4y+4y+17y=0arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
EVERYTHING on Axial Loading Normal Stress in 10 MINUTES - Mechanics of Materials; Author: Less Boring Lectures;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jQ-fNqZWrNg;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY