
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
10th Edition
ISBN: 9780134319650
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 3, Problem 3.6RP
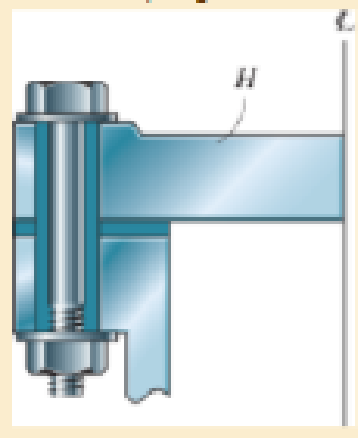
diameter steel bolts. If the clamping force in each bolt is 800 lb, determine the normal strain in the bolts. If σY = 40 ksi and Est = 29 (103) ksi, what is the strain in each bolt when the nut is unscrewed so that the clamping force is released?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
turbomachienery
auto controls
auto controls
Chapter 3 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Ch. 3.4 - Define a homogeneous material.Ch. 3.4 - Indicate the points on the stress-strain diagram...Ch. 3.4 - Define the modulus of elasticity E.Ch. 3.4 - At room temperature, mild steel is a ductile...Ch. 3.4 - Engineering stress and strain are calculated using...Ch. 3.4 - As the temperature increases the modulus of...Ch. 3.4 - A 100-mm-long rod has a diameter of 15 mm. If an...Ch. 3.4 - A bar has a length of 8 in. and cross-sectional...Ch. 3.4 - A 10-mm-diameter rod has a modulus of elasticity...Ch. 3.4 - The material for the 50-mm-long specimen has the...
Ch. 3.4 - The material for the 50-mm-long specimen has the...Ch. 3.4 - If the elongation of wire BC is 0.2 mm after the...Ch. 3.4 - A tension test was performed on a steel specimen...Ch. 3.4 - Data taken from a stress-strain test for a ceramic...Ch. 3.4 - Data taken from a stress-strain test for a ceramic...Ch. 3.4 - The stress-strain diagram for a steel alloy having...Ch. 3.4 - The stress-strain diagram for a steel alloy having...Ch. 3.4 - The stress-strain diagram for a steel alloy having...Ch. 3.4 - The rigid beam is supported by a pin at C and an...Ch. 3.4 - The rigid beam is supported by a pin at C and an...Ch. 3.4 - Acetal plastic has a stress-strain diagram as...Ch. 3.4 - The stress-strain diagram for an aluminum alloy...Ch. 3.4 - The stress-strain diagram for an aluminum alloy...Ch. 3.4 - The stress-strain diagram for an aluminum alloy...Ch. 3.4 - A bar having a length of 5 in. and cross-sectional...Ch. 3.4 - The rigid pipe is supported by a pin at A and an...Ch. 3.4 - The rigid pipe is supported by a pin at A and an...Ch. 3.4 - Direct tension indicators are sometimes used...Ch. 3.4 - The rigid beam is supported by a pin at C and an...Ch. 3.4 - The rigid beam is supported by a pin at C and an...Ch. 3.4 - The stress-strain diagram for a bone is shown, and...Ch. 3.4 - The stress-strain diagram for a bone is shown and...Ch. 3.4 - The two bars are made of a material that has the...Ch. 3.4 - The two bars are made of a material that has the...Ch. 3.4 - The pole is supported by a pin at C and an A-36...Ch. 3.4 - The bar DA is rigid and is originally held in the...Ch. 3.7 - A 100-mm-long rod has a diameter of 15 mm. If an...Ch. 3.7 - A solid circular rod that is 600 mm long and 20 mm...Ch. 3.7 - A 20-mm-wide block is firmly bonded to rigid...Ch. 3.7 - A 20-mm-wide block is bonded to rigid plates at...Ch. 3.7 - The acrylic plastic rod is 200 mm long and 15 mm...Ch. 3.7 - The plug has a diameter of 30 mm and fits within a...Ch. 3.7 - The elastic portion of the stress-strain diagram...Ch. 3.7 - The elastic portion of the stress-strain diagram...Ch. 3.7 - The brake pads for a bicycle tire are made of...Ch. 3.7 - The lap joint is connected together using a 1.25...Ch. 3.7 - The lap joint is connected together using a 1.25...Ch. 3.7 - The rubber block is subjected to an elongation of...Ch. 3.7 - The shear stress-strain diagram for an alloy is...Ch. 3.7 - A shear spring is made from two blocks of rubber,...Ch. 3 - The elastic portion of the tension stress-strain...Ch. 3 - The elastic portion of the tension stress-strain...Ch. 3 - The rigid beam rests in the horizontal position on...Ch. 3 - The wires each have a diameter of 12 in., length...Ch. 3 - The wires each have a diameter of 12 in., length...Ch. 3 - diameter steel bolts. If the clamping force in...Ch. 3 - The stress-strain diagram for polyethylene, which...Ch. 3 - The pipe with two rigid caps attached to its ends...Ch. 3 - The 8-mm-diameter bolt is made of an aluminum...Ch. 3 - An acetal polymer block is fixed to the rigid...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 1 Pleasearrow_forwardA spring cylinder system measures the pressure. Determine which spring can measure pressure between 0-1 MPa with a large excursion. The plate has a diameter of 20 mm. Also determine the displacement of each 0.1 MPa step.Spring power F=c x fF=Springpower(N)c=Spring constant (N/mm)f=Suspension (mm) How do I come up with right answer?arrow_forwardA lift with a counterweight is attached to the ceiling. The attachment is with 6 stainless and oiled screws. What screw size is required? What tightening torque? - The lift weighs 500 kg and can carry 800 kg. - Counterweight weight 600 kg - Durability class 12.8 = 960 MPa- Safety factor ns=5+-Sr/Fm= 0.29Gr =0.55arrow_forward
- Knowing that a force P of magnitude 750 N is applied to the pedal shown, determine (a) the diameter of the pin at C for which the average shearing stress in the pin is 40 MPa, (b) the corresponding bearing stress in the pedal at C, (c) the corresponding bearing stress in each support bracket at C. 75 mm 300 mm- mm A B P 125 mm 5 mm C Darrow_forwardAssume the B frame differs from the N frame through a 90 degree rotation about the second N base vector. The corresponding DCM description is: 1 2 3 4 5 6 9 # adjust the return matrix values as needed def result(): dcm = [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0] return dcmarrow_forwardFind the reaction at A and B The other response I got was not too accurate,I need expert solved answer, don't use Artificial intelligence or screen shot it solvingarrow_forward
- A six cylinder petrol engine has a compression ratio of 5:1. The clearance volume of each cylinder is 110CC. It operates on the four-stroke constant volume cycle and the indicated efficiency ratio referred to air standard efficiency is 0.56. At the speed of 2400 rpm. 44000KJ/kg. Determine the consumes 10kg of fuel per hour. The calorific value of fuel average indicated mean effective pressure.arrow_forwardThe members of a truss are connected to the gusset plate as shown in (Figure 1). The forces are concurrent at point O. Take = 90° and T₁ = 7.5 kN. Part A Determine the magnitude of F for equilibrium. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. F= 7.03 Submit ? kN Previous Answers Request Answer × Incorrect; Try Again; 21 attempts remaining ▾ Part B Determine the magnitude of T2 for equilibrium. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Figure T₂ = 7.03 C T2 |? KN Submit Previous Answers Request Answer × Incorrect; Try Again; 23 attempts remaining Provide Feedbackarrow_forwardConsider the following acid-base reaction: Fe3+(aq) +3H2O -Fe(OH)3 (s) + 3H* ← A. Using thermodynamics, calculate the equilibrium constant K at 25°C (The AG° of formation of Fe(OH)3(s) is -699 kJ/mol). B. Using the value of K you calculated in part a, if a solution contains 10-4 M Fe3+ and has a pH of 7.5, will Fe(OH)3(s) precipitate? Show all calculations necessary to justify your answer. Note that the reaction as written is for precipitation, not dissolution like Ksp-arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
An Introduction to Stress and Strain; Author: The Efficient Engineer;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aQf6Q8t1FQE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY