
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
The correct sequence for the four reactions of the
Concept Introduction:
The
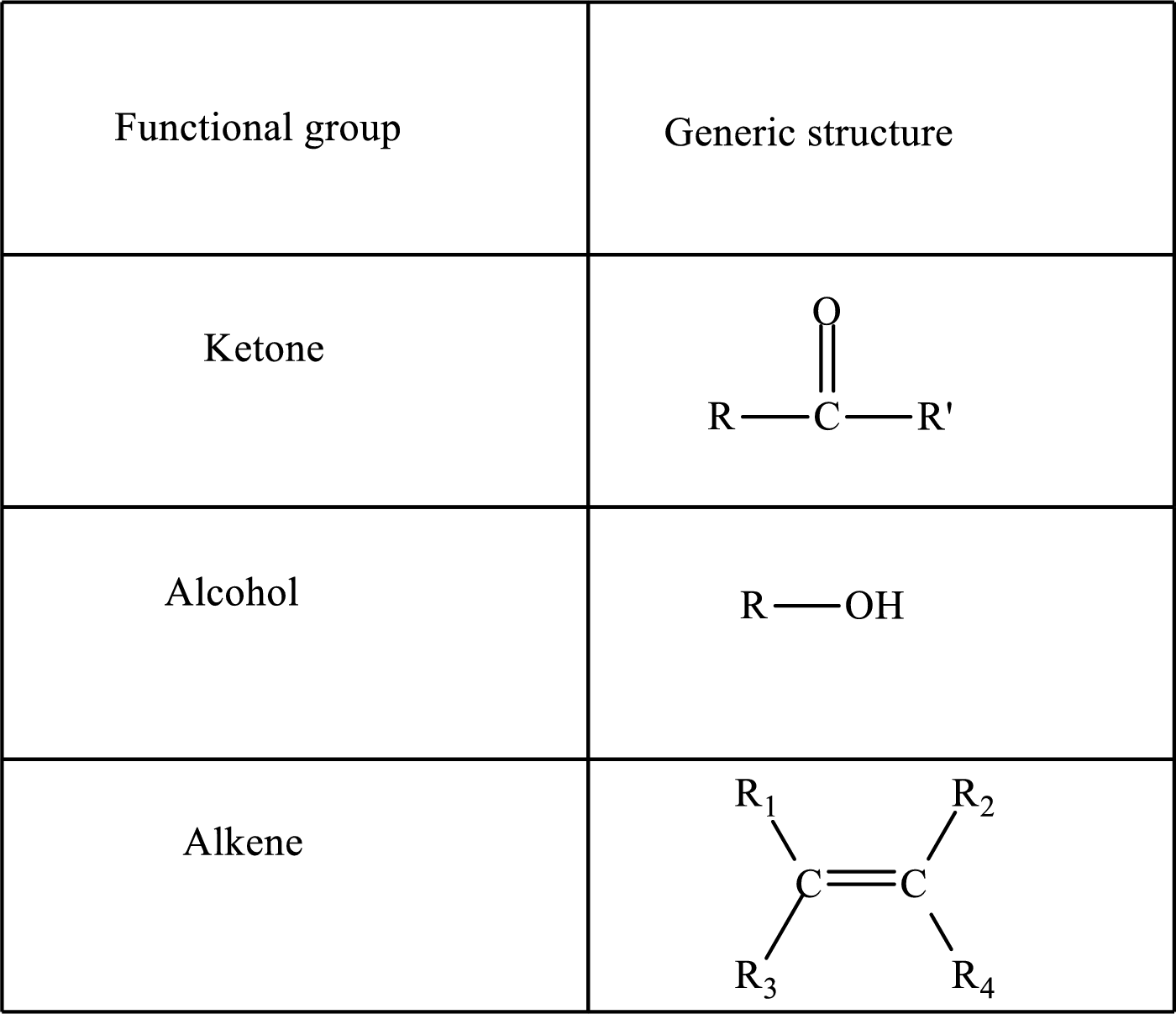
Here, R and
Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons that contain covalently bonded hydrogen and carbon atoms. In secondary alcohol, the carbon atom of the hydroxyl group
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 25 Solutions
Study Guide with Selected Solutions for Stoker's General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry, 7th
- Draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. N O' 1. H2O, pyridine 2. neutralizing work-up く 8 W aarrow_forwardIdeal Gas Law Practice Name If you need a refresher on Ideal Gas Law, go back to your Ideal Gas Law Reading Assignment from last week! On all of the following, you'll need to make sure to convert pressures to atm and convert temperatures to Kelvin in order to be able to use the R gas constant on your equation sheet! Given: Ideal Gas Law = then P= pressure V = volume R= ideal gas consent PV=nRT namount of substance n=PV/TR P=nRT/V I = temperature V=nRT/P T=PV/nR R=PV/nT 1. What pressure is required to contain 0.023 moles of nitrogen gas in a 4.2 L container at a temperature of 20.°C? 2. Oxygen gas is collected at a pressure of 123 kPa in a container which has a volume of 10.0 L. What temperature must be maintained on 0.500 moles of this gas in order to maintain this pressure? Express the temperature in degrees Celsius. 3. How many moles of chlorine gas would occupy a volume of 35.5 L at a pressure of 100.0 kPa and a temperature of 100. °C? After determining the number of moles,…arrow_forward1. The following conversion includes chemistry we have covered very recently, some chemistry from last term, and chemistry from the first chapter of this unit. Provide curly arrows and an explanation for this mechanism. Use the reagents in the order given. You do not need any other reagents. 1. NaOEt OEt 2.arrow_forward
- COOEt COOEt Step 1 Step 2 Step 3 COOEt COOEt COOH Step 6 OH Step 4 Step 7 (racemic) cyclizes under conditions (8) OTS Step 5 Step 8 ОН OH (racemic) Frontalin (racemic) Shown above are the steps in one of the several published syntheses of Frontalin, a pheromone of the western pine beetle. From the choices provided, show the reagents and conditions by which step 3 of this synthesis might be accomplished. List the reagent(s) in order that will accomplish this transformation. No more than 4 steps are required. List your answer as a single letter (single-step transformation) or a series of letters (multi-step transformation) with no commas separating them. For example, "ab" corresponds to: 1. Eto Na+ 2. NaOH, H₂O NOTE: The order in which you list your letters matters! Reagents: a. Eto Na* g. NaCN b. NaOH, H₂O h. SOCI₂ c. H3O+, heat i. (CH3)2CuLi, ether, -78°C d. LiAlH4 j. H₂O e. p-TsCI, pyridine k. RCO3H f. Br I. H3O+ 1,024arrow_forwardK ← nationa Login - Paymentivet MapQue Draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts and the carboxylic acid side product. N 1. excess LiAlH4 2. H₂O ✓ W aarrow_forwardDraw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts and the alcohol side product. 1. H3O+, heat 2. Neutralizing work-up Drawing Qarrow_forward
- Indicate the procedure (reagent Z) to go from compound A1 to compound A2. A1 Z P(C6H5)3 A2arrow_forwardPlease help with this graph.arrow_forwardogin - PaymentN MapQuest 3 Overview - SAP NetW... Draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. CI 1. NaBH4 2. H₂O C Clever | Portal Job Op Problem Atoms, Bonds and Rings Draw or tap a new bond toarrow_forward
- 2. Draw the remaining two resonance structures for the carbocation intermediate in the meta nitration of methyl benzoate AND explain why the meta orientation is preferred. Hint: how is the placement of the cation favorable after addition of nitronium relative to the electron withdrawing group? (2 pts) H NO2 CO₂Mearrow_forwardLabel all absorptions over 1500 cm-1. Please be specific and mark IR if needed for explanation. Compound OH sp^3 C-H C=O C-O Triglyceridearrow_forwardIdentify the intermediate that is INITIALLY formed in a saponification reaction (hydrolysis of an ester). III -OH H₂O HO OH HO O || A B C III D IV IVarrow_forward
 General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,

