
(a)
Interpretation- To name the given compound.
Introduction-
- Identify the longest parent chain.
- Identify the substituents.
- In
alkenes , the lowest number is given to double bonds rather than substituents. - The position of the double bond is mentioned while naming.
- If the substituents are more than one, prefixes like di, tri, tetra, etc., are used.
- The name of the compound starts with substituents with their position in the parent chain. They are written in alphabetical order.
- Numbers and names are separated by dash while a number are separated by commas.
- The chain name is based on the number of carbon atoms present like meth, eth, prop, but, pent, hex, hept, oct, non, dec,
- Suffix “ene” is used for the
alkane parent chain and “yl is used for substituents. - Alkenes show cis-trans isomerism. If the same groups are present on the same side of the double bond, it is “cis”. If the same groups are present on the opposite side of the double bond, it is “trans”.
(a)
Answer to Problem 46A
The name of the compound is
Explanation of Solution
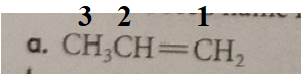
The compound has the longest parent chain with three carbon atoms. Hence the parent name chain will be prop with suffix “ene”.
Therefore, the name of the compound is
Therefore, the name of the compound is
(b)
Interpretation- To name the given compound.
Introduction- IUPAC nomenclature follows some rules for naming the compounds:
- Identify the longest parent chain.
- Identify the substituents.
- In alkenes, the lowest number is given to double bonds rather than substituents.
- The position of the double bond is mentioned while naming.
- If the substituents are more than one, prefixes like di, tri, tetra, etc., are used.
- The name of the compound starts with substituents with their position in the parent chain. They are written in alphabetical order.
- Numbers and names are separated by dash while a number are separated by commas.
- The chain name is based on the number of carbon atoms present like meth, eth, prop, but, pent, hex, hept, oct, non, dec,…
- Suffix “ene” is used for the alkane parent chain and “yl is used for substituents.
- Alkenes show cis-trans isomerism. If the same groups are present on the same side of the double bond, it is “cis”. If the same groups are present on the opposite side of the double bond, it is “trans”.
(b)
Answer to Problem 46A
The name of the compound is
Explanation of Solution
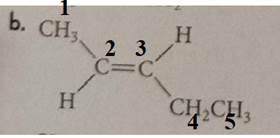
The compound has the longest parent chain with five carbon atoms. Hence, the parent name chain will be pent with the suffix “ene”. The double bond is present at the second carbon.
Same group, hydrogen is present on the opposite side of the double bond; hence, it shows a trans isomer.
Therefore, the name of the compound is
Therefore, the name of the compound is
(c)
Interpretation- To name the given compound.
Introduction- IUPAC nomenclature follows some rules for naming the compounds:
- Identify the longest parent chain.
- Identify the substituents.
- In alkenes, the lowest number is given to double bonds rather than substituents.
- The position of the double bond is mentioned while naming.
- If the substituents are more than one, prefixes like di, tri, tetra, etc., are used.
- The name of the compound starts with substituents with their position in the parent chain. They are written in alphabetical order.
- Numbers and names are separated by dash while a number are separated by commas.
- The chain name is based on the number of carbon atoms present like meth, eth, prop, but, pent, hex, hept, oct, non, dec,…
- Suffix “ene” is used for the alkane parent chain and “yl is used for substituents.
- Alkenes show cis-trans isomerism. If the same groups are present on the same side of the double bond, it is “cis”. If the same groups are present on the opposite side of the double bond, it is “trans”.
(c)
Answer to Problem 46A
The name of the compound is
Explanation of Solution
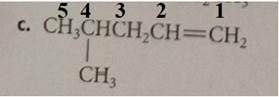
The compound has the longest parent chain with five carbon atoms. Hence the parent name chain will be pent with the suffix “ene”. The double bond is present at first carbon.
Substituent has one carbon atom, and it is present on the fourth carbon atom of the parent chain.
Therefore, the name of the compound is
Therefore, the name of the compound is
(d)
Interpretation- To name the given compound.
Introduction- IUPAC nomenclature follows some rules for naming the compounds:
- Identify the longest parent chain.
- Identify the substituents.
- In alkenes, the lowest number is given to double bonds rather than substituents.
- The position of the double bond is mentioned while naming.
- If the substituents are more than one, prefixes like di, tri, tetra, etc are used.
- The name of the compound starts with substituents with their position in the parent chain. They are written in alphabetical order.
- Numbers and names are separated by dash while a number are separated by commas.
- The chain name is based on the number of carbon atoms present like meth, eth, prop, but, pent, hex, hept, oct, non, dec,…
- Suffix “ene” is used for the alkane parent chain and “yl is used for substituents.
- Alkenes show cis-trans isomerism. If the same groups are present on the same side of the double bond, it is “cis”. If the same groups are present on the opposite side of the double bond, it is “trans”.
(d)
Answer to Problem 46A
The name of the compound is
Explanation of Solution
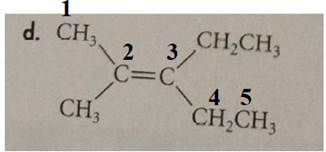
The compound has the longest parent chain with five carbon atoms. Hence the parent name chain will be pent with the suffix “ene”. The double bond is present at the second carbon.
Methyl substituent is present at the second carbon and ethyl substituent is present at the third carbon.
Methyl substituents are present on the same side of the double bond. Hence this is a cis isomer.
Therefore, the name of the compound is
Therefore, the name of the compound is
Chapter 22 Solutions
Chemistry 2012 Student Edition (hard Cover) Grade 11
- > Can the molecule on the right-hand side of this organic reaction be made in good yield from no more than two reactants, in one step, by moderately heating the reactants? ? Δ • If your answer is yes, then draw the reactant or reactants in the drawing area below. You can draw the reactants in any arrangement you like. If your answer is no, check the box under the drawing area instead. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Х © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accesarrow_forwardPredict the major products of the following organic reaction: O O + A ? Some important notes: • Draw the major product, or products, of the reaction in the drawing area below. • If there aren't any products, because no reaction will take place, check the box below the drawing area instead. • Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products that are enantiomers. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. eserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center >arrow_forward(EXM 2, PRBLM 3) Here is this problem, can you explain it to me and show how its done. Thank you I need to see the work for like prbl solving.arrow_forward
- can someone draw out the reaction mechanism for this reaction showing all bonds, intermediates and side products Comment on the general features of the 1H-NMR spectrum of isoamyl ester provided belowarrow_forwardWhat would be the best choices for the missing reagents 1 and 3 in this synthesis? 1. PPh3 3 2. n-BuLi • Draw the missing reagents in the drawing area below. You can draw them in any arrangement you like. • Do not draw the missing reagent 2. If you draw 1 correctly, we'll know what it is. • Note: if one of your reagents needs to contain a halogen, use bromine. Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forwardIdentify the missing organic reactants in the following reaction: X + Y H+ two steps Note: This chemical equation only focuses on the important organic molecules in the reaction. Additional inorganic or small-molecule reactants or products (like H2O) are not shown. In the drawing area below, draw the skeletal ("line") structures of the missing organic reactants X and Y. You may draw the structures in any arrangement that you like, so long as they aren't touching. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Х :arrow_forward
- I am struggling with the IUPAC (sys H Reply ☑Mark as Unreadarrow_forwardDon't used hand raiting and don't used Ai solution and correct answerarrow_forwardH R Part: 1/2 :CI: is a/an electrophile Part 2 of 2 Draw the skeletal structure of the product(s) for the Lewis acid-base reaction. Include lone pairs and formal charges (if applicable) on the structures. 4-7: H ö- H Skip Part Check X :C1: $ % L Fi Click and drag to start drawing a structure. MacBook Pro & ㅁ x G 0: P Add or increase positive formal cha Save For Later Submit ©2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Centearrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





