
a.
Interpretation: To give the isomerization reaction between pentane and 2-methyl butane.
Concept Introduction: A chemical process in which the compound is changed into different isomers is known as an isomerization reaction.
a.
Answer to Problem 82A
The isomerization reaction between pentane and 2-methyl butane is shown as follows:
Explanation of Solution
Pentane and 2-methyl butane are structural isomers or they can be classified as chain isomers.
Pentane isomerizes into 2-methyl butane and 2,2-dimethyl propane.
The isomerization reaction can be depicted as follows:
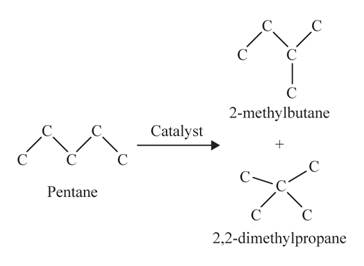
b.
Interpretation: To give the type of isomers.
Concept Introduction: The isomers in which the arrangement of atoms is in a different order while the molecular formulas of the compound remain the same are known as structural isomers.
b.
Answer to Problem 82A
Pentane and 2-methyl butane are chain isomers.
Explanation of Solution
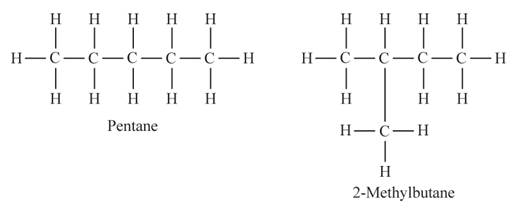
In chain isomers, the molecular formula is the same for both compounds while how carbon chains are arranged is different.
Both pentane and 2-methyl butane have the same molecular formula that is
c.
Interpretation: To predict which isomer has the lowest boiling point.
Concept Introduction: The isomers in which the arrangement of atoms is in a different order while the molecular formulas of the compound remain the same are known as structural isomers.
c.
Answer to Problem 82A
2-methyl butane has the lowest boiling point than pentane.
Explanation of Solution
The boiling point is the temperature at which the vapor pressure of the substance becomes identical to the pressure surrounding the liquid.
The boiling point decreases as the branching in the compound increases. Both pentane and 2-methyl butane are chain isomers of each other. In pentane, the carbon atoms are arranged in a straight-chain isomer while in 2-methyl butane the carbon atoms are arranged in branches.
Therefore, the boiling point of 2-methyl butane is less than pentane.
Chapter 22 Solutions
Chemistry 2012 Student Edition (hard Cover) Grade 11
- 1. Determine the relationship between the following molecules as identical, diastereomers, or enantiomers (6 points, 2 points each). OH OH OH A-A OH HOT HO- ACHN and HO- ACHN OH HO HO ° OH and OH OH SH and ...SHarrow_forward20,0 Complete the electron pushing mechanism to y drawing the necomery unicaciones and carved on for Step 1: Add curved arms for the tint step, traiment with NalilĻ. The Nation 458 Step 2: Added for the second step, inalment with), how the "counterion bar Step 3: Daw the products of the last simplom organic and one incoganic spacient, including all nonbondingarrow_forwardplease provide the structure for this problem, thank you!arrow_forward
- Draw the Fischer projection from the skeletal structure shown below. HO OH OH OH OH H Q Drawing Atoms, Bonds and Rings Charges I ☐ T HO H H OH HO I CH2OH H OH Drag H OH -CH2OH CHO -COOH Undo Reset Remove Donearrow_forwardplease provide the structure for this problem, thank youarrow_forwardpresented by Morallen Lig Intermine the hand product for the given mution by adding atoms, bonds, nonhonding diarion panda скуль Step 3: Comp the draw the product Step 2: Agama workup Compithe 429 ملولةarrow_forward
- Reaction A 0,0arrow_forwardpresented by Morillon Leaning Predict the organic product for the min кусур HSC Adithane carved arnown to come than that to the condon slchroruis in acid in in aquishri with ноюarrow_forward6.15PM Sun Mar 30 K Draw the major product of this reaction. Include any relevant stereochemistry. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Problem 1 of O H [PhзPCH2CH3]*C|¯ NaH Drawing > Q Atoms, Bonds and Draw or tap a nearrow_forward
- 8:17 PM Sun Mar 30 Draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. HSCH2CH2CH2SH, BF3 Probler Drawing Ato Bonds Clarrow_forwardpresented by Mr L How the coprion. (Il Done in no wraction, dew the starting redential) доarrow_forward8:16 PM Sun Mar 30 K Draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Proble 1. CH3MgBr 2. H3O+ F Drawingarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





