
Concept explainers
Northern blot analysis is performed on cellular mRNA isolated from E. coli. The probe used in the northern blot analysis hybridizes to a portion of the lacY sequence. Below is an example of the gel from northern blot analysis for a wild
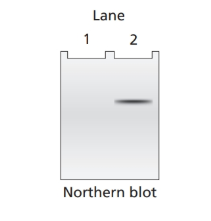
a. Lac+ bacteria with the genotype
b. Lac- bacteria with the genotype
c. Lac- bacteria with the genotype
d. Lac+ bacteria with the genotype
e. Lac- bacteria with the genotype
f. Lac- bacteria with the genotype
g. Lac- bacteria with the genotype
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 14 Solutions
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (2nd Edition)
- DNA samples from four individuals were cleaved with the same MW restriction endonuclease. The DNA fragments were separated by gel clectrophoresis, transferred to a membrane, and hybridized with a 12 kb 10 kb DNA probe complementary to a region between sites C and D (see 8 kb hybridization line). The image of the southern blot shows the labeled DNA bands and 6 kb molecular weight (MW) markers. The lane labels I, II, III, and IV -5 kb correspond to individuals I, II, III, and IV. Assume that fragments such as C-D and C-E are clearly resolved in this gel system. Fragment sizes are as given: A-B is 4 kb, B-C is I kb, C-D is 5 kb, and D-E is 650 bp. Individual I has five cleavage sites (A, B, C, D, and E) for the restriction endonuclease. DNA homologous to probe Which individual has at least one point mutation that eliminates restriction site C only? O II IV cannot be determined II Which individual has at least one point mutation that climinates restriction sites B and C? III O IV cannot be…arrow_forwardAfter characterizing the DNA composition of various cats, you identify a protein-coding gene in tigers called stripes and wish to study the structure of the protein product STRIPES. This requires that you purify recombinant ridges from E. coli. First, the stripes gene must be amplified by PCR and then inserted into an appropriate plasmid for bacterial expression. Such a plasmid is diagrammed below. ori CAP Binding Site من Promoter MCS The restriction sites for Aatll and Kpnl are: Aatll 5'-GACGTC-3' Kpnl = 5'-GGTACC-3' Laco (Operator) -Kpnl Aatll The coding strand for the stripes gene is shown below, with start and stop codons in bold. 5'-ATGCAACAGTAGCTGAAGCCCAGTGACACCATCGAAAATGTGAAGGCCAAGATGAGGCTCATCTTTGCAGGCAAGCAGCTG GAAGATGGCCGTACTCTTTCTGACTATGCGTCTGAGAGGTGGTATGCAGATCTTCGTGAAGACCCTGACCGGCAAGACCAATGT GAAGGCCAAGATCCAGGATAAAGAAGGCATCCCTCCCGACCAGCAGAGGGCACTCTTTCTGACTACAACATCCAGAAGGAGTCG ACCCTGCACCTGGTCCTGCTGACCGGCAAGACCATCACTCTGGAGGTGGAGCCCAGTGACACCATCGAAAATCCCGACCAGCAG…arrow_forwardYou are attempting to prepare a single gene knockout library using the pRL27 transposon system. You grow the donor E. coli in Luria broth containing both kanamycin and diaminopimelic acid (DAP) and your recipient Serratia rubidaea in plain Luria broth. You combine an equal ratio of donor and recipient cultures and plate the mixture onto Luria agar supplemented with DAP. After 24 hours incubation at 37°C, you create a cell slurry and plate the cells onto Luria agar aupplemented with kanamycin. After 24 hours incubation at 37°C, you find that no colonies grow. What best explains this outcome? A. Failure to supplement media with DAP B. Failure to remove antiobiotic containing media C. Failure to incubate for a sufficient length of time D. Failure to incubate at the appropiate temperature E. Failure to use the proper mating mix ratioarrow_forward
- Decide on two restriction sites that you can use to clone this into pL4440’s MCS. Identify their sequence and explain why. Tip: The plasmid map is showed below, details of restriction site sequences can be found at https://enzymefinder.neb.com/#!#nebheaderarrow_forwardMany resistance mechanisms are encoded on plasmids. These mechanisms are of great clinical significance, because they can spread very easily through horizontal gene transfer. A culture of the bacterial isolate is grown, and plasmid DNA is isolated using a spin column-based solid phase extraction method. The purified plasmid DNA is then submitted for next-generation sequencing. Bioinformatic analyses of the sequencing results suggests that the following gene is likely involved in antibiotic resistance: > putative antibiotic resistance gene ATGCGTGTATTAGCCTTATCGGCTGTGTTTTTGGTGGCATCGATT ATCGGAATGCCTGCGGTAGCAAAGGAATGGCAAGAAAACAAAAGT TGGAATGCTCACTTTACTGAACATAAATCACAGGGCGTAGTTGTG CTCTGGAATGAGAATAAGCAGCAAGGATTTACCAATAATCTTAAA CGGGCGAACCAAGCATTTTTACCCGCATCTAGTGCGAAAATTCCC AATAGCTTGATCGCCCTCGATTTGGGCGTGGTTAAGGATGAACAC CAAGTCTTTAAGTGGGATGGACAGACGCGCGATATCGCCACTTGG AATCGCGATCATAATCTAATCACCGCGATGAAATATTCAGTTGTG CCTGTTTATCAAGAATTTGCCCGCCAAATTGGCGAGGCACGTATG…arrow_forwardGenomic DNA from a family where sickle-cell disease is known to be hereditary, is digested with the restriction enzyme MstII and run in a Southern Blot. The blot is hybridised with two different 0.6 kb probes, both probes (indicated in red in the diagram below) are specific for the β-globin gene (indicated as grey arrow on the diagram below). The normal wild-type βA allele contains an MstII restriction site indicated with the asterisk (*) in the diagram below; in the mutated sickle-cell βS allele this restriction site has been lost. What size bands would you expect to see on the Southern blots using probe 1 and probe 2 for an individual with sickle cell disease (have 2 βS alleles)? Probe 1 Probe 2 (a) 0.6kb 0.6kb and 1.2kb (b) 0.6kb and 1.8kb 0.6kb, 1.2kb and 1.8kb (c) 1.2kb 0.6kb (d) 1.8kb 1.8kb a. (a) b. (b) c. (c) d. (d)arrow_forward
- Mouse genomic DNA is treated with a restriction endonuclease and electrophoresed in an agarose gel. A radioactive probe made from the human gene rxr-1 is used to perform a Southern blot. The experiment was repeated three times. Explain the results of these repeated experiments:arrow_forwardDecide on two restriction sites that you can use to clone this into pL4440’s MCS. Identify their sequence. Tip: The plasmid map is in Figure 3, details of restriction site sequences can be found at https://enzymefinder.neb.com/#!#nebheaderarrow_forwardPlease DESCRIBE, in outline form, the method you will use to select for bacterial cells that have taken up the pL311 plasmid, and to screen those cells for the presence of plasmids that are likely to contain a cloned gene. Be sure to mention the specific media you will use. In addition, please explain the rationale behind this specific selection and screening procedure. (Remember that you have available the following types of media: (i) media containing neither kanamycin nor X-gal, (ii) media containing BOTH kanamycin and X-gal, (iii) media containing tetracycline, and (iv) media containing ampicillin.arrow_forward
- Match the following Conjugation terms with the most appropriate description in the image: F- recombinant F- strain F+ strain HFR strainarrow_forwardUsing the plasmid map of pBCH2.0 provided above, predict how many DNA fragments would be formed if this plasmid was digested with restriction enzyme BamHI.arrow_forwardFrom an Escherichia coli strain, five Hfr strains were isolated. The location and orientation of the transfer origin of each Hfr strain is shown in Figure 1. You want to use these five strains to map the locus responsible for thiamine synthesis, called thi. Each Hfr strain is sensitive to rifampicin (Rifs) and thi*. Conjugation experiments are performed between each of the Hfr strains and an F strain Rif Thi™. 0 T leu 10 20 T nadD pyrC trp 40 T his 60 70 2) The results are shown in the following table: Donor strain Hfr1 Hfr2 Hfr3 Hfr4 Hfr5 cysG 80 90 1) What is the selection medium used in these conjugation experiments metA Colonies Thi+ 1000 0 400 0 25 100 Hfr1 Hfr2 Figure 1: Chromosome map of Escherichia coli. Five Hfr strains (Hfr1 to Hfr5) were isolated and the location and orientation of the origin of transfer is shown by the arrows in each Hfr strain. Distances in minutes are shown. Leu: leucine biosynthesis; nadD: NAD biosynthesis; pyrC: pyrimidine biosynthesis; trp: tryptophan…arrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





