
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (2nd Edition)
2nd Edition
ISBN: 9780321948908
Author: Mark F. Sanders, John L. Bowman
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 14, Problem 33P
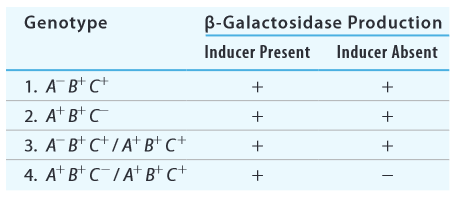
The following hypothetical genotypes have genes A, B, and C corresponding to lacI,lacO, andlacZ but not necessarily in that order. Data in the table indicate whether
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
The lac genotypes are as shown below:
P+OcZ-Y+A+// P¯O+Z+Y+A+
(i)
The lac operon consists of three structural genes, lacZ, lacY and lacA. Which
structural genes are involved in lactose metabolism? Explain.
(ii)
Draw and explain how lactose repress the gene expression in lac IS/I- heterozygote.
(iii)
What is the function of the promoter in the bacterial operon?
Indicate the presence of the the B galactosidase and permease. Please explain and follow the instructions in the picture
After irradiating wild-type cells of Neurospora (a haploid fungus), a geneticist finds two leucine-requiringauxotrophic mutants. He combines the two mutants ina heterokaryon and discovers that the heterokaryon isprototrophic.a. Were the mutations in the two auxotrophs in the samegene in the pathway for synthesizing leucine or in twodifferent genes in that pathway? Explain.b. Write the genotype of the two strains according toyour model.c. What progeny and in what proportions would youpredict from crossing the two auxotrophic mutants?(Assume independent assortment.)
Chapter 14 Solutions
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (2nd Edition)
Ch. 14 - 12.1 Bacterial genomes frequently contain groups...Ch. 14 - Transcriptional regulation of operon gene...Ch. 14 - Why is it essential that bacterial cells be able...Ch. 14 - Identify similarities and differences between an...Ch. 14 - The transcription of -galactosidase and permease...Ch. 14 - 12.6 Is attenuation the product of an allosteric...Ch. 14 - The trpL region contains four repeated DNA...Ch. 14 - The CAP binding site in the lac promoter is the...Ch. 14 - What role does cAMP play in transcription of lac...Ch. 14 - How would a cap- mutation that produces an...
Ch. 14 - Explain the circumstances under which attenuation...Ch. 14 - Consider the transcription of genes of the...Ch. 14 - Describe the lytic and lysogenic life cycles of ...Ch. 14 - 12.14 Define antisense RNA, and describe how it...Ch. 14 - 12.15 Attenuation of trp operon transcription is...Ch. 14 - 12.16 In the lac operon, what are the likely...Ch. 14 - Identify which of the following lac operon haploid...Ch. 14 - Prob. 18PCh. 14 - 12.19 List possible genotypes for lac operon...Ch. 14 - Suppose each of the genotypes you listed in parts...Ch. 14 - 12.21 Four independent mutants (mutants A to D)...Ch. 14 - Suppose the lac operon partial diploid...Ch. 14 - Prob. 23PCh. 14 - 12.24 A repressible operon system, like the trp...Ch. 14 - 12.25 What is the likely effect of each of the...Ch. 14 - 12.26 Suppose that base substitution mutations...Ch. 14 - 12.27 Two different mutations affect. Mutant...Ch. 14 - How would mutations that inactivate each of the...Ch. 14 - The bacterial insertion sequence IS 10 uses...Ch. 14 - 12.34 Northern blot analysis is performed on...Ch. 14 - 12.37 The electrophoresis gel shown in part (a) is...Ch. 14 - Prob. 32PCh. 14 - The following hypothetical genotypes have genes A,...Ch. 14 - For an E. coli strain with the lac operongenotype...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- For the genotypes and conditions (lactose present or absent) shown in the following Table 2, predict whether the expression of beta-galactosidase is inducible (I), noninducible (N) or constitutive (C). Explain your reason. Table 2 Genotype I*p*o°z+ Condition (i) No lactose (ii) (iii) (iv) I*P*O*Z+ I*P•O*Z* I$P*O°Z* Lactose Lactose Lactose (v) IP*0°Z+ No lactosearrow_forwardDescribe how polymorphisms is found at 13910-C/T and 22018-G/A in the regulatory area of the lactase gene (LCT). And elaborate the mechanism for two polymorphisms causing mutation from 13910-C/T and 22018-G/A to 13910-C/C or 22018-G/G variants in lactase intolerance disorder. also, how LCT gene is corelated to lactase intolerance disorder?arrow_forwardConsider the mechanism of the enzyme RNase: What would happen to the Km (i.e., would it increase, decrease, or stay the same) if the his12 was mutated to a lysine? Explain. What would happen to the Kcat (i.e., would it increase, decrease, or stay the same) if the his12 was mutated to a valine? Explain.arrow_forward
- A particular type of anemia in humans, called b-thalassemia,results from a severe reduction or absence of the normal b-globinchain of hemoglobin. However, the g@globin chain, normally onlyexpressed during fetal development, can functionally substitutefor b-globin. A variety of studies have explored the use of thenucleoside 5-azacytidine for the expression of g-globin in adultpatients with b-thalassemia.(a) How might 5-azacytidine lead to expression of g-globin inadult patients?(b) Explain why this drug may also have some adverse side effects.arrow_forwardCTP synthetase catalyzes the glutamine-dependent conversion of UTP to CTP. The enzyme is allosterically inhibited by the product, CTP. Mamma- lian cells defective in this allosteric inhibition are found to have a complex phenotype: They require thymidine in the growth medium, they have unbal- anced nucleotide pools, and they have an elevated spontaneous mutation rate. Explain the likely basis for these observations.arrow_forwardConsiderable effort has been directed toward determining the genes in which sequence variation contributes to the development of type 2 diabetes. Approximately 800 genes have been implicated. Propose an explanation for this observation.arrow_forward
- Yeast cells are grown with galactose as the sole carbon source and ATP levels are abundant. Describe and diagram how GAL1 gene expression will be changed (or unchanged) in 1) a ΔGal3 mutant and 2) a ΔGal4 mutant in comparison to WT. (Δ is a symbol for deletion.) WT: ΔGal3: ΔGal4:arrow_forwardFor each of the E. coli strains that follow, indicate theeffect of the genotype on the expression of the trpEand trpC genes in the presence or absence of tryptophan. [In the wild type (R+ P+ o+ att+ trpE+ trpC+),trpC and trpE are fully repressed in the presence oftryptophan and are fully expressed in the absence oftryptophan.]R = repressor gene; Rnproduct cannot bind tryptophan; R− product cannot bind operatoro = operator for the trp operon; o− cannot bind repressoratt = attenuator; att− is a deletion of the attenuatorP = promoter; P− is a deletion of the trp operonpromotertrpE− and trpC− are null (loss-of-function) mutationsa. R+ P− o+ att+ trpE+ trpC+b. R− P+ o+ att+ trpE+ trpC+c. RnP+ o+ att+ trpE+ trpC+d. R− P+ o+ att− trpE+ trpC+e. R+ P+ o− att+ trpE+ trpC−/R− P+ o+ att+trpE− trpC+f. R+ P− o+ att+ trpE+ trpC−/R− P+ o+ att+trpE− trpC+g. R+ P+ o− att− trpE+ trpC−/R− P+ o− att+trpE− trpC+arrow_forwardWhy is it adaptive for the structural genes for using lactose to be under the control of a single promoter (i.e., synthesize a polycistronic message rather than three monocistronic messages)? a. For efficient absorption and catabolism of lactose, structural genes send a single signal. This is why polycistronic message is favored more than the monocistronic message since the former involves transmission of numerous messages in initiation and termination. b. Polycistronic message is favored more than the monocistronic message. c. Polycistronic message is favored more than the monocistronic message since the former involves transmission of numerous messages in initiation and termination. d. For an efficient absorption and catabolism of lactose, structural genes send a single signal only. e. Polycistronic message is favored more than the monocistronic message since the former involves transmission of single message in initiation and termination.arrow_forward
- Scientists studied gene expression and phenotypes of the YJL213W gene in yeast to determine how phosphate was transported based on two different genotypes. The PHO84 locus of the gene is a phosphate transporter and the PHO4 locus is a regulator of genes that respond to phosphate availability. Two genotypes were compared and are shown in the graph: BY (solid black line, triangles) and RM (dashed line, Xs). Which of the following statements describes the correlation between the genotype, phosphate concentration, and YJL213W expression based on the data? A - In RM genotypes, a lower PHO4 activation level led to less YJL213W expression and a lower rate of phosphate transport. B - In RM genotypes, a greater PHO4 activation level led to less YJL213W expression and a lower rate of phosphate transport. C = In BY genotypes, a lower activation level of PHO4 led to more YJL213W expression and a higher rate of phosphate transport. D - In BY genotypes a greater activation level of…arrow_forwardFor the lac genotypes shown in the following table, predict whether the structural genes (Z) are constitutive, permanently repressed, or inducible in the presence of lactose. Genotype Constitutive Repressed Inducible I+O+Z+ * I-O+Z+ I-OCZ+ I-OCZ+/F=O+ I+OCZ+/F=O+ ISO+Z+ ISO+Z+/F=I+arrow_forwardExplain how the following mutations would affect transcription of the yeast GAL1 gene in the presence of galactose. (a) A deletion within the GAL4 gene that removes the region encoding amino acids 1 to 100. (b) A deletion of the entire GAL3 gene. (c) A mutation within the GAL80 gene that blocks the ability of Gal80 protein to interact with Gal3p. (d) A deletion of one of the four UASG elements upstream from the GAL1 gene. (e) A point mutation in the GAL1 core promoter that alters the sequence of the TATA box.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning

Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781305389892
Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Mitochondrial mutations; Author: Useful Genetics;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GvgXe-3RJeU;License: CC-BY