
Concept explainers
Four independent
The strains have the following
Mutant A is lac-, but transcription of operon genes is induced by lactose.
Mutant B is lac- and has uninducible transcription of operon genes.
Mutant C is lac+ and has constitutive transcription of operon genes.
Mutant D is lac+ and has constitutive transcription of operon genes.
A microbiologist develops donor and recipient varieties of each mutant strain and crosses them with the results shown below. The table indicates whether inducible, constitutive, or noninducible transcription occurs, along with lac+ and lac- growth habit for each partial diploid. Assume each strain has a single mutation.
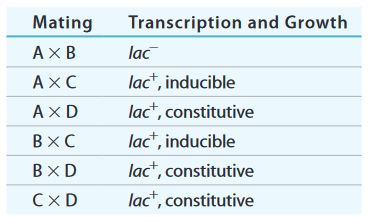
Use the information to identify which lac operon gene is mutated in each strain.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 14 Solutions
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (2nd Edition)
- A number of mutations affect the expression of the lac operon in E. coli. Consider each genotype below and complete the table using “+” to indicate that the gene is expressed, and “−” to indicate that gene is not expressed.arrow_forwardA number of mutations affect the expression of the lac operon in E. coli. The genotypes of several E. coli strains are shown below. ("+" indicates a wild-type gene with normal function and "-" indicates a loss-of-function allele.) Please predict which of the following strains would have the highest beta-galactosidase enzyme activity, when grown in the lactose medium. CAP It P+ O`Z+ CAP+ I P+ O+ Zt CAP+ It P- O+ Z+ CAP+ It P+ 0+ Zarrow_forwardGive the levels of Beta-galactosidase activity (high or low or zero) expected for the following partial diploids for the lac operon strains.arrow_forward
- A number of mutations affect the expression of the lac operon in E. coli. The genotypes of several E. coli strains are shown below. ("+" indicates a wild-type gene with normal function and "-" indicates a loss-of-function allele.) Please predict which of the following strains would have the lowest beta-galactosidase enzyme activity, when grown in the lactose medium. OF POZY Ort Ptot Z¹ Yt Ort p²o+z¹Y+ Orpt ot ztyarrow_forwardA number of mutations affect the expression of the lac operon in E. coli. The genotypes of several E. coli strains are shown below. ("+" indicates a wild-type gene with normal function and "-" indicates a loss-of-function allele.) Please predict which of the following strains would have the lowest beta-galactosidase enzyme activity, when grown in the lactose medium. Orpt o* z* r* Orpt ot z* Y OrptoztY Orrotzr OrPotz*Yarrow_forwardThe streptolysin S toxin made by S. pyogenes is encoded by a 9-gene operon, sagABCDEFGHI. Thinking about what a 3-line diagram would look like for this operon, answer the following questions. Write numeric answers only. For example, if your answer is 6 promoters, write only 6. 1) How many promoters control the expression of these genes? 2) How many locations does RNA Polymerase bind to get full expression of these genes? 3) How many ribosome binding sites are needed for full protein expression? 4) How many start codons will be needed for full protein expression? 5) How many mRNA strands will be produced with full operon expression? 6) How many proteins will be produced with full protein expression? 1arrow_forward
- You have isolated a series of mutants affecting regulation of the lac operon. All of these are constitutive, that is, they express the lac operon all the time. You also have both mutant and wild-type alleles for each mutant in all combinations, and on F ′ plasmids, which can be introduced into cells to make the cell diploid for the relevant genes. How would you use these tools to determine which mutants affect DNA binding sites on DNA, and which affect proteins that bind to DNA?arrow_forwardWhich of the following lac operon genotypes would allow for functional versions of all the structural enzymes of the lac operon to be expressed constitutively even in the absence of lactose? Group of answer choices I+ O+ Z+ Y+ A+ I- O+ Z- Y- A- I+ OC Z+ Y+ A+ IS O+ Z+ Y+ A+ I+ O+ Z- Y+ A+arrow_forwardThe following shows the genotype of a partial diploid bacterial cell - where one chromosomal region containing the lac operon in E,coli is given, and the other fragment is from a plasmid carrying another lac operon from another source. The two are separated by a slash (/). The possible answers indicate with a ʺ+ʺ or a ʺ-ʺ whether β-galactosidase would be expected to be produced at induced levels under two circumstances: 1) first in the absence of lactose and 2) second in the presence of lactose. (Assume that glucose is not present in the medium.)Genotype F: I+ Oc Z-/ Fʹ I- O+ Z+ KEY:I+ = wild-type repressorI- = mutant repressor (unable to bind to the operator)Is = mutant repressor (insensitive to lactose)O+ = wild-type operatorOc = constitutive operator (insensitive to repressor)arrow_forward
- The following table lists 4 bacterial strains that are partial diploids for lac operon genes. Given the activity of beta-galactosidase measured for each strain in the absence (-lac) or presence (+lac) of lactose, complete the table by choosing the appropriate symbol (+, -, C, S) to indicate the allele of the gene or site missing from the table (blue numbers). + = wildtype, - = null mutation, c = constitutive, s =super repressor chromosome plasmid B-gal act. strain 10 Z A 1 C B 3 4 + C + 6 D 9 + 1 [Select] 3 [Select] 5 [Select] 7 [ Select] 9 [Select] | 0 2 + + 5 + 7 10 Z + -lac +lac 0.062 0.058 0.003 0.004 0.062 0.117 0.003 0.060 + 8 + 2 [Select] 4 [Select] 6 [Select] 8 [Select] 10 [Select]arrow_forward1) The logic of the Lac operon was deciphered by using bacterial lac-operon mutants. Crucial to the experiments was creation of partial diploid cells in which operon from a wild-type cell is introduced into the mutant cell [thus there are 2 copies of the operon], and its ability to restore repression is assessed. Three classes of mutants were found that affect expression of the lac operon. Two of these resulted in constitutive expression of the operon, and the other eliminated all expression, even in the presence of lactose. Use the information above to complete the following table indicating with a (Y) yes or (N= No) if enzymatic activity of B-Gal will be detected (protein made and functional). Assume there is no glucose. Remember: Promoter for operon controls ALL genes downstream of it, coding sequence of the genes themselves matter (so if transcription is occurring but structural gene is producing a non-functional protein there will be no activity detected) For the lac operon…arrow_forwardStrain P77 has a mutation in the lacO that prevents it from being bound by the lacI protein. Otherwise all other parts of the operon are functional. 1. Can strain P77 metabolize lactose if it is present? 2. If lactose is absent, will strain P77 transcribe its lac operon? 3. If lactose is present, will strain P77 transcribe its lac operon?arrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





