
Concept explainers
The electrophoresis gel shown in part (a) is from a DNase footprint analysis of an operon transcription control region. DNA sequence analysis of a
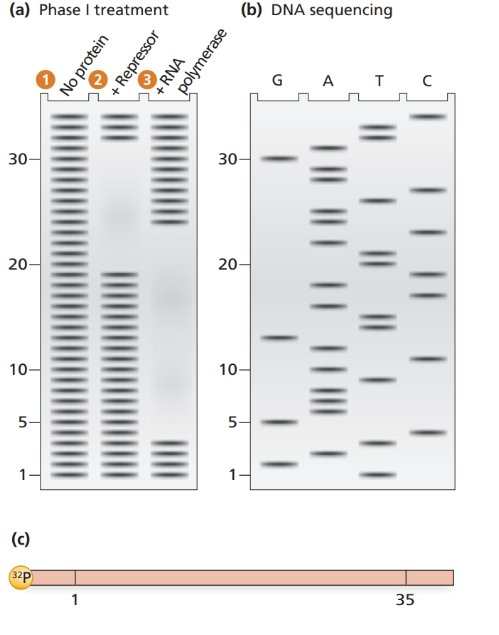
a. Determine the DNA sequence of the region examined.
b. Locate the regions of the sequence protected by repressor protein and by RNA polymerase.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 14 Solutions
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (2nd Edition)
- The diagram below represents a hypothetical operon in the bacterium E. coli. The operon consists of two structural genes (A and B), which code for the enzymes “Aase" and "Base", respectively, and also includes P (promoter) and O (operator) regions as shown. A В When a certain compound (X) is added to the growth medium of E. coli, the separate enzymes "Aase" and "Base" are both synthesized at a 50-fold higher rate than in the absence of X. (X has a molecular weight of about 200.) Which of the following statements is true of the operon described above? The region of the A gene that codes for the carboxyl-terminal amino acid of “Aase" is near the left end of the A gene. The P region contains nucleotide sequences to which the RNA polymerase holoenzyme (including the o subunit) binds specifically but which the core enzyme does not recognize. The addition of X to the growth medium causes a repressor protein to bind tightly to the O region. The mRNA copied from this operon will be covalently…arrow_forwardThe following shows the genotype of a partial diploid bacterial cell - where one chromosomal region containing the lac operon in E,coli is given, and the other fragment is from a plasmid carrying another lac operon from another source. The two are separated by a slash (/). The possible answers indicate with a ʺ+ʺ or a ʺ-ʺ whether β-galactosidase would be expected to be produced at induced levels under two circumstances: 1) first in the absence of lactose and 2) second in the presence of lactose. (Assume that glucose is not present in the medium.)Genotype F: I+ Oc Z-/ Fʹ I- O+ Z+ KEY:I+ = wild-type repressorI- = mutant repressor (unable to bind to the operator)Is = mutant repressor (insensitive to lactose)O+ = wild-type operatorOc = constitutive operator (insensitive to repressor)arrow_forwardThe following logo plot represents the preferred cis-regulatory sequences (i.e. transcription factor binding site) of bHLH transcription factor FOSL1. C 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 position Would you expect this sequence to be recognized by a monomer, a homodimer, or a heterodimer of the protein? Explain your answer. (short phrases are sufficient; please write your answer into the template below) A- В I A -l expect FOSL1 to bind as a: (monomer, homodimer, heterodimer; please choose) B - short explanation: information content (bit) !!arrow_forward
- Predict the level of genetic activity of the lac operon as well as the status of the lac repressor and the CAP protein under the cellular conditions listed in the accompanying table. Lactose Glucose (a) - - (b) + - (c) - + (d) + +arrow_forwardThe lac operon consists of three structural genes, lacZ, lacY and lacA that are transcribed as a single polycistronic mRNA. The new lac strain of Escherichia coli are as shown below: P+O+Z+Y+A+// P+O+Z+Y+A¯ (i) Illustrate how lactose induces the gene expression in lac 1 $// I-. (ii) Explain the function of the lacP and laco in the bacterial operon.arrow_forwardGive the levels of Beta-galactosidase activity (high or low or zero) expected for the following partial diploids for the lac operon strains.arrow_forward
- Explain why (a) inactivation of the O2 or O3 sequence of the lac operon causes only a twofold loss in repression, and (b) inactivation of both O2 and O3 reduces repression ∼70-fold.arrow_forwardGive only typing answer with explanation and conclusionarrow_forwardSuppose you have six strains of E. coli. One is wildtype, and each of the other five has a single one of thefollowing mutations: lacZ−, lacY−, lacI−, oc, andlacIS. For each of these six strains, describe thephenotype you would observe using the following assays. [Notes: (1) IPTG is a colorless synthetic molecule that acts as an inducer of lac operon expressionbut cannot serve as a carbon source for bacterialgrowth because it cannot be cleaved byβ-galactosidase; (2) X-gal cannot serve as a carbonsource for growth; (3) E. coli requires active lactosepermease (the product of lacY) to allow lactose,X-gal, or IPTG into the cells.] Colony color in medium containing glycerol as theonly carbon source and X-gal, but no IPTG.d. Colony color in medium containing high levels ofglucose as the only carbon source, X-gal, andIPTG.e. Colony color in medium containing high levels ofglucose as the only carbon source and X-gal, butno IPTGarrow_forward
- For each of the E. coli strains containing lac operon alleles listed, indicate whether the strain is inducible, constitutive, or unable to express beta-galactosidase and permease. (P+ and P- are functional and nonfunctional promoters, respectively) I+ P+ o+ Z- Y+ / I+ P+ oc Z+ Y+ I+ P+ o+ Z+ Y+ / I- P+ oc Z+ Y- I+ P+ o+ Z- Y+ / I- P+ oc Z+ Y- I- P- o+ Z+ Y- / I+ P+ oc Z- Y+ IS P+ o+ Z+ Y+ / I- P+ o+ Z+ Y-arrow_forwardTrp operon of E. coli is an inducible sytem since it turns on in the presence of tryptophan. In most bacteria, protein synthesis is initiated with a modified methionine residue (N-formylmethionine), whereas unmodified methionines initiate protein synthesis in eukaryotes. Both DNA replication and transcription follow a 5’ to 3’ direction of polarity. Write T if the statement is true and write F if the statement is falsearrow_forwardThe lac operon consists of three structural genes, lacZ, lacY and lacA that are transcribed as a single polycistronic mRNA. You are given a new strain of Escherichia coli with the following lac operon genotype: p+0°Z•Y*A +// P*O*Z*Y+ A- (i) Explain how the lac I gene affects gene expression. (ii) Explain the function of the lacP in the bacterial operon. (iii) Which part of the lac operon is cis-dominant? Explain.arrow_forward
 Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
