
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (2nd Edition)
2nd Edition
ISBN: 9780321948908
Author: Mark F. Sanders, John L. Bowman
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 14, Problem 24P
A repressible operon system, like the trpoperon, contains three genes, G, Z, and W. Operon genes are synthesized when the end product of the operon synthesis pathway is absent, but there is no synthesis when the end product is present. One of these genes is an operator, one is a regulatory protein, and the other is a structural enzyme involved in synthesis of the endproduct. In the table below,
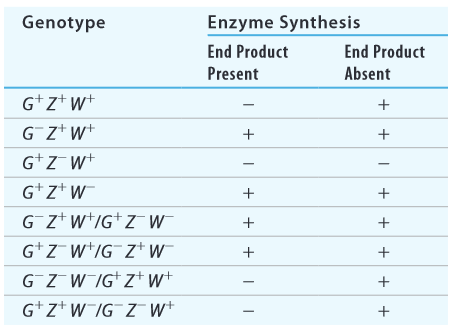
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
The streptolysin S toxin made by S. pyogenes is encoded by a 9-gene
operon, sagABCDEFGHI. Thinking about what a 3-line diagram would look like for this
operon, answer the following questions. Write numeric answers only. For example, if your
answer is 6 promoters, write only 6.
1) How many promoters control the expression of these genes?
2) How many locations does RNA Polymerase bind to get full expression of these genes?
3) How many ribosome binding sites are needed for full protein expression?
4) How many start codons will be needed for full protein expression?
5) How many mRNA strands will be produced with full operon expression?
6) How many proteins will be produced with full protein expression?
1
A number of mutations affect the expression of the lac operon in E. coli. Consider each genotype below and complete the table using “+” to indicate that the gene is expressed, and “−” to indicate that gene is not expressed.
Which of the following lac operon genotypes would allow for functional versions of all the structural enzymes of the lac operon to be expressed constitutively even in the absence of lactose?
Group of answer choices
I+ O+ Z+ Y+ A+
I- O+ Z- Y- A-
I+ OC Z+ Y+ A+
IS O+ Z+ Y+ A+
I+ O+ Z- Y+ A+
Chapter 14 Solutions
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (2nd Edition)
Ch. 14 - 12.1 Bacterial genomes frequently contain groups...Ch. 14 - Transcriptional regulation of operon gene...Ch. 14 - Why is it essential that bacterial cells be able...Ch. 14 - Identify similarities and differences between an...Ch. 14 - The transcription of -galactosidase and permease...Ch. 14 - 12.6 Is attenuation the product of an allosteric...Ch. 14 - The trpL region contains four repeated DNA...Ch. 14 - The CAP binding site in the lac promoter is the...Ch. 14 - What role does cAMP play in transcription of lac...Ch. 14 - How would a cap- mutation that produces an...
Ch. 14 - Explain the circumstances under which attenuation...Ch. 14 - Consider the transcription of genes of the...Ch. 14 - Describe the lytic and lysogenic life cycles of ...Ch. 14 - 12.14 Define antisense RNA, and describe how it...Ch. 14 - 12.15 Attenuation of trp operon transcription is...Ch. 14 - 12.16 In the lac operon, what are the likely...Ch. 14 - Identify which of the following lac operon haploid...Ch. 14 - Prob. 18PCh. 14 - 12.19 List possible genotypes for lac operon...Ch. 14 - Suppose each of the genotypes you listed in parts...Ch. 14 - 12.21 Four independent mutants (mutants A to D)...Ch. 14 - Suppose the lac operon partial diploid...Ch. 14 - Prob. 23PCh. 14 - 12.24 A repressible operon system, like the trp...Ch. 14 - 12.25 What is the likely effect of each of the...Ch. 14 - 12.26 Suppose that base substitution mutations...Ch. 14 - 12.27 Two different mutations affect. Mutant...Ch. 14 - How would mutations that inactivate each of the...Ch. 14 - The bacterial insertion sequence IS 10 uses...Ch. 14 - 12.34 Northern blot analysis is performed on...Ch. 14 - 12.37 The electrophoresis gel shown in part (a) is...Ch. 14 - Prob. 32PCh. 14 - The following hypothetical genotypes have genes A,...Ch. 14 - For an E. coli strain with the lac operongenotype...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The trp operon in E. coli encodes enzymes essential for the biosynthesis of tryptophan. In the operon, trpR gene encodes the repressor. A trpR repressor cannot bind tryptophan. The trpO is the operator. trpA encodes the enzyme tryptophan synthetase. For the enzyme (A), indicate with a + or-whether or not it is made when there is tryptophan and when there is no tryptophan. Without Tryptophan With Tryptophan R'O A /R* O' A R'O' A/R* Oʻ A R*OA/R' O Aarrow_forwardThe diagram below represents a hypothetical operon in the bacterium E. coli. The operon consists of two structural genes (A and B), which code for the enzymes “Aase" and "Base", respectively, and also includes P (promoter) and O (operator) regions as shown. A В When a certain compound (X) is added to the growth medium of E. coli, the separate enzymes "Aase" and "Base" are both synthesized at a 50-fold higher rate than in the absence of X. (X has a molecular weight of about 200.) Which of the following statements is true of the operon described above? The region of the A gene that codes for the carboxyl-terminal amino acid of “Aase" is near the left end of the A gene. The P region contains nucleotide sequences to which the RNA polymerase holoenzyme (including the o subunit) binds specifically but which the core enzyme does not recognize. The addition of X to the growth medium causes a repressor protein to bind tightly to the O region. The mRNA copied from this operon will be covalently…arrow_forwardA number of mutations affect the expression of the lac operon in E. coli. The genotypes of several E. coli strains are shown below. ("+" indicates a wild-type gene with normal function and "-" indicates a loss-of-function allele.) Please predict which of the following strains would have the highest beta-galactosidase enzyme activity, when grown in the lactose medium. CAP It P+ O`Z+ CAP+ I P+ O+ Zt CAP+ It P- O+ Z+ CAP+ It P+ 0+ Zarrow_forward
- A strain of E. coli has the genotypes shown below at the lac operon, where I = regulator gene, P = promoter, O = operator, Z = βgalactosidase gene, and Y = permease gene. The superscript+ indicates a wild-type allele,c indicates a constitutive mutation, and− indicates a defective mutation. For each genotype, indicate whether the enzyme will be synthesized or not synthesized when lactose is present or absent by placing a + for synthesis occurring and a − for synthesis not occurring in the appropriate blank. Explain your reasoning for each answer.arrow_forwardA constitutive mutation in the lac operon may be of several types. [Note that constitutive means that the structural genes are always expressed, even if lactose is absent.] Name two types of constitutive mutations. Group of answer choices LacY- and LacI- LacOc and LacZ- LacZ- and LacI- LacY- and LacA- LacI- and LacOcarrow_forwardDetermine the outcome for the lac operon genotype shown below: I*p*o°z*y/I*p*o*z*x* Assume lactose is absent. Select one: O Functional beta-galactosidase and functional permease are produced. O Only functional beta-galactosidase is produced. Functional permease is NOT produced. O Only functional permease is produced. Functional beta-galactosidase is NOT produced. O Functional beta-galactosidase is NOT produced. Functional permease is NOT produced.arrow_forward
- The lac operon consists of three structural genes, lacZ, lacY and lacA that are transcribed as a single polycistronic mRNA. You are given a new strain of Escherichia coli with the following lac operon genotype: p+0°Z•Y*A +// P*O*Z*Y+ A- (i) Explain how the lac I gene affects gene expression. (ii) Explain the function of the lacP in the bacterial operon. (iii) Which part of the lac operon is cis-dominant? Explain.arrow_forwardThe map of the lac operon is: POZY The promoter (P) region is the start site of transcription through the binding of the RNA polymerase molecule before actual MRNA production. Mutationally altered promoters (P') cannot bìnd the RNA polymerase molecule. Certain predictions can be made about the effect of P mutations. Use your knowledge of the lactose system to complete the table below. Insert a "+" where enzyme is produced and a "-" where enzyme is not produced. Indicate whether the partial diploid strain is lac* (able to grow on lactose-only medium) or lac( cannot grow in lactose medium). B-Galactosidase Permease Phenotype (Lac or Number Genotype No Lactose Lactose No Lactose Lactose Lac) P*O*Z*Y# Example lac+ I*p*O*z*Y* a Ip*o+z*Y* I*p*oCz*Y C I*p*o+z*Yarrow_forwardThe symbols A, B, C, D, E represent all the components of the lac operon, excluding LacA. The symbols are not in the order of the lac operon. Minus and plus signs represent activity of lacZ or LacY in the absence or presence of IPTG. LacI+ or LacI-, and LacO+ or LacOC alleles were used. Which of the symbols represents each of the lac operon components?arrow_forward
- Two closely linked open reading frames (ORFs) have been identified on the E. coli chromosome and they are predicted to encode genes sugX sugY which is involved in the catabolism (utilization) of a non-glucose sugar. In the figure below, the top line (with the big arrow) is the coding strand, and the bottom line is the non-coding (template) strand of the operon. Since the RNA sequence would be the “same” as the coding strand, please label (show the location of), in relation to the ORFs, the promoter(s) and 4 other genetic elements in this region that may be involved in the transcription and translation of sugX and sugY as well as the regulation of their expression. (Note: genetic elements are the regions of DNA or RNA.) If you are not comfortable with the coding strand of the DNA, feel free to draw the mRNA strand underneath and label the relevant features on the RNA strand, but the RNA strand must be aligned with the DNA strands in position and scale. Leader(s)/antileader(s) and…arrow_forwardSupply the words “off" or “on" in the blanks below: In an inducible operon, transcription is normally and must be turned In a repressible operon, transcription is normally and must be turned Briefly describe the overall function of the structural genes in the lac operon. Briefly describe the overall function of the structural genes in the trp operon. For the following descriptions of the bacterial lac operon, determine if lactose is present (P) or absent (A). The repressor is bound to the operator. The repressor is inactive. RNA polymerase transcribes the structural genes. Allolactose is bound to the repressor For the following descriptions of the bacterial trp operon, determine if tryptophan levels are high (H) or low (L). The repressor is bound to the operator. The repressor is inactive. RNA polymerase transcribes the structural genes. Tryptophan is bound to the repressor.arrow_forwardFigure 5 shows the lac operon structure in Escherichia coli. a) Name structures P, Q and R. b) Name substance S. c) What is the enzyme encoded by gene I. Give its function. d) What will happen if substance S is absent in the medium?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning

Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781337392938
Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. Berg
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Bacterial Genomics and Metagenomics; Author: Quadram Institute;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_6IdVTAFXoU;License: Standard youtube license