
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The rainstorm which dropped the most rain needs to be determined on the basis of given data:
| Strom number | Height | Volume (cm3) |
| 1 | 1 cm | 2.5 |
| 2 | 2.5 cm | 6.3 |
| 3 | 0.5 cm | 1.1 |
| 4 | 8 cm | 20.0 |
| 5 | 5 cm | 12.5 |
Concept Introduction: The dimensional analysis is the method to convert one unit to another with the help of convertor factor.
The conversion factor represents the relation between two units and is used to convert one to another. Both Inch and centimeter are units of length and can be converted into each other whereas cm3 is the unit of volume.
(a)
Answer to Problem 7E
Storm 4 dropped most of rain because the volume is maximum in storm 4. Thus, volume and height are used to determine the storm with most rain.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
| Strom number | Height | Volume (cm3) |
| 1 | 1 cm | 2.5 |
| 2 | 2.5 cm | 6.3 |
| 3 | 0.5 cm | 1.1 |
| 4 | 8 cm | 20.0 |
| 5 | 5 cm | 12.5 |
According to given data the storm number 4 dropped most of rain. This is because volume is highest in storm 4 that is 20.0 cm3.
(b)
Interpretation: The pattern in the rainstorm needs to be determined with below data.
| Strom number | Height | Volume (cm3) |
| 1 | 1 cm | 2.5 |
| 2 | 2.5 cm | 6.3 |
| 3 | 0.5 cm | 1.1 |
| 4 | 8 cm | 20.0 |
| 5 | 5 cm | 12.5 |
Concept Introduction: The dimensional analysis is the method to convert one unit to another with the help of convertor factor.
The conversion factor represents the relation between two units and is used to convert one to another. Both Inch and centimeter are units of length and can be converted into each other whereas cm3 is the unit of volume.
(b)
Answer to Problem 7E
The volume of rain increases from storm 1 to storm 5 therefore it is an increasing pattern.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
| Strom number | Height | Volume (cm3) |
| 1 | 1 cm | 2.5 |
| 2 | 2.5 cm | 6.3 |
| 3 | 0.5 cm | 1.1 |
| 4 | 8 cm | 20.0 |
| 5 | 5 cm | 12.5 |
According to given data the volume of rain and height increase from storm 1 to 5. Therefore it exhibits the increasing pattern.
(c)
Interpretation: The graph between height and volume that show the proportionality of height with volume needs to be drawn.
| Strom number | Height | Volume (cm3) |
| 1 | 1 cm | 2.5 |
| 2 | 2.5 cm | 6.3 |
| 3 | 0.5 cm | 1.1 |
| 4 | 8 cm | 20.0 |
| 5 | 5 cm | 12.5 |
Concept Introduction: The dimensional analysis is the method to convert one unit to another with the help of convertor factor.
The conversion factor represents the relation between two units and is used to convert one to another. Both Inch and centimeter are units of length and can be converted into each other whereas cm3 is the unit of volume.
(c)
Answer to Problem 7E
Explanation of Solution
Given:
| Strom number | Height | Volume (cm3) |
| 1 | 1 cm | 2.5 |
| 2 | 2.5 cm | 6.3 |
| 3 | 0.5 cm | 1.1 |
| 4 | 8 cm | 20.0 |
| 5 | 5 cm | 12.5 |
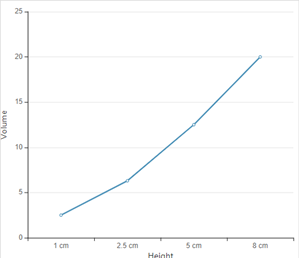
According to given data the graph between height and volume is as given below;
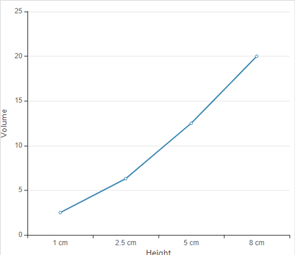
The straight line in curve reflects that with increase in height, the volume of rain increase. Thus height is directly proportional to volume of rain.
(d)
Interpretation: The reason for all the data points to not lie exactly on a straight line needs to be explained.
| Storm number | Height | Volume (cm3) |
| 1 | 0.5 cm | 1.1 |
| 2 | 1 cm | 2.5 |
| 3 | 2.5 cm | 6.3 |
| 4 | 5 cm | 12.5 |
| 5 | 8 cm | 20.0 |
Concept Introduction: The dimensional analysis is the method to convert one unit to another with the help of convertor factor.
The conversion factor represents the relation between two units and is used to convert one to another. Both Inch and centimeter are units of length and can be converted into each other whereas cm3 is the unit of volume.
(d)
Answer to Problem 7E
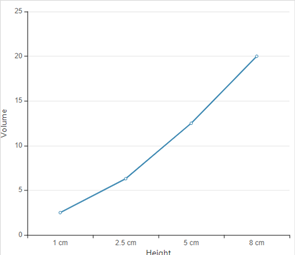
In the given graph, all the data points do not all lie exactly on a straight line because with the height is not increasing in exact proportion of volume of rain fall.
Explanation of Solution
According to given data the graph between height and volume is as given below;
| Strom number | Height | Volume (cm3) |
| 1 | 0.5 cm | 1.1 |
| 2 | 1 cm | 2.5 |
| 3 | 2.5 cm | 6.3 |
| 4 | 5 cm | 12.5 |
| 5 | 8 cm | 20.0 |
In the given graph, all the data points do not all lie exactly on a straight line because with the height is not increasing in exact proportion of volume of rain fall.
(e)
Interpretation: The volume of rainfall at 6.0 cm height needs to be determined.
| Storm number | Height | Volume (cm3) |
| 1 | 0.5 cm | 1.1 |
| 2 | 1 cm | 2.5 |
| 3 | 2.5 cm | 6.3 |
| 4 | 5 cm | 12.5 |
| 5 | 8 cm | 20.0 |
Concept Introduction: The dimensional analysis is the method to convert one unit to another with the help of convertor factor.
The conversion factor represents the relation between two units and is used to convert one to another. Both Inch and centimeter are units of length and can be converted into each other whereas cm3 is the unit of volume.
(e)
Answer to Problem 7E
At 6.0 height = 15.0 cm3 volume
Explanation of Solution
According to given data the graph between height and volume is as given below;
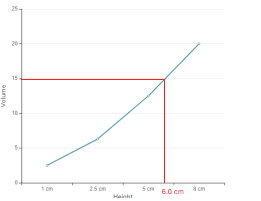
In the platted graph, at height 6.0 cm, the volume of rain fall is 15.0 cm3.
Chapter U3 Solutions
Living by Chemistry
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology (5th Edition)
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
- Highlight the chirality (or stereogenic) center(s) in the given compound. A compound may have one or more stereogenic centers. OH OH OH OH OH OHarrow_forwardUsing wedge-and-dash bonds, modify the bonds on the chiral carbon in the molecule below so the molecule has R stereochemical configuration. NH H Br X टेarrow_forwardProvide photos of models of the following molecules. (Include a key for identification of the atoms) 1,2-dichloropropane 2,3,3-trimethylhexane 2-bromo-3-methybutanearrow_forward
- Please draw the structure in the box that is consistent with all the spectral data and alphabetically label all of the equivalent protons in the structure (Ha, Hb, Hc....) in order to assign all the proton NMR peaks. The integrations are computer generated and approximate the number of equivalent protons. Molecular formula: C13H1802 14 13 12 11 10 11 (ppm) Structure with assigned H peaks 2.08 3.13arrow_forwardA 0.10 M solution of acetic acid (CH3COOH, Ka = 1.8 x 10^-5) is titrated with a 0.0250 M solution of magnesium hydroxide (Mg(OH)2). If 10.0 mL of the acid solution is titrated with 10.0 mL of the base solution, what is the pH of the resulting solution?arrow_forwardFirefly luciferin exhibits three rings. Identify which of the rings are aromatic. Identify which lone pairs are involved in establishing aromaticity. The lone pairs are labeled A-D below.arrow_forward
- A 0.10 M solution of acetic acid (CH3COOH, Ka = 1.8 x 10^-5) is titrated with a 0.0250 M solution of magnesium hydroxide (Mg(OH)2). If 10.0 mL of the acid solution is titrated with 10.0 mL of the base solution, what is the pH of the resulting solution?arrow_forwardGiven a complex reaction with rate equation v = k1[A] + k2[A]2, what is the overall reaction order?arrow_forwardPlease draw the structure in the box that is consistent with all the spectral data and alphabetically label all of the equivalent protons in the structure (Ha, Hb, Hc....) in order to assign all the proton NMR peaks. The integrations are computer generated and approximate the number of equivalent protons. Molecular formula: C13H1802 14 13 12 11 10 11 (ppm) Structure with assigned H peaks 2.08 3.13arrow_forward
- CHEMICAL KINETICS. One of the approximation methods for solving the rate equation is the steady-state approximation method. Explain what it consists of.arrow_forwardCHEMICAL KINETICS. One of the approximation methods for solving the rate equation is the limiting or determining step approximation method. Explain what it consists of.arrow_forwardCHEMICAL KINETICS. Indicate the approximation methods for solving the rate equation.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





