
Concept explainers
Measuring Area from a Boundary: The Planimeter
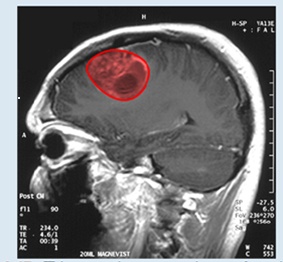
Figure 6.47 This magnetic resonance image of a patient’s brain shows a tumor, which is highlighted in red. (credit: modification of wood’ by Christaras A Wikimedia Commons)
Imagine you are a doctor who has just received a magnetic resonance image of your patent’s brain. The brain has a tumor (Figure 6.47). How large is the tumor? To be precise, what is the area of the red region? The red cross-section of the tumor has an irregular shape, and therefore it is unlikely that you would be able o find a set of equations or inequalities for the region and then be able to calculate its area by conventional means. You could approximate the area by chopping the region into tiny squares (a Riemann sum approach), but this method always gives an answer with some error.
Instead of trying to measure the area of the region directly, we can use a device called a rolling planimeter to calculate the area of the region exactly, simply by measuring its boundary. In this project you investigate how a planimeter works, and you use Green’s theorem to show the device calculates area correctly.
A rolling planimeter is a device that measures the area of a planar region by tracing out the boundary of that region (Figure 6.48). To measure the area of a region, we simply run the tracer of the planimeter around the boundary of the region. The planimeter measures the number of turns through which the wheel rotates as we (race the boundary; the area of the shape is proportional to this number of wheel ruins. We can derive the precise proportionality equation using Green’s theorem. As the (racer moves around the boundary of the region, the tracer arm rotates and the roller moves back and forth (but does no; rotate).
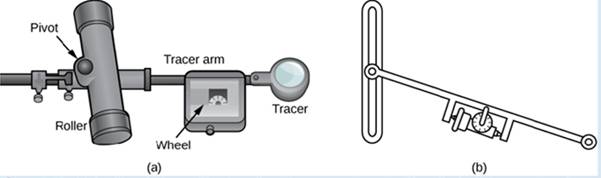
Figure 6.48 (a) A rolling planimeter. The pivot allows the tracer arm to rotate. The roller itself does not rotate; it only moves back and forth. (b) An interior view of a rolling planimeter. Notice that the wheel cannot rum if the planimeter is moving back and forth th the tracer arm perpendicular to the roller.
Let C denote the boundary of region D. the area to be calculated. As the tracer traverses curve C, assume the roller moves along the y-axis (since the roller does not rotate, one can assume it moves along a straight line). Use the coordinates (x, y) to represent points on boundary C, and coordinates (0, y) to represent the position of the pivot. As the planimeter traces C. the pivot moves along the y-axis while the tracer arm rotates on the pivot.  Watch a short animation (http://www.openstaxcollege.org/I/20_pianimeter) of a planimeter in action. Begin the analysis by considering the motion of the tracer as it moves from point (x, y) counterclockwise to point (x + dx. y + dy) that is close to (x, y) (Figure 6.49). The pivot also moves, from point (0, y) to nearby point (0, y + dy). How much does the wheel turn as a result of this motion? To answer this question, break the motion into two parts. First, roll the pivot along they-axis from (0. y) to (0, y + dy) without rotating the tracer arm. The tracer arm then ends up a point (x, y + dy) while maintaining a constant angle with the x-axis. Second, rotate the tracer arm by an angle d
Watch a short animation (http://www.openstaxcollege.org/I/20_pianimeter) of a planimeter in action. Begin the analysis by considering the motion of the tracer as it moves from point (x, y) counterclockwise to point (x + dx. y + dy) that is close to (x, y) (Figure 6.49). The pivot also moves, from point (0, y) to nearby point (0, y + dy). How much does the wheel turn as a result of this motion? To answer this question, break the motion into two parts. First, roll the pivot along they-axis from (0. y) to (0, y + dy) without rotating the tracer arm. The tracer arm then ends up a point (x, y + dy) while maintaining a constant angle with the x-axis. Second, rotate the tracer arm by an angle d
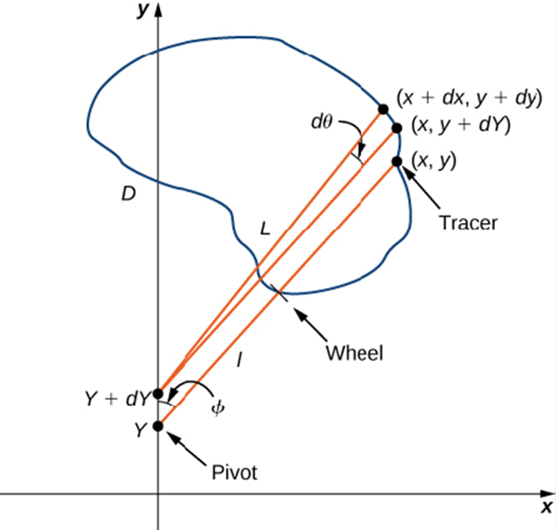
Figure 6.49 Mathematical analysis of the motion of the planimeter.
8. Use step 7 t0 show that the total wheels roll is
Total wheel roll =
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 6 Solutions
Calculus Volume 3
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
Elementary Statistics (13th Edition)
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
A Problem Solving Approach To Mathematics For Elementary School Teachers (13th Edition)
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardFind all solutions of the polynomial congruence x²+4x+1 = 0 (mod 143). (The solutions of the congruence x² + 4x+1=0 (mod 11) are x = 3,4 (mod 11) and the solutions of the congruence x² +4x+1 = 0 (mod 13) are x = 2,7 (mod 13).)arrow_forwardhttps://www.hawkeslearning.com/Statistics/dbs2/datasets.htmlarrow_forward
- Determine whether each function is an injection and determine whether each is a surjection.The notation Z_(n) refers to the set {0,1,2,...,n-1}. For example, Z_(4)={0,1,2,3}. f: Z_(6) -> Z_(6) defined by f(x)=x^(2)+4(mod6). g: Z_(5) -> Z_(5) defined by g(x)=x^(2)-11(mod5). h: Z*Z -> Z defined by h(x,y)=x+2y. j: R-{3} -> R defined by j(x)=(4x)/(x-3).arrow_forwardDetermine whether each function is an injection and determine whether each is a surjection.arrow_forwardLet A = {a, b, c, d}, B = {a,b,c}, and C = {s, t, u,v}. Draw an arrow diagram of a function for each of the following descriptions. If no such function exists, briefly explain why. (a) A function f : AC whose range is the set C. (b) A function g: BC whose range is the set C. (c) A function g: BC that is injective. (d) A function j : A → C that is not bijective.arrow_forward
- Let f:R->R be defined by f(x)=x^(3)+5.(a) Determine if f is injective. why?(b) Determine if f is surjective. why?(c) Based upon (a) and (b), is f bijective? why?arrow_forwardLet f:R->R be defined by f(x)=x^(3)+5.(a) Determine if f is injective.(b) Determine if f is surjective. (c) Based upon (a) and (b), is f bijective?arrow_forwardPlease as many detarrow_forward
- Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage

 Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL  Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781305652224Author:Charles P. McKeague, Mark D. TurnerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781305652224Author:Charles P. McKeague, Mark D. TurnerPublisher:Cengage Learning




