
Concept explainers
Interpretation: The set of resonance structures for following cation should be determined.
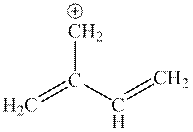
Concept introduction: Lewis structure is a representation of molecules in which dots are shown to represent unshared electrons and lines are shown to represent bonds. These lines and dots represent distribution of electrons in the molecule.
When one single structure is unable to describe all the properties of a single-molecule, a phenomenon called resonance comes into play. This arises when two or more than two Lewis structures are possible for one molecule. All such structures are called resonating structures and have same placement of atoms in them but these have different locations of bond pairs and lone pairs. The resonating structures are inter-convertible with each other. The resultant of all the resonating or contributing structures is called the resonance hybrid.
Rules to form resonance structure are as follows:
1. Use arrow types 1 and 2 for the resonance structure of anions in the movement of negative charge.
2. Use only arrow type 3 to move a positive charge for the resonance structure of cations.
3. The sigma bond should not be broken. Any atom must not move from its place and the total number of electrons must be the same in all resonance structures.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 5 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
- Hi, I need your help with the drawing, please. I have attached the question along with my lab instructions. Please use the reaction from the lab only, as we are not allowed to use outside sources. Thank you!arrow_forwardHi, I need your help i dont know which one to draw please. I’ve attached the question along with my lab instructions. Please use the reaction from the lab only, as we are not allowed to use outside sources. Thank you!arrow_forward5. Write the formation reaction of the following complex compounds from the following reactants: 6. AgNO₃ + K₂CrO₂ + NH₄OH → 7. HgNO₃ + excess KI → 8. Al(NO₃)₃ + excess NaOH →arrow_forward
- Indicate whether the product formed in the reaction exhibits tautomerism. If so, draw the structure of the tautomers. CO₂C2H5 + CH3-NH-NH,arrow_forwardDraw the major product of this reaction N-(cyclohex-1-en-1-yl)-1-(pyrrolidino) reacts with CH2=CHCHO, heat, H3O+arrow_forwardDraw the starting material that would be needed to make this product through an intramolecular Dieckmann reactionarrow_forward
- Draw the major product of this reaction. Nitropropane reacts + pent-3-en-2-one reacts with NaOCH2CH3, CH3CHOHarrow_forwardIndicate whether the product formed in the reaction exhibits tautomerism. If so, draw the structure of the tautomers. OC2H5 + CoHs-NH-NH,arrow_forwardExplain how substitutions at the 5-position of barbituric acid increase the compound's lipophilicity.arrow_forward
- Explain how substitutions at the 5-position of phenobarbital increase the compound's lipophilicity.arrow_forwardName an interesting derivative of barbituric acid, describing its structure.arrow_forwardBriefly describe the synthesis mechanism of barbituric acid from the condensation of urea with a β-diketone.arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co





