
Concept explainers
Interpretation: The illegal arrows in below set of arrows should be determined.
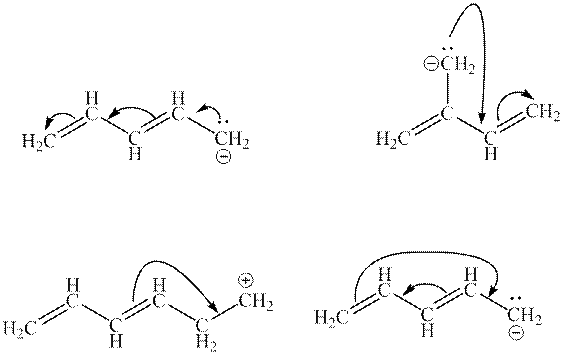
Concept introduction: Lewis structure is a representation of molecules in which dots are shown to represent unshared electrons and lines are shown to represent bonds. These lines and dots represent distribution of electrons in the molecule.
When one single structure is unable to describe all the properties of a single-molecule, a phenomenon called resonance comes into play. This arises when two or more than two Lewis structures are possible for one molecule. All such structures are called resonating structures and have same placement of atoms in them but these have different locations of bond pairs and lone pairs. The resonating structures are inter-convertible with each other. The resultant of all the resonating or contributing structures is called the resonance hybrid.
Rules to form resonance structure are as follows:
1. Use arrow types 1 and 2 for the resonance structure of anions in the movement of negative charge.
2. Use only arrow type 3 to move a positive charge for the resonance structure of cations.
3. The sigma bond should not be broken. Any atom must not move from its place and total number of electrons must be the same in all resonance structures.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 5 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
- Can I please get help with this?arrow_forwardUse the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation to calculate pH of a buffer containing 0.050M benzoic acidand 0.150M sodium benzoate. The Ka of benzoic acid is 6.5 x 10-5arrow_forwardA. Draw the structure of each of the following alcohols. Then draw and name the product you would expect to produce by the oxidation of each. a. 4-Methyl-2-heptanol b. 3,4-Dimethyl-1-pentanol c. 4-Ethyl-2-heptanol d. 5,7-Dichloro-3-heptanolarrow_forward
- What is the pH of a 1.0 L buffer made with 0.300 mol of HF (Ka = 6.8 × 10⁻⁴) and 0.200 mol of NaF to which 0.160 mol of NaOH were added?arrow_forwardCan I please get help with this.arrow_forwardDetermine if the following salt is neutral, acidic or basic. If acidic or basic, write the appropriate equilibrium equation for the acid or base that exists when the salt is dissolved in aqueous solution. If neutral, simply write only NR. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. N₂H₅ClO₄arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
