
(a)
To find:The domain of function.
(a)
Answer to Problem 56E
The domain of function is all the real numbers except
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The function is
Calculation:
Consider the function.
.
The function is valid for all the real numbers except
Therefore, the domain of function is all the real numbers except
(b)
To find:The intercepts.
(b)
Answer to Problem 56E
The y- intercept is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The function is
Calculation:
Solve
So, x- intercept is
Solve
So, y- intercept is
Therefore, the y- intercept is
(c)
To find:The asymptotes.
(c)
Answer to Problem 56E
The slant asymptote is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The function is
Calculation:
In given function degree of numerator is one more than the degree of denominator. The graph will have slant asymptote which can be calculated by dividing numerator with denominator.
Here the slant asymptote will be
Therefore, the slant asymptote is
(d)
To find:The sketch of graph.
(d)
Answer to Problem 56E
The graph is shown in Figure-(1).
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The function is
Calculation:
The below table shows additional points,
| Test Interval | Value of x | Value of f | Sign | Point of f |
| -1 | Negative | |||
| 1 | Positive |
Draw the sketch for the function by using the equations of asymptotes.
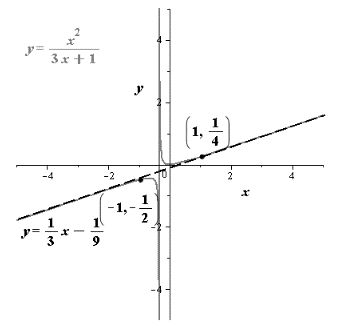
Figure-(1)
Therefore, the graph is shown in Figure-(1).
Chapter 2 Solutions
Precalculus with Limits
- A helicopter pilot needs to travel to a regional airport 25 miles away. She flies at an actual heading of N16.26°E with an airspeed of 110 mph, and there is a wind blowing directly east at 20 mph. (a) Determine the compass heading that the pilot needs to reach her destination. (b) How long will it take her to reach her destination?arrow_forwardQuestion 3. the given integral is convergent or divergent: Use the comparison test to determine whether or not * sin*(x + 1) 7x3 (a) |. d.x g8 + x4 + 1 -dx (b) 2.x4 + x + 1arrow_forward-d.x tan xarrow_forward
- 48. f(x) = { 4 x if x < 2 2x 2 if x 2arrow_forwardГ 49. -x+1 if x 1 Answer ->arrow_forwardA Content X MindTap - Cengage Learning x Function Evaluations x + /ui/evo/index.html?elSBN=9780357038406&id=339416021&snapshotld=877369& GE MINDTAP , Limits, and the Derivative ⭑ វា a ANSWEI 16. Refer to the graph of the function f in the following figure. कर्ट AA C 54 -3-2 7 7 Ay 6. S 5. y=f(x) 4 3. 2. 1 -3- 34567 8 00 9 10 a. Find the value of ƒ (7). b. Find the values of x corresponding to the point(s) on the graph of ƒ located at a height of 5 units from the x-axis. c. Find the point on the x-axis at which the graph of ƒ crosses it. What is the value of f (x) at this point? d. Find the domain and range of f. MacBook Pro G Search or type URL + > % Λ & 5 6 7 29 ( 8 9 0arrow_forward
- Morgan F. - C X A Courses MindTap - Cengage Learning Х Domain of Square Roots X + gage.com/static/nb/ui/evo/index.html?elSBN 9780357038406&id=339416021&snapshotld=877369& CENGAGE MINDTAP 2: Functions, Limits, and the Derivative 47. x if x < 0 f(x) = 2x+1 if x 0 Answerarrow_forwardA Content MindTap - Cengage Learning × Function Evaluations * + c/nb/ui/evo/index.html?elSBN 9780357038406&id=339416021&snapshotld=877369& GAGE MINDTAP ions, Limits, and the Derivative 15. Refer to the graph of the function f in the following figure. 6 y = f(x) 5 4+ 3- 2- 1 + 2 -1 3 4 5 6 a. Find the value of ƒ (0). Answer-> b. Find the value of x for which (i) f (x) = 3 and (ii) f (x) = 0. Answer ▾ c. Find the domain of f. Answer + d. Find the range of f. Answer+ MacBook Proarrow_forwardAnswer-> 12. Let g be the function defined by Find g(-2), g(0), g (2), and g (4). - +1 if x <2 g(x) = √√√x-2 if x 2arrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





