
Concept explainers
To write : the polynomial as the product of linear factors and list all the zeros of function
Answer to Problem 70E
The function as product of linear factors:
The zeros of the function are:
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Concept Involved:
Linear Factorization Theorem:If
Complex Zeros Occur in Conjugate Pairs: Let f be a polynomial function that has real coefficients. If
Synthetic Division (for a Cubic Polynomial):To divide
| In case when we have a polynomial with a missing term, insert placeholders with zero coefficients for missing powers of the variable. Vertical pattern: Add terms in columns Diagonal pattern: Multiply results by k. This algorithm for synthetic division works only for divisors of the form x - k. Remember that |
The Division Algorithm: If
Graph:
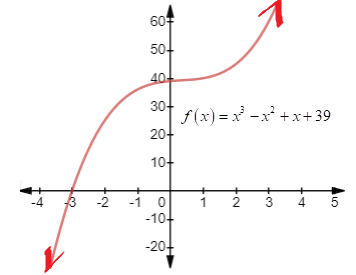
Interpretation:
From the graph of the function we can pick possible zeros of the function as
Calculation:
Use synthetic division to find the other zeros of the function
If
To find other zeros of the polynomial
We can solve this equation using completing the square method by subtracting 5 on both sides of the equation
Simplify on both sides of the equation
In order to make the left side expression as perfect square trinomial, we need to add square of half of coefficient of x on both sides
Simplify on right side of the equation
Write the left side as a perfect square
Rewrite the right side of the equation
Take square root on both sides
Simplifying square root on both sides of the equation
Replace
Add 2 on both sides of the equation
Simplify in left side of the equation
List the zeros of the functions given:
If
So
Write the function
Conclusion:
The zeros of the given function
The function written as product of linear factors:
Chapter 2 Solutions
EBK PRECALCULUS W/LIMITS
- For number 9 The answer is A Could you show me howarrow_forwardThe answer is B, Could you please show the steps to obtain the answerarrow_forward2. Suppose that U(x, y, z) = x² + y²+ z² represents the temperature of a 3-dimensional solid object at any point (x, y, z). Then F(x, y, z) = -KVU (x, y, z) represents the heat flow at (x, y, z) where K > 0 is called the conductivity constant and the negative sign indicates that the heat moves from higher temperature region into lower temperature region. Answer the following questions. (A) [90%] Compute the inward heat flux (i.e., the inward flux of F) across the surface z = 1 - x² - y². (B) [10%] Use the differential operator(s) to determine if the heat flow is rotational or irrotational.arrow_forward
- Could you show why the answer is B Using polar coordinates and the area formulaarrow_forward1. The parametric equations x = u, y = u cos v, z = usin v, with Ou≤ 2, 0 ≤ v ≤ 2π represent the cone that is obtained by revolving (about x-axis) the line y = x (for 0 ≤ x ≤2) in the xy-plane. Answer the following questions. (A) [50%] Sketch the cone and compute its surface area, which is given by dS = [ | Ər Or ди მა × du dv with S being the cone surface and D being the projection of S on the uv-plane. (B) [50%] Suppose that the density of the thin cone is σ(x, y, z) = 0.25x gr/cm². Compute the total mass of the cone.arrow_forwardThe value of sin (2V · F) at x = 3, y = 3, z = −4, where F -0.592 -0.724 0.661 -0.113 -0.822 -0.313 0.171 0.427 = (-2x² + -4,2yz − x − 3, −5xz - 2yz), isarrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





