
Concept explainers
(a)
Apply the coefficient test on function
(a)
Answer to Problem 20RE
The coefficient of highest power is positive graph will rise at LHS and also rise at RHS, the graph will rise at RHS and also rise at RHS.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
To apply the leading coefficient test on the
equation
The highest power is even and the coefficient of highest power is positive. So by leading coefficient test that when the highest power is even and the coefficient of highest power is positive graph will rise at LHS and also rise at RHS, the graph will rise at RHS and also rise at RHS.
(b)
Find the real zeros of the polynomial.
(b)
Answer to Problem 20RE
The zeros are 1,−3,0
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Find the zeros of this equation by equation it with 0, One of the zeros of this equation can be directly seen. It is x=0. For the other part of the equation
First equate it to zero and then find its roots.
So,
Zeros of such equations are found by first finding some of the roots by hit and trial and solving the rest. So,
Now, take out this factor from the equation and the rest of the equations will be Quadratic equation.
So the zeros are 1,−3,0
(c)
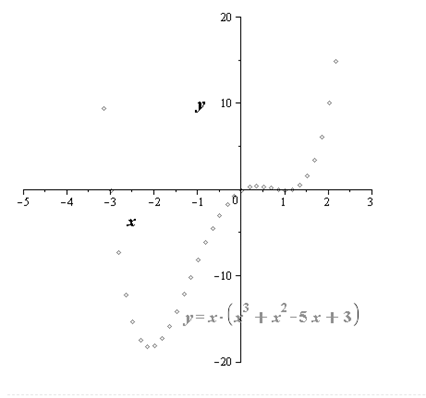
Plotting sufficient points.
(c)
Answer to Problem 20RE
Points are plotted below.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Plot points for graph. For the points the graph will be like this,
(d)
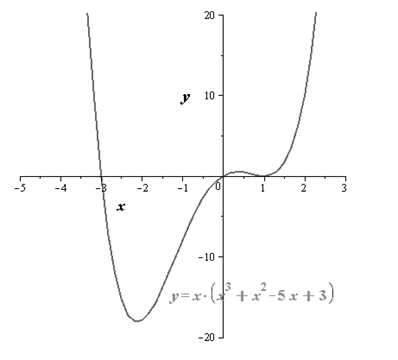
Sketch
the continuous graph.
(d)
Answer to Problem 20RE
9532815067
Explanation of Solution
Given:
So the continuos graph is as follows,
Chapter 2 Solutions
EBK PRECALCULUS W/LIMITS
- 2. Find the leading term (2 points): f(x) = −3x(2x − 1)²(x+3)³ -arrow_forward1- √ √ √³ e³/√xdy dx 1 cy² 2- √ √² 3 y³ exy dx dy So 3- √ √sinx y dy dx 4- Jo √² Sy² dx dyarrow_forwardA building that is 205 feet tall casts a shadow of various lengths æ as the day goes by. An angle of elevation is formed by lines from the top and bottom of the building to the tip of the shadow, as de seen in the following figure. Find the rate of change of the angle of elevation when x 278 feet. dx Round to 3 decimal places. Γ X radians per footarrow_forward
- Use the information in the following table to find h' (a) at the given value for a. x|f(x) g(x) f'(x) g(x) 0 0 0 4 3 1 4 4 3 0 2 7 1 2 7 3 3 1 2 9 4 0 4 5 7 h(x) = f(g(x)); a = 0 h' (0) =arrow_forwardUse the information in the following table to find h' (a) at the given value for a. x f(x) g(x) f'(x) g'(x) 0 0 3 2 1 1 0 0 2 0 2 43 22 4 3 3 2 3 1 1 4 1 2 0 4 2 h(x) = (1/(2) ²; 9(x) h' (3)= = ; a=3arrow_forwardThe position of a moving hockey puck after t seconds is s(t) = tan a. Find the velocity of the hockey puck at any time t. v(t) ===== b. Find the acceleration of the puck at any time t. -1 a (t) = (t) where s is in meters. c. Evaluate v(t) and a (t) for t = 1, 4, and 5 seconds. Round to 4 decimal places, if necessary. v (1) v (4) v (5) a (1) = = = = a (4) = a (5) = d. What conclusion can be drawn from the results in the previous part? ○ The hockey puck is decelerating/slowing down at 1, 4, and 5 seconds ○ The hockey puck has a constant velocity/speed at 1, 4, and 5 seconds ○ The hockey puck is accelerating/speeding up at 1, 4, and 5 secondsarrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





