
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: To indicate whether
Concept introduction: Electron transport chain is a sequence of biochemical reactions in which electrons and hydrogen atoms from the citric acid cycle are transferred to various intermediate carriers and finally reacts with molecular oxygen to form a water molecule.
There are four complexes associated with the electron transport chain that is present in the inner mitochondrial membrane. The four complexes that help in the electron transfer in the electron transport chain are:
Complex I:
Complex II:
Complex III:
Complex IV:
An overview of the electron transport chain is as follows:
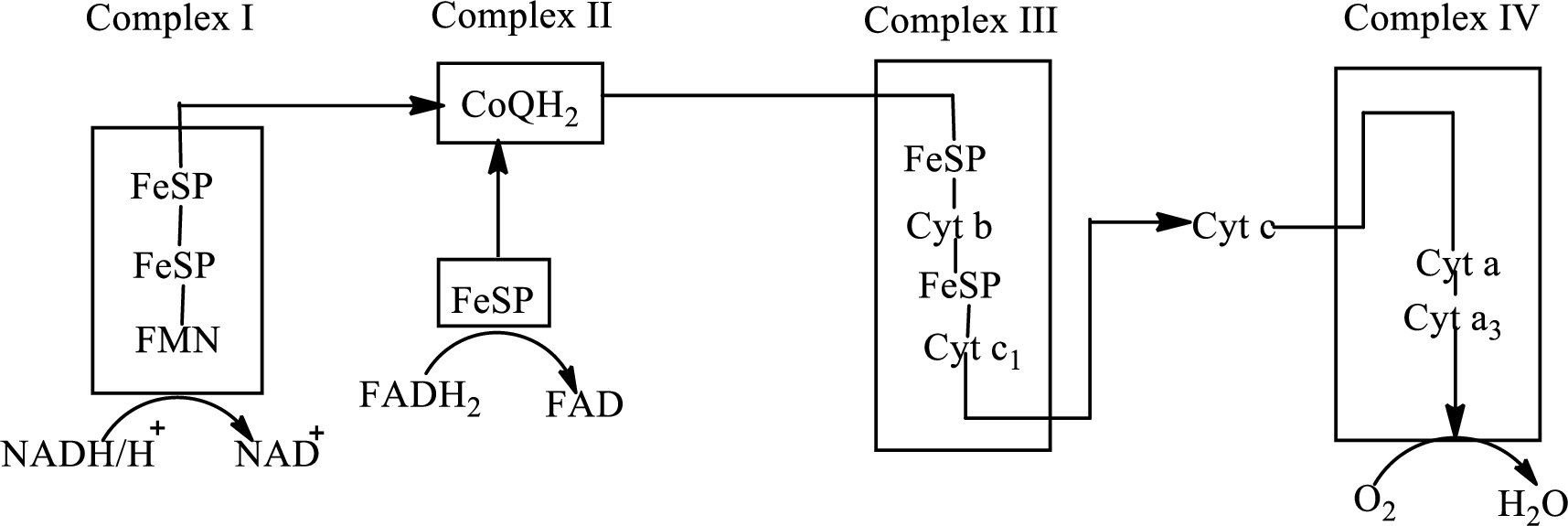
Redox
Here A is oxidized form and AH is reduced form.
(a)
Answer to Problem 23.87EP
Explanation of Solution
(b)
Interpretation: To indicate whether
Concept introduction: Electron transport chain is a sequence of biochemical reactions in which electrons and hydrogen atoms from the citric acid cycle are transferred to various intermediate carriers and finally reacts with molecular oxygen to form a water molecule.
There are four complexes associated with the electron transport chain that is present in the inner mitochondrial membrane. The four complexes that help in the electron transfer in the electron transport chain are:
Complex I:
Complex II:
Complex III:
Complex IV:
An overview of the electron transport chain is as follows:
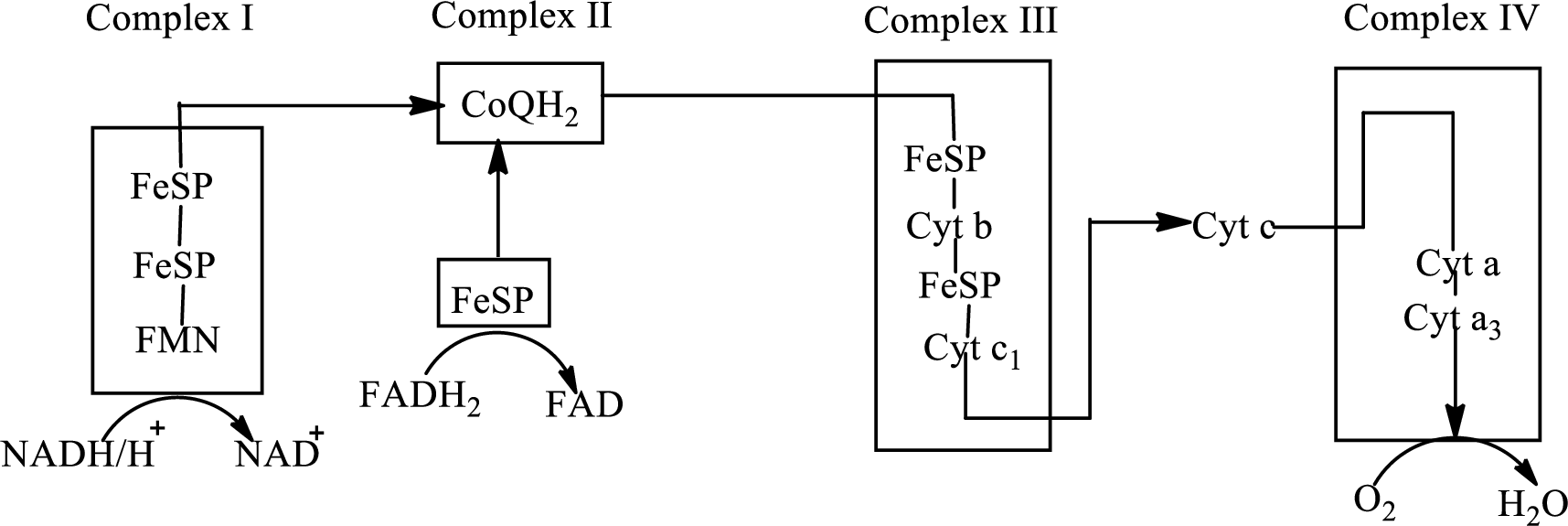
Redox reactions involve oxidation and reduction reaction occurring simultaneously so that one species is oxidized and the other one is reduced. The species that gain hydrogen or electron is known as reduced form and the species that loss hydrogen or electron is known as oxidized form. The general representation of redox reaction is
Here A is oxidized form and AH is reduced form.
(b)
Answer to Problem 23.87EP
Explanation of Solution
(c)
Interpretation: To indicate whether
Concept introduction: Electron transport chain is a sequence of biochemical reactions in which electrons and hydrogen atoms from the citric acid cycle are transferred to various intermediate carriers and finally reacts with molecular oxygen to form a water molecule.
There are four complexes associated with the electron transport chain that is present in the inner mitochondrial membrane. The four complexes that help in the electron transfer in the electron transport chain are:
Complex I:
Complex II:
Complex III:
Complex IV:
An overview of the electron transport chain is as follows:
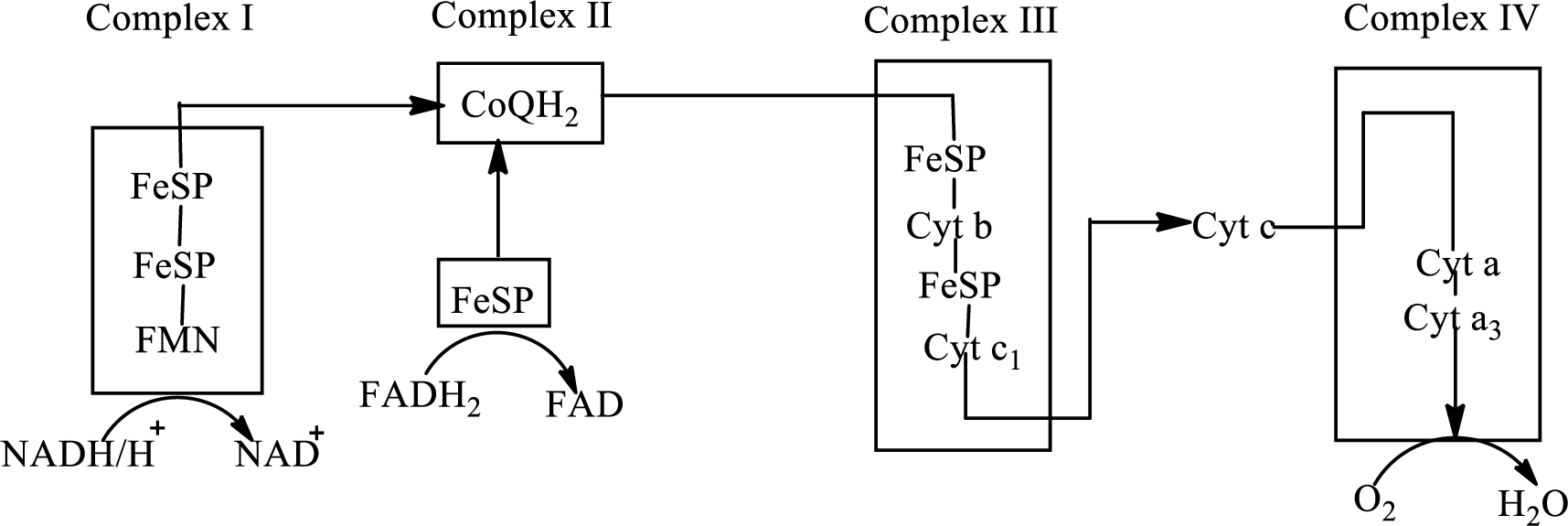
Redox reactions involve oxidation and reduction reaction occurring simultaneously so that one species is oxidized and the other one is reduced. The species that gain hydrogen or electron is known as reduced form and the species that loss hydrogen or electron is known as oxidized form. The general representation of redox reaction is
Here A is oxidized form and AH is reduced form.
(c)
Answer to Problem 23.87EP
NADH is the reduced form of the nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide.
Explanation of Solution
In complex I, electrons are transferred from the
The reaction of the oxidation of
Here,
(d)
Interpretation: To indicate whether is in its oxidized form or its reduced form.
Concept introduction: Electron transport chain is a sequence of biochemical reactions in which electrons and hydrogen atoms from the citric acid cycle are transferred to various intermediate carriers and finally reacts with molecular oxygen to form a water molecule.
There are four complexes associated with the electron transport chain that is present in the inner mitochondrial membrane. The four complexes that help in the electron transfer in the electron transport chain are:
Complex I:
Complex II:
Complex III:
Complex IV:
An overview of the electron transport chain is as follows:
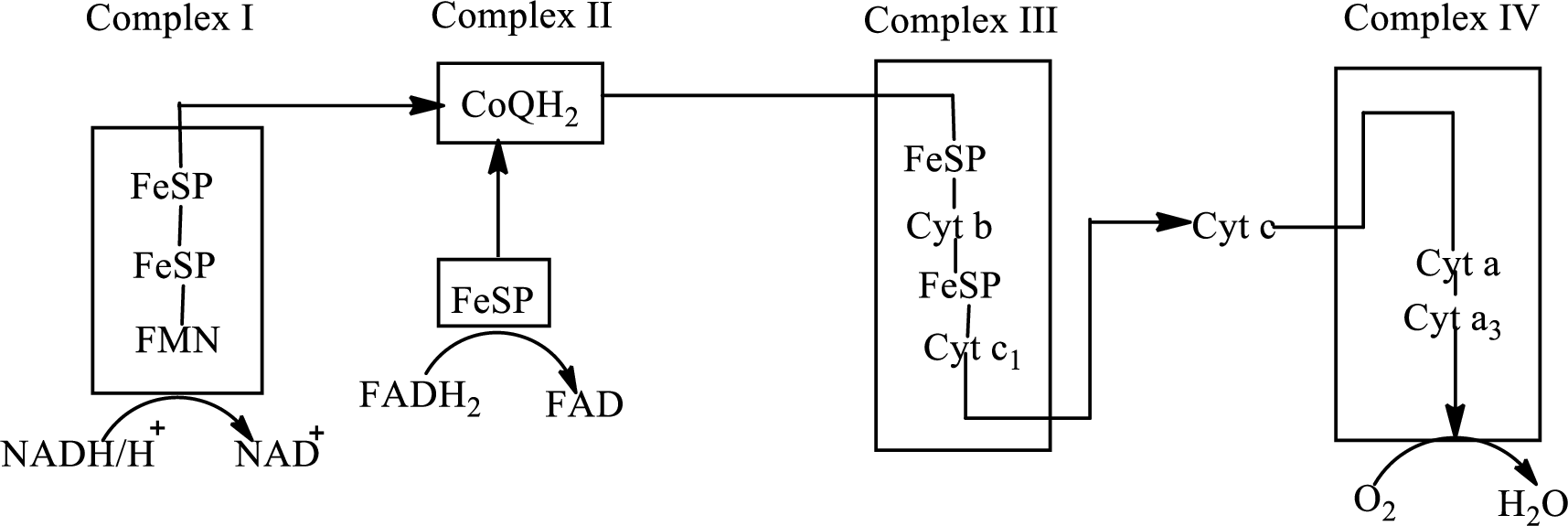
Redox reactions involve oxidation and reduction reaction occurring simultaneously so that one species is oxidized and the other one is reduced. The species that gain hydrogen or electron is known as reduced form and the species that loss hydrogen or electron is known as oxidized form. The general representation of redox reaction is
Here A is oxidized form and AH is reduced form.
(d)
Answer to Problem 23.87EP
FAD is the oxidized form of the flavin adenine dinucleotide.
Explanation of Solution
In the complex II, electrons are transferred from the
Here,
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 23 Solutions
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry
- Done 18:19 www-awu.aleks.com Chapter 12 HW Question 27 of 39 (5 points) | Question Attempt: 1 of Unlimited .. LTE סוי 9 ✓ 20 ✓ 21 × 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 Answer the following questions about the given alkane. Part: 0 / 2 Part 1 of 2 Classify each carbon atom as a 1º, 2º, 3º, or 4°. Highlight in red any 1° carbons, highlight in blue any 2° carbons. highlight in green any 3° carbons, and leave any 4° carbons unhighlighted. Skip Part Check Save For Later © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Privacy Center | Accessibility ☑ คarrow_forward< Done 19:22 www-awu.aleks.com Chapter 12 HW Question 4 of 39 (2 points) | Question Attempt: 5 of Unlimited : .. LTE סוי 1 ✓ 2 ✓ 3 = 4 ✓ 5 ✓ 6 ✓ 7 ✓ 8 ✓ 9 = 10 11 ✓ 12 Consider the molecule (CH3)2CHCH2CHCн for the following questions. Part 1 of 2 Which of the following molecules is/are constitutional isomer(s) to (CH3)2CHCH2CH2CH3? Check all that apply. Part 2 of 2 (CH3),C(CH2)2CH3 CH3 H,C-CH-CH-CH, CH 3 None of the above. ☑ Which of the following molecules is/are identical molecules to (CH3)2CHCH2CH2CH₁₂? Check all that apply. CH3 H,C-CH-CH₂-CH2-CH, CH3(CH2)2CH(CH3)2 CH2-CH2-CH3 HỌC-CH=CH, 乂 ☑ а None of the above Check Save For Later Submit Assignment © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center Accessibilityarrow_forward18:11 LTE ا... US$50 off hotels is waiting for you Book now, hotels in Nashville are going fast QUTSLIVII 25 61 69 points) | QuestIVIT ALLēm... now Give the IUPAC name for each compound. Part 1 of 3 Part 2 of 3 X ☑ Х Check Save For Later Submit © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. TOMS CT US ...vacy Center | Accessibilityarrow_forward
- Done 19:17 www-awu.aleks.com Chapter 12 HW Question 29 of 39 (6 points) | Question Attempt: 1 of Unlimited .III LTE סוי 27 28 = 29 30 31 32 = 33 34 35 Consider this structure. CH3CH2CH2 Part 1 of 3 3 CH2 CH2CH3 - C-CH2CH 3 H CH₂ Give the IUPAC name of this structure. 3-ethyl-3,4-dimethylheptane Part: 1/3 Part 2 of 3 Draw the skeletal structure. Skip Part < Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Save For Later Submit © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibility Хarrow_forward18:57 .III LTE www-awu.aleks.com Chapter 12 HW Question 31 of 39 (8 points) | Question Attem... Give the IUPAC name of each compound. Part 1 of 4 Part 2 of 4 Х Х Check Save For Later Submit © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. TOMS OF US vacy Center | Accessibilityarrow_forwardWhat is the missing reactant in this organic reaction? CH3-C-CH2-NH2 + R - CH3 O: 0 CH3-N-CH2-C-NH-CH2-C-CH3 + H2O Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the condensed structure of R. If there is more than one reasonable answer, you can draw any one of them. If there is no reasonable answer, check the No answer box under the drawing area. Note for advanced students: you may assume no products other than those shown above are formed. Explanation Check Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure. C © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center Accesarrow_forward
- Done 18:17 • www-awu.aleks.com Chapter 12 HW Question 24 of 39 (4 points) | Question Attempt: 1 of Unlimited ▼ 20 ✓ 21 × 22 23 24 25 26 raw the structure corresponding to each IUPAC name. Part 1 of 2 .III LTE 22 27 28 סוי 29 29 3 A skeletal structure corresponding to the IUPAC name 3-ethyl-4-methylhexane. Part 2 of 2 Click and drag to start drawing a structure. A condensed structure corresponding to the IUPAC name 2,2,4- trimethylpentane. Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure. Check Save For Later Submit < Х ப: G © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibility : Garrow_forwardDone 18:25 www-awu.aleks.com .III LTE Chapter 12 HW Question 29 of 39 (6 points) | Question Attempt: 1 of Unlimi... Oli 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 Consider this structure. CH2 CH2CH2 CH2CH2CH₂ C -C. -CH2CH3 H CH Part: 0 / 3 Part 1 of 3 Give the IUPAC name of this structure. Skip Part < Check ☑ Save For Later © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibility ....................arrow_forwardCalculate Ecell at 25.0 oC using the following line notation. Zn(s)|Zn+2(aq, 0.900 M)||Cu+2(aq, 0.000200 M)|Cu(s)arrow_forward
- Predict the product of this organic reaction: O OH + H + OH A P + H2O Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the skeletal ("line") structure of P. If there isn't any P because this reaction won't happen, check the No reaction box under the drawing area. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. X G ☐ :arrow_forward0.0994 g of oxalic acid dihydrate is titrated with 10.2 mL of potassium permanganate. Calculate the potassium permanganate concentration. Group of answer choices 0.0433 M 0.135 M 0.0309 M 0.193 Marrow_forwardExperts...can any one help me solve these problems?arrow_forward
 General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry In FocusChemistryISBN:9781305084476Author:Tro, Nivaldo J., Neu, Don.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry In FocusChemistryISBN:9781305084476Author:Tro, Nivaldo J., Neu, Don.Publisher:Cengage Learning





