
(a)
Interpretation: To classify each of the following molecules as (1) an oxidizing agent, (2) a reducing agent, or (3) neither an oxidizing agent nor a reducing agent.
a. NADH
b. ATP
c. FAD
d. CoA–SH
Concept introduction: The sum of various
ATP is a
Flavin adenine dinucleotideexists in two forms: oxidized form
Coenzyme A (CoA) is a coenzyme which is utilized in various metabolic reactions. The functions of coenzyme A include oxidation of pyruvate in the citric cycle and fatty acid oxidation.
Oxidizing agents are those species which gets reduced and oxidizes the other species present in the chemical reaction. Reducing agent is those species which gets oxidized and reduces the other species present in a chemical reaction. Generally, oxidizing agents are electron acceptor and reducing agents are electron donor.
(a)
Answer to Problem 23.44EP
Explanation of Solution
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide exists in two forms:
Here
(b)
Interpretation: To classify each of the following molecules as (1) an oxidizing agent, (2) a reducing agent, or (3) neither an oxidizing agent nor a reducing agent.
a. NADH
b. ATP
c. FAD
d. CoA–SH
Concept introduction: The sum of various chemical reactions occurring in the human body is called metabolism and the reactions individually are known as metabolic reactions. During these metabolic reactions, the various metabolic intermediates are formed for the short time to complete the reactions.ATP,
ATP is a nucleotide which provides energy for the completion of various metabolic reactions occurring in our human body. The structure of ATP consists of adenine base, ribose sugar unit and the three phosphate groupconnected to each other by phosphoanhydride bonds.
Flavin adenine dinucleotideexists in two forms: oxidized form
Coenzyme A (CoA) is a coenzyme which is utilized in various metabolic reactions. The functions of coenzyme A include oxidation of pyruvate in the citric cycle and fatty acid oxidation.
Oxidizing agents are those species which gets reduced and oxidizes the other species present in the chemical reaction. Reducing agent is those species which gets oxidized and reduces the other species present in a chemical reaction. Generally, oxidizing agents are electron acceptor and reducing agents are electron donor.
(b)
Answer to Problem 23.44EP
ATP molecule is neither a reducing agent nor an oxidizing agent in metabolic reactions.
Explanation of Solution
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is anucleotide which structural component is one unit of the adenine base, one unit of ribose sugar and three units of a phosphate group. It can be converted into its monophosphate form(AMP) and diphosphate form(ADP) by losing a phosphate group. The reaction to this change is:
Here ATP is not involved in electron transfer hence it is neither a reducing agent nor an oxidizing agent.
(c)
Interpretation: To classify each of the following molecules as (1) an oxidizing agent, (2) a reducing agent, or (3) neither an oxidizing agent nor a reducing agent.
a. NADH
b. ATP
c. FAD
d. CoA–SH
Concept introduction: The sum of various chemical reactions occurring in the human body is called metabolism and the reactions individually are known as metabolic reactions. During these metabolic reactions, the various metabolic intermediates are formed for the short time to complete the reactions.ATP,
ATP is a nucleotide which provides energy for the completion of various metabolic reactions occurring in our human body. The structure of ATP consists of adenine base, ribose sugar unit and the three phosphate groupconnected to each other by phosphoanhydride bonds.
Flavin adenine dinucleotideexists in two forms: oxidized form
Coenzyme A (CoA) is a coenzyme which is utilized in various metabolic reactions. The functions of coenzyme A include oxidation of pyruvate in the citric cycle and fatty acid oxidation.
Oxidizing agents are those species which gets reduced and oxidizes the other species present in the chemical reaction. Reducing agent is those species which gets oxidized and reduces the other species present in a chemical reaction. Generally, oxidizing agents are electron acceptor and reducing agents are electron donor.
(c)
Answer to Problem 23.44EP
Explanation of Solution
Flavin adenine dinucleotide exists in two forms:
Here
(d)
Interpretation: To classify each of the following molecules as (1) an oxidizing agent, (2) a reducing agent, or (3) neither an oxidizing agent nor a reducing agent.
a. NADH
b. ATP
c. FAD
d. CoA–SH
Concept introduction: The sum of various chemical reactions occurring in the human body is called metabolism and the reactions individually are known as metabolic reactions. During these metabolic reactions, the various metabolic intermediates are formed for the short time to complete the reactions.ATP,
ATP is a nucleotide which provides energy for the completion of various metabolic reactions occurring in our human body. The structure of ATP consists of adenine base, ribose sugar unit and the three phosphate groupconnected to each other by phosphoanhydride bonds.
Flavin adenine dinucleotideexists in two forms: oxidized form
Coenzyme A (CoA) is a coenzyme which is utilized in various metabolic reactions. The functions of coenzyme A include oxidation of pyruvate in the citric cycle and fatty acid oxidation.
Oxidizing agents are those species which gets reduced and oxidizes the other species present in the chemical reaction. Reducing agent is those species which gets oxidized and reduces the other species present in a chemical reaction. Generally, oxidizing agents are electron acceptor and reducing agents are electron donor.
(d)
Answer to Problem 23.44EP
Coenzyme A (CoA–SH) molecule is neither a reducing agent nor an oxidizing agent in metabolic reactions.
Explanation of Solution
Coenzyme A (CoA) is a coenzyme whose structure is based on the B vitamin pantothenic acid. Its structure consists of three subunits: 2-Aminoethanethiol, pantothenic acid, and phosphorylated ADP.
Coenzyme A is always in equilibrium with its acetyl form and therefore helps in transfer of acetyl group in metabolic reaction. The reaction for this change is
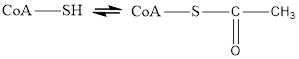
Here Coenzyme A (CoA) is not involved in electron transfer hence it is neithera reducing agent nor an oxidizing agent.
a.
b. ATP molecule is neither a reducing agent nor an oxidizing agent in metabolic reactions.
c.
d. Coenzyme A (CoA–SH) molecule is neither a reducing agent nor an oxidizing agent in metabolic reactions.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 23 Solutions
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry
- For Raman spectroscopy/imaging, which statement is not true regarding its disadvantages? a) Limited spatial resolution. b) Short integration time. c) A one-dimensional technique. d) Weak signal, only 1 in 108 incident photons is Raman scattered. e) Fluorescence interference.arrow_forwardUsing a cell of known pathlength b = 1.25115 x 10-3 cm, a water absorption spectrum was measured. The band at 1645 cm-1, assigned to the O-H bending, showed an absorbance, A, of 1.40. a) Assuming that water density is 1.00 g/mL, calculate the water molar concentration c (hint: M= mole/L) b) Calculate the molar absorptivity, a, of the 1645 cm-1 band c) The transmitted light, I, can be written as I= Ioexp(-xb), where x is the absorption coefficient (sometimes designated as alpha), Io is the input light, and b is the cell pathlength. Prove that x= (ln10)*x*c. (Please provide a full derivation of the equation for x from the equation for I). d) Calculate x for the 1645 cm-1 bandarrow_forwardI need help with the follloaingarrow_forward
- For a CARS experiment on a Raman band 918 cm-1, if omega1= 1280 nm, calculate the omega2 in wavelength (nm) and the CARS output in wavelength (nm).arrow_forwardI need help with the following questionarrow_forwardFor CARS, which statement is not true regarding its advantages? a) Contrast signal based on vibrational characteristics, no need for fluorescent tagging. b) Stronger signals than spontaneous Raman. c) Suffers from fluorescence interference, because CARS signal is at high frequency. d) Faster, more efficient imaging for real-time analysis. e) Higher resolution than spontaneous Raman microscopy.arrow_forward
- Draw the major product of the Claisen condensation reaction between two molecules of this ester. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Incorrect, 5 attempts remaining 1. NaOCH3/CH3OH 2. Acidic workup Select to Draw O Incorrect, 5 attempts remaining The total number of carbons in the parent chain is incorrect. Review the reaction conditions including starting materials and/or intermediate structures and recount the number of carbon atoms in the parent chain of your structure. OKarrow_forwardUsing a cell of known pathlength b = 1.25115 x 10-3 cm, a water absorption spectrum was measured. The band at 1645 cm-1, assigned to the O-H bending, showed an absorbance, A, of 1.40. a) Assuming that water density is 1.00 g/mL, calculate the water molar concentration c (hint: M= mole/L) b) Calculate the molar absorptivity, a, of the 1645 cm-1 band c) The transmitted light, I, can be written as I= Ioexp(-xb), where x is the absorption coefficient (sometimes designated as alpha), Io is the input light, and b is the cell pathlength. Prove that x= (ln10)*x*c d) Calculate x for the 1645 cm-1 bandarrow_forwardConvert 1.38 eV into wavelength (nm) and wavenumber (cm-1) (c = 2.998 x 108 m/s; h = 6.626 x 10-34 J*s).arrow_forward
 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Chemistry In FocusChemistryISBN:9781305084476Author:Tro, Nivaldo J., Neu, Don.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry In FocusChemistryISBN:9781305084476Author:Tro, Nivaldo J., Neu, Don.Publisher:Cengage Learning
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning





