
(a)
Interpretation: The more basic
Concept Introduction:
If the lone pair of electrons on nitrogen atom in amine compound is delocalized, that compound is resonance stabilized. It is also involved in
To find: Decide the more basic amine compound in the given pairs of compounds (a)
Get a compound where lone pairs on nitrogen atoms are delocalized
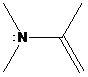
(b)
Interpretation: The more basic amine compound has to be found for the given pairs of compounds
Concept Introduction:
If the lone pair of electrons on nitrogen atom in amine compound is delocalized, that compound is resonance stabilized. It is also involved in aromatic stabilization. As a result, a number of resonance structures are drawn for the delocalization of electrons in the structures. So, the compound has less basic character. If the lone pair of electrons on nitrogen atom in amine compound is localized, that compound doesn’t involve in resonance stabilization. So, that compound has more basic character.
To find: Decide the more basic amine compound in the given pairs of compounds (b)
Get a compound where lone pairs on nitrogen atoms are delocalized
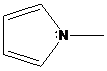
(c)
Interpretation: The more basic amine compound has to be found for the given pairs of compounds
Concept Introduction:
If the lone pair of electrons on nitrogen atom in amine compound is delocalized, that compound is resonance stabilized. It is also involved in aromatic stabilization. As a result, a number of resonance structures are drawn for the delocalization of electrons in the structures. So, the compound has less basic character. If the lone pair of electrons on nitrogen atom in amine compound is localized, that compound doesn’t involve in resonance stabilization. So, that compound has more basic character.
To find: Decide the more basic amine compound in the given pairs of compounds (c)
Get a compound where lone pairs on nitrogen atoms are delocalized

(d)
Interpretation: The more basic amine compound has to be found for the given pairs of compounds
Concept Introduction:
If the lone pair of electrons on nitrogen atom in amine compound is delocalized, that compound is resonance stabilized. It is also involved in aromatic stabilization. As a result, a number of resonance structures are drawn for the delocalization of electrons in the structures. So, the compound has less basic character. If the lone pair of electrons on nitrogen atom in amine compound is localized, that compound doesn’t involve in resonance stabilization. So, that compound has more basic character.
To find: Decide the more basic amine compound in the given pairs of compounds (d)
Get a compound where lone pairs on nitrogen atoms are delocalized
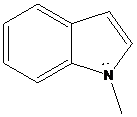
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 22 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-PRINT MULTI TERM
- 6. Show how you would accomplish the following transformations. (Show the steps and reagents/solvents needed) 2-methylpropene →2,2-dimethyloxiran Iarrow_forward4) Answer the following exercise with curved arrows indicating who is a nucleophile or Who is the electrophile? 2.44 Predict the structure of the product formed in the reaction of the organic base pyridine with the organic acid acetic acid, and use curved arrows to indicate the direction of electron flow. 7 H3C OH N Pyridine Acetic acidarrow_forwardUsing the data provided please help me answer this question. Determine the concentration of the iron(Ill) salicylate in the unknown directly from to graph and from the best fit trend-line (least squares analysis) of the graph that yielded a straight line.arrow_forward
- Please help me figure out what the slope is and how to calculate the half life Using the data provided.arrow_forwardCurved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Follow the curved arrows and draw the structure of the missing reactants, intermediates, or products in the following mechanism. Include all lone pairs. Ignore stereochemistry. Ignore inorganic byproducts. H Br2 (1 equiv) H- Select to Draw Starting Alkene Draw Major Product I I H2O 四: ⑦.. Q Draw Major Charged Intermediate Iarrow_forwardNH (aq)+CNO (aq) → CO(NH2)2(s) Experiment [NH4] (M) [CNO] (M) Initial rate (M/s) 1 0.014 0.02 0.002 23 0.028 0.02 0.008 0.014 0.01 0.001 Calculate the rate contant for this reaction using the data provided in the table.arrow_forward
- 2CIO2 + 20H-1 CIO31 + CIO2 + H2O Experiment [CIO2], M [OH-1], M 1 0.0500 0.100 23 2 0.100 0.100 3 0.100 0.0500 Initial Rate, M/s 0.0575 0.230 0.115 ... Given this date, calculate the overall order of this reaction.arrow_forward2 3 .(be)_[Ɔ+(be)_OI ← (b²)_IƆO+ (be)_I Experiment [1-] M 0.005 [OCI-] 0.005 Initial Rate M/min 0.000275 0.0025 0.005 0.000138 0.0025 0.0025 0.000069 4 0.0025 0.0025 0.000140 Calculate the rate constant of this reaction using the table data.arrow_forward1 2 3 4 I(aq) +OCl(aq) → IO¯¯(aq) + Cl¯(aq) Experiment [I-] M 0.005 [OCI-] 0.005 Initial Rate M/min 0.000275 0.0025 0.005 0.000138 0.0025 0.0025 Calculate the overall order of this reaction using the table data. 0.0025 0.000069 0.0025 0.000140arrow_forward
- H2O2(aq) +3 I¯(aq) +2 H+(aq) → 13(aq) +2 H₂O(l)· ••• Experiment [H2 O2]o (M) [I]o (M) [H+]。 (M) Initial rate (M/s) 1 0.15 0.15 0.05 0.00012 234 0.15 0.3 0.05 0.00024 0.3 0.15 0.05 0.00024 0.15 0.15 0.1 0.00048 Calculate the overall order of this reaction using the table data.arrow_forwardThe U. S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) sets limits on healthful levels of air pollutants. The maximum level that the EPA considers safe for lead air pollution is 1.5 μg/m³ Part A If your lungs were filled with air containing this level of lead, how many lead atoms would be in your lungs? (Assume a total lung volume of 5.40 L.) ΜΕ ΑΣΦ = 2.35 1013 ? atoms ! Check your rounding. Your final answer should be rounded to 2 significant figures in the last step. No credit lost. Try again.arrow_forwardY= - 0.039 (14.01) + 0.7949arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





