
(a)
Interpretation: Major products for the given set of reactions have to be found.
Concept Introduction:
The nitro group present in the compound is reduced to amino group by using Fe, Zn, Sn or SnCl2 in the presence of aqueous acid followed by the treatment with base such as NaOH. This reaction is more mild approach. It can be carried out in the presence of the other
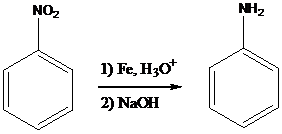
To find: Using a reduction followed by base treatment, prepare the major product of (a)
Find the reaction of the starting material of (a) with Fe, H3O+
(b)
Interpretation: Major products for the given set of reactions have to be found.
Concept Introduction:
Sodium cyanoborohydride is a strong reducing agent than sodium borohydride. It reduces the carbonyl group into amine group in a rapid way. So, it is called as reductive amination reactions.
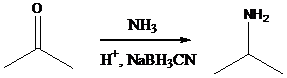
Aldehyde or ketone group is reacted with primary amine in the presence of sodium cyanoborohydride as a reducing agent and a proton source in the reaction medium to produce secondary amines.
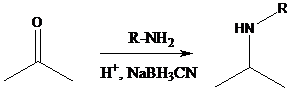
Aldehyde or ketone group is reacted with secondary amine in the presence of sodium cyanoborohydride as a reducing agent and a proton source in the reaction medium to produce tertiary amines.
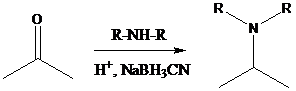
To find: Using a reductive amination, prepare the major product of (b)
Decide the reaction and the nature of the product
(c)
Interpretation: Major products for the given set of reactions have to be found.
Concept introduction:
The reduction of lithium aluminum hydride on nitriles followed by water work-up gives amine with an additional carbon atom in their chain. This type of reaction is applied to increase the carbon skeleton and change in the identity of the functional group.
To find: The major product of the reaction (c)
Give for the formation of lithium salt by reduction

(d)
Interpretation: Major products for the given set of reactions have to be found.
Concept introduction:
The reduction of lithium aluminum hydride on nitriles followed by water work-up gives amine with an additional carbon atom in their chain. This type of reaction is applied to increase the carbon skeleton and change in the identity of the functional group.
To find: The major product of the reaction (d)
Give for the formation of lithium ion by reduction
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 22 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-PRINT MULTI TERM
- When anisole is treated with excess bromine, the reaction gives a product which shows two singlets in 1H NMR. Draw the product.arrow_forward(ii) Draw a reasonable mechanism for the following reaction: CI NaOH heat OH (hint: SNAr Reaction) :arrow_forwardDraw the major product in each of the following reaction:arrow_forward
- Draw the mechanism for the following Friedel-Craft reaction. AlBr3 Brarrow_forward(a) Draw the structures of A and B in the following reaction. (i) NaNH2, NH3(1) A + B (ii) H3O+arrow_forwardFor the reaction 2 N2O5(g) → 4 NO2(g) + O2(g), the following mechanism has been proposed: N2O5 →> NO₂+ NO3_(K1) NO2 + NO3 → N2O5 (k-1) NO2 + NO3 → → NO2 + O2 + NO (K2) NO + N2O5- NO2 + NO2 + NO2 (K3) d[N₂O5] __2k‚k₂[N2O5] Indicate whether the following rate expression is acceptable: dt k₁₁+ k₂arrow_forward
- Consider the following decomposition reaction of N2O5(g): For the reaction 2 N2O5(g) → 4 NO2(g) + O2(g), the following mechanism has been proposed: N2O5 → NO2 + NO3 (K1) NO2 + NO3 → N2O5 (k-1) NO2 + NO3 → NO2 + O2 + NO (K2) NO + N2O5 → NO2 + NO2 + NO2 (K3) Indicate whether the following rate expression is acceptable: d[N2O5] = -k₁[N₂O₂] + K¸₁[NO₂][NO3] - K¸[NO₂]³ dtarrow_forwardIn a reaction of A + B to give C, another compound other than A, B or C may appear in the kinetic equation.arrow_forwardFor the reaction 2 N2O5(g) → 4 NO2(g) + O2(g), the following mechanism has been proposed: N2O5 →> NO₂+ NO3_(K1) NO2 + NO3 → N2O5 (k-1) NO2 + NO3 → → NO2 + O2 + NO (K2) NO + N2O5- NO2 + NO2 + NO2 (K3) d[N₂O5] __2k‚k₂[N2O5] Indicate whether the following rate expression is acceptable: dt k₁₁+ k₂arrow_forward
- Given the reaction R + Q → P, indicate the rate law with respect to R, with respect to P and with respect to P.arrow_forwardSteps and explanations. Also provide, if possible, ways to adress this kind of problems in general.arrow_forwardk₁ Given the reaction A B, indicate k-1 d[A] (A). the rate law with respect to A: (B). the rate law with respect to B: d[B] dt dtarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





