
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The compound has to be indicated whether it contains an amino group, a monosubstituted amino group, a disubstituted amino group, or not an amine.
Concept Introduction:
Amine is an organic derivative. If in ammonia one or more alkyl, cycloalkyl, or aryl groups are substituted instead of hydrogen atom then it is known as amine. Depending on the number of substitution the
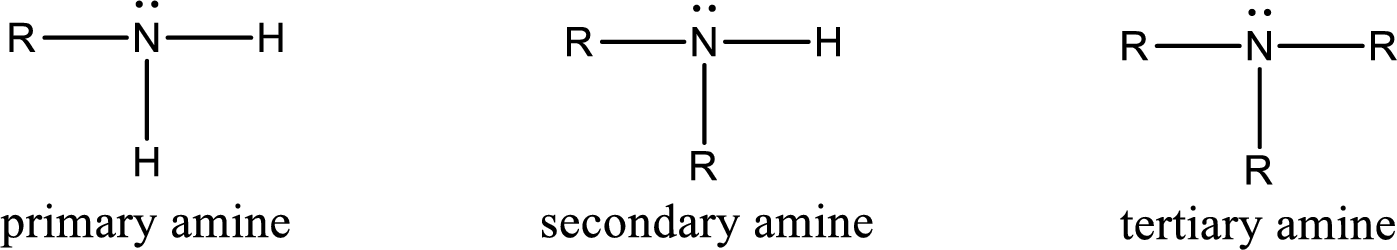
Amides are also organic derivative. In an amide, the nitrogen atom is bonded to a carbonyl group. The general structural formula of amide can be given as shown below,
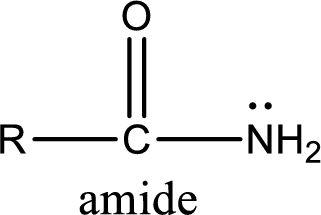
The difference between amine and amide is that in amine, the nitrogen atom is bonded to a hydrocarbon chain. In case of amides, the nitrogen atom is bonded to a carbonyl group.
(b)
Interpretation:
The compound has to be indicated whether it contains an amino group, a monosubstituted amino group, a disubstituted amino group, or not an amine.
Concept Introduction:
Amine is an organic derivative. If in ammonia one or more alkyl, cycloalkyl, or aryl groups are substituted instead of hydrogen atom then it is known as amine. Depending on the number of substitution the amines are classified as primary, secondary or tertiary amine. Primary amine is the one in which only one hydrogen atom in ammonia is replaced by a hydrocarbon group. Secondary amine is the one in which only two hydrogen atoms in ammonia is replaced by a hydrocarbon group. Tertiary amine is the one in which all three hydrogen atoms in ammonia is replaced by a hydrocarbon group. The generalized structural formula for all the amines is,
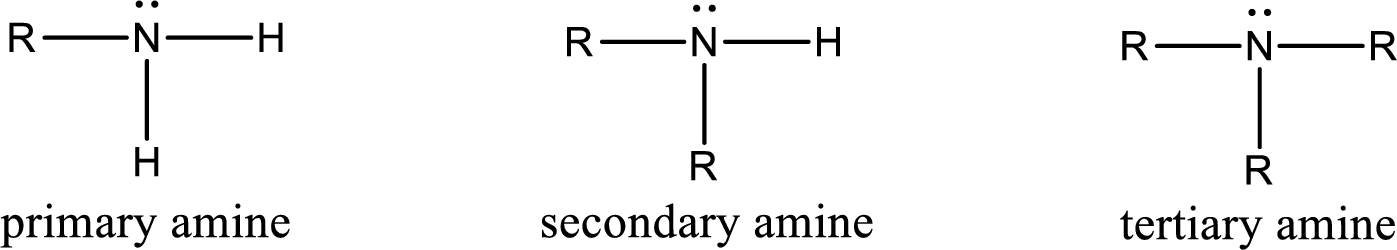
Amides are also organic derivative. In an amide, the nitrogen atom is bonded to a carbonyl group. The general structural formula of amide can be given as shown below,
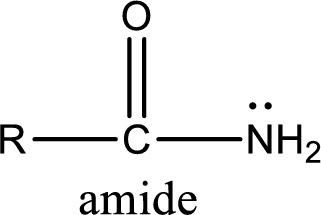
The difference between amine and amide is that in amine, the nitrogen atom is bonded to a hydrocarbon chain. In case of amides, the nitrogen atom is bonded to a carbonyl group.
(c)
Interpretation:
The compound has to be indicated whether it contains an amino group, a monosubstituted amino group, a disubstituted amino group, or not an amine.
Concept Introduction:
Amine is an organic derivative. If in ammonia one or more alkyl, cycloalkyl, or aryl groups are substituted instead of hydrogen atom then it is known as amine. Depending on the number of substitution the amines are classified as primary, secondary or tertiary amine. Primary amine is the one in which only one hydrogen atom in ammonia is replaced by a hydrocarbon group. Secondary amine is the one in which only two hydrogen atoms in ammonia is replaced by a hydrocarbon group. Tertiary amine is the one in which all three hydrogen atoms in ammonia is replaced by a hydrocarbon group. The generalized structural formula for all the amines is,
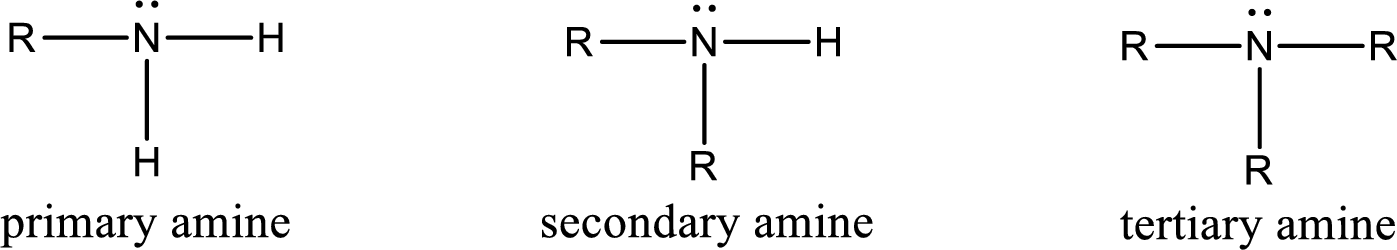
Amides are also organic derivative. In an amide, the nitrogen atom is bonded to a carbonyl group. The general structural formula of amide can be given as shown below,
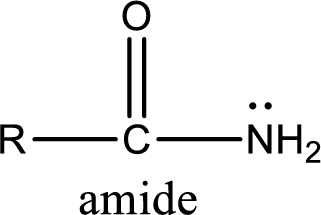
The difference between amine and amide is that in amine, the nitrogen atom is bonded to a hydrocarbon chain. In case of amides, the nitrogen atom is bonded to a carbonyl group.
(d)
Interpretation:
The compound has to be indicated whether it contains an amino group, a monosubstituted amino group, a disubstituted amino group, or not an amine.
Concept Introduction:
Amine is an organic derivative. If in ammonia one or more alkyl, cycloalkyl, or aryl groups are substituted instead of hydrogen atom then it is known as amine. Depending on the number of substitution the amines are classified as primary, secondary or tertiary amine. Primary amine is the one in which only one hydrogen atom in ammonia is replaced by a hydrocarbon group. Secondary amine is the one in which only two hydrogen atoms in ammonia is replaced by a hydrocarbon group. Tertiary amine is the one in which all three hydrogen atoms in ammonia is replaced by a hydrocarbon group. The generalized structural formula for all the amines is,
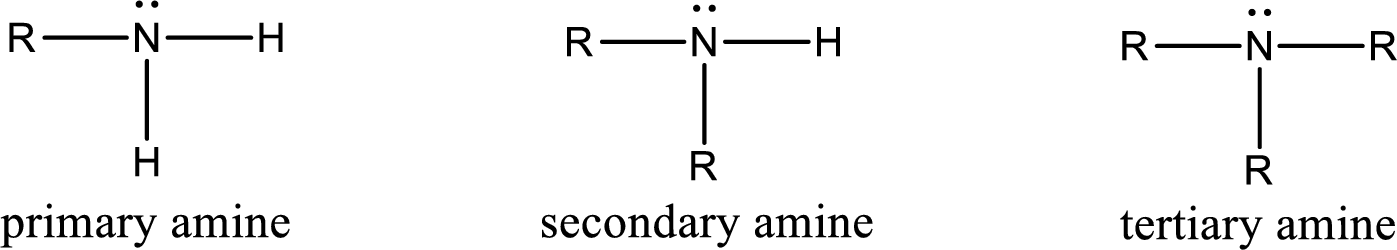
Amides are also organic derivative. In an amide, the nitrogen atom is bonded to a carbonyl group. The general structural formula of amide can be given as shown below,
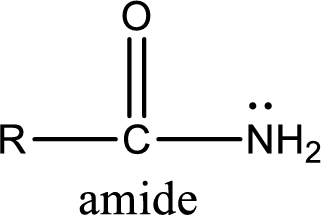
The difference between amine and amide is that in amine, the nitrogen atom is bonded to a hydrocarbon chain. In case of amides, the nitrogen atom is bonded to a carbonyl group.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 17 Solutions
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry Seventh Edition
- Anwser these Discussion Questions: Part One Why were the plants kept in the dark prior to the experiment? Why is this important? Why is it important to boil the leaf? Explain why it was necessary to use boiling alcohol? What is the purpose of the iodine? Part Two What was the purpose of keeping the leaf in the dark and then covering it with a cardboard cut-out? What conclusions can you draw from this part of the lab? Part Three 7. In this experiment what was the purpose of adding the soda lime? 8. Why was a sealed bag placed around each plant? 9. What happened in the control plants? 10. What was the result on photosynthesis? Part Four 11. Why was a variegated leaf used in this experiment? !2. What conclusions can you draw about starch production in a variegated leaf?arrow_forwardHow did the color differences between the two bacterial species you used in this experiment help you determine if the streak plate method you performed was successful?arrow_forwardseries of two-point crosses were carried out among six loci (a, b, c, d, e and f), producing the following recombination frequencies. According to the data below, the genes can be placed into how many different linkage groups? Loci a and b Percent Recombination 50 a and c 14 a and d 10 a and e 50 a and f 50 b and c 50 b and d 50 b and e 35 b and f 20 c and d 5 c and e 50 c and f 50 d and e 50 d and f 50 18 e and f Selected Answer: n6 Draw genetic maps for the linkage groups for the data in question #5. Please use the format given below to indicate the genetic distances. Z e.g. Linkage group 1=P____5 mu__Q____12 mu R 38 mu 5 Linkage group 2-X_____3 mu__Y_4 mu sanightarrow_forward
- What settings would being able to isolate individual bacteria colonies from a mixed bacterial culture be useful?arrow_forwardCan I get a handwritten answer please. I'm having a hard time understanding this process. Thanksarrow_forwardSay you get AATTGGCAATTGGCAATTGGCAATTGGCAATTGGCAATTGGCAATTGGC 3ʹ and it is cleaved with Mspl restriction enzyme - how do I find how many fragments?arrow_forward
- Which marker does this DNA 5ʹ AATTGGCAATTGGCAATTGGCAATTGGCAATTGGCAATTGGCAATTGGC 3ʹ show?arrow_forwardThe Z value of LOD for two genes is 4, what does it mean for linkage and inheritance?arrow_forwardBiology How will you make a 50-ul reaction mixture with 2uM primer DNA using 10 uM primer DNA stocksolution and water?arrow_forward
 Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337711067Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna BalacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337711067Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna BalacPublisher:Cengage Learning Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax





