
a)
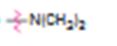
Interpretation:
Whether N,N-dimethylamino group is an activator or deactivator and whether it is a o-, p-director or m-director is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
In
Electron releasing groups, except halogens, normally are activators and ortho & para directors. Electron withdrawing groups normally are deactivators and meta directors. Halogens are ortho & para directing but are deactivating.
To state:
Whether N,N-dimethylamino group is an activator or deactivator and whether it is a, o-, p-director or m-director.
b)
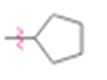
Interpretation:
Whether cyclopentyl group is an activator or deactivator and whether it is an o-, p-director or m-director is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
In aromatic substitution reactions the activating or deactivating and orienting effects of a substituent attached to the benzene ring can be decided from its resonance and inductive effects. The orientation is decided by the resonance effect while the activating or deactivating effect is decided both by resonance and inductive effects. Both effects may reinforce or oppose each other. However the resonance effect is much stronger than the inductive effect.
Electron releasing groups, except halogens, normally are activators and ortho & para directors. Electron withdrawing groups normally are deactivators and meta directors. Halogens are ortho & para directing but are deactivating.
To state:
Whether cyclopentyl group is an activator or deactivator and whether it is an o-, p-director or m-director.
c)
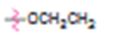
Interpretation:
Whether ethoxy group is an activator or deactivator and whether it is an o-, p-director or m-director is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
In aromatic substitution reactions the activating or deactivating and orienting effects of a substituent attached to the benzene ring can be decided from its resonance and inductive effects. The orientation is decided by the resonance effect while the activating or deactivating effect is decided both by resonance and inductive effects. Both effects may reinforce or oppose each other. However the resonance effect is much stronger than the inductive effect.
Electron releasing groups, except halogens, normally are activators and ortho & para directors. Electron withdrawing groups normally are deactivators and meta directors. Halogens are ortho & para directing but are deactivating.
To state:
Whether ethoxy group is an activator or deactivator and whether it is an o-, p-director or m-director.
d)
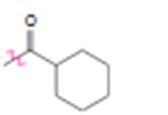
Interpretation:
Whether the carbonyl group is an activator or deactivator and whether it is a o-, p-director or m-director is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
In aromatic substitution reactions the activating or deactivating and orienting effects of a substituent attached to the benzene ring can be decided from its resonance and inductive effects. The orientation is decided by the resonance effect while the activating or deactivating effect is decided both by resonance and inductive effects. Both effects may reinforce or oppose each other. However the resonance effect is much stronger than the inductive effect.
Electron releasing groups, except halogens, normally are activators and ortho & para directors. Electron withdrawing groups normally are deactivators and meta directors. Halogens are ortho & para directing but are deactivating.
To state:
Whether carbonyl group is an activator or deactivator and whether it is a o-, p-director or m-director.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 16 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Draw the product of the E2 reaction shown below. Include the correct stereochemistry. Ignore any inorganic byproducts. + Br CH3 Q Strong Base Drawing Atoms, Bonds and Rings Charges Undo Reset H "Br H N Br. Remove Done .N. Drag To Panarrow_forwardCurved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Use the reaction conditions provided and follow the curved arrows to draw the product of this elementary step in an elimination mechanism. Include all lone pairs and charges as appropriate. Ignore stereochemistry. Ignore byproducts. + Br: .. 8 0.01 M NaOH heat Drawing Q Atoms, Bonds and Rings Charges and Lone Pairs Draw or tap a new bond to see suggestions. Undo Reset Remove Done + Drag To Panarrow_forward+ Draw the product of the E2 reaction shown below. Include the correct stereochemistry. Ignore any inorganic byproducts. Ph CH2CH3 H H3C H Br DBN [૪] Drawing Atoms, Bonds and Rings H | OH Charges ―00 H. C | Undo Reset Br I Remove Done Drag To Pan +arrow_forward
- Reaction A Now the production A ΠIn the product of reaction i 12 Dear the product of actionarrow_forwardMacmillan Learnin When an unknown amine reacts with an unknown acid chloride, an amide with a molecular mass of 163 g/mol (M* = 163 m/z) is formed. In the infrared spectrum, important absorptions appear at 1661, 750 and 690 cm-1. The 13C NMR and DEPT spectra are provided. Draw the structure of the product as the resonance contributor lacking any formal charges. 13C NMR DEPT 90 200 160 120 80 40 0 200 160 120 80 DEPT 135 200 160 120 80 40 0 Draw the unknown amide. 40 40 0arrow_forwardDraw the major product karmed when I reach with the epoxide. Use walge dah bonds, including hydrogen al alcach genic center, to show the chemistry of the product Beeldraw any hydrogen akams on coxygen where applicablearrow_forward
- Curved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s). Be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond-making steps. H I Select to Add Arrows + H H 'H Q H2O H2O CI:O .H H H H I Select to Add Arrows I : C H2O H H H Select to Add Arrows 'Harrow_forward+ Draw an alkyl halide that produces ONLY the following alkene in an E2 elimination. Ignore any inorganic byproducts. Drawing Strong Base Q Atoms, Bonds and Rings Charges HO Br H2N Undo Reset Remove Done Drag To Panarrow_forwardFor the dehydrohalogenation (E2) reaction shown, draw the major organic product. Хок Br tert-butanol heat Select Drew Templates More Erase CH QQQarrow_forward
- Macmillan Learning Draw the major, neutral organic product for each substitution reaction. For this question, assume that each substitution reaction goes to completion. Disregard elimination. Reaction A. CI H₂O Select Draw Templates More Erase C Harrow_forwardMacmillan Learning Reaction B: CI HO_ 곳으 / Select Draw Templates More с € H D Erasearrow_forwardWhen 2-bromo-93-dimethylbutane is heated with sodium methoxide, one majors.. në la formed. 4th attempt Part 1 (0.5 point) t Ji See Periodic Table See Hint Draw the major alkene product and all other byproducts. Be sure to include lone-pair electrons and charges. Part 2 (0.5 point) What type of mechanism is occuring? Choose one: AS1 3rd attempt X H 41 See Hint Part 1 (0.5 point) Feedback See Periodic Table See Hintarrow_forward

 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning


