
a)

Interpretation:
The major product(s) obtainable from sulfonation of fluorobenzene is/are to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
The substituents attached to the ring have a strong influence on the incoming electrophile. Electron releasing substituent groups, except halogens, activate the ring and direct the incoming electrophile to the o- and p- positions. Halogens are o- and p- directors but they deactivate the ring. Electron withdrawing substituent groups deactivate the ring and direct the incoming electrophile to the m- position.
To predict:
The major products obtainable from sulfonation of fluorobenzene.
Answer to Problem 51AP
The major products obtainable from sulfonation of fluorobenzene are o-flurobenzenesulfonic acid and p- flurobenzenesulfonic acid.
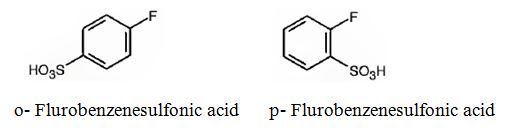
Explanation of Solution
Fluorine attached to an aromatic ring is an o- and p- directing deactivating group. Hence it directs the electrophile, SO3H+ to these positions.
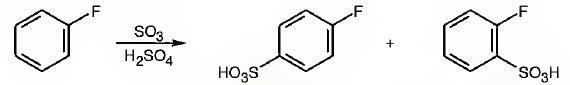
The major products obtainable from sulfonation of fluorobenzene are o-flurobenzenesulfonic acid and p- flurobenzenesulfonic acid.

b)
Interpretation:
The major product(s) obtainable from sulfonation of m-bromophenol is/are to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Electrophilic substitution of disubstituted benzenes follows three simple rules. (i) If the directing influence of both the substituents reinforce each other, a single product results. (ii) If the directing influences of both the substituent groups oppose each other, the most powerful activating group among them has the dominant influence but usually a mixture of products results. (iii) In meta disubstituted compounds, further substitution in between the groups occurs only rarely, due to steric reasons.
To predict:
The major product(s) obtainable from sulfonation of m-bromophenol.
Answer to Problem 51AP
The major products produced during the sulfonation of m-bromophenol are 2-bromo-4-hydroxybenzenesulfonicacid (I) and 4-bromo-2-hydroxybenzenesulfonicacid (II).
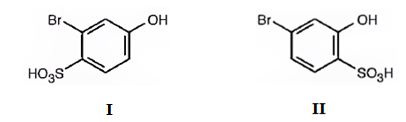
Explanation of Solution
The Br is an ortho and para directing and deactivating group while -OH group is also an ortho and para directing and highly activating group. Hence the -OH group decides the position at which the electrophilic substitution reaction will occur. The electrophile, SO3H+, enters into the ortho and para positions with respect to -OH group to produce 2-bromo-4-hydroxybenzenesulfonicacid (I) and 4-bromo-2-hydroxybenzenesulfonicacid (II).
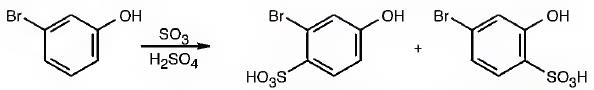
The major products produced during the sulfonation of m-bromophenol are 2-bromo-4-hydroxybenzenesulfonicacid (I) and 4-bromo-2-hydroxybenzenesulfonicacid (II).

c)
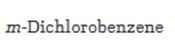
Interpretation:
The major product(s) obtainable from sulfonation of m-dichlorobenzene is/are to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Electrophilic substitution of disubstituted benzenes follows three simple rules. (i) If the directing influence of both the substituents reinforce each other, a single product results. (ii) If the directing influences of both the substituent groups oppose each other, the most powerful activating group among them has the dominant influence but usually a mixture of products results. (iii) In meta disubstituted compounds, further substitution in between the groups occurs only rarely, due to steric reasons.
To predict:
The major product(s) obtainable from sulfonation of m-dichlorobenzene.
Answer to Problem 51AP
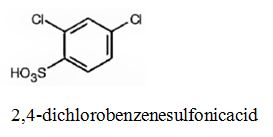
The major product produced during the sulfonation of m-dichlorobenzene is 2,4-dichlorobenzenesulfonicacid.
Explanation of Solution
In electrophilic substitution reactions, Cl is an ortho and para directing and deactivating group. Hence the electrophile, SO3H+, can enter into the ortho and para positions with respect to both Cl atoms. The ortho position in between the two Cl atoms is not favored for steric reasons. Hence the SO3H gets substituted in the p-position to a Cl which happens to be the ortho position to another Cl to yield 2,4-dichlorobenzenesulfonicacid.
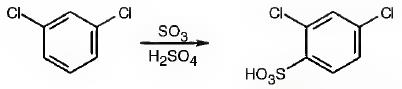
The major product produced during the sulfonation of m-dichlorobenzene is 2,4-dichlorobenzenesulfonicacid(I).

d)

Interpretation:
The major product(s) obtainable from sulfonation of 2,4-dibromophenol is/are to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Electrophilic substitution of di and trisubstituted benzenes follows three simple rules. (i) If the directing influence of both the substituents reinforce each other, a single product results. (ii) If the directing influences of both the substituent groups oppose each other, the most powerful activating group among them has the dominant influence but usually a mixture of products results. (iii) In meta disubstituted compounds, further substitution in between the groups occurs only rarely, due to steric reasons.
To predict:
The major product(s) obtainable from sulfonation of 2,4-dibromophenol.
Answer to Problem 51AP
The major product produced during the sulfonation of 2,4-dibromophenol is 3,5-dibromo-2-hydroxybenzenesulfonicacid.
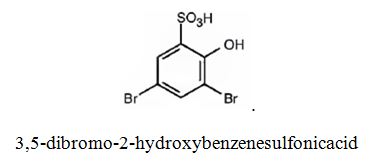
Explanation of Solution
In aromatic electrophilic substitution reactions Br is an ortho and para directing and deactivating group while –OH group also though ortho and para directing is a highly activating group. Hence the –OH group decides the position at which the electrophilic substitution reaction will occur. The electrophile, SO3H+, enters into the ortho and para positions with respect to –OH group. The para position and one ortho position to –OH are blocked by substituents. Hence the SO3H+ enters into the another ortho position to –OH group available to produce 3,5-dibromo-2-hydroxybenzenesulfonicacid.
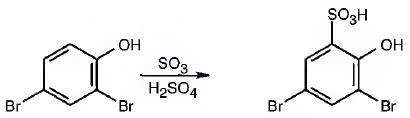
The major product produced during the sulfonation of 2,4-dibromophenol is 3,5-dibromo-2-hydroxybenzenesulfonicacid.

Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Determine the structures of the missing organic molecules in the following reaction: X+H₂O H* H+ Y OH OH Note: Molecules that share the same letter have the exact same structure. In the drawing area below, draw the skeletal ("line") structures of the missing organic molecules X and Y. You may draw the structures in any arrangement that you like, so long as they aren't touching. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. X Sarrow_forwardPredict the major products of this organic reaction. If there aren't any products, because nothing will happen, check the box under the drawing area instead. No reaction. HO. O :☐ + G Na O.H Click and drag to start drawing a structure. XS xs H₂Oarrow_forwardWhat are the angles a and b in the actual molecule of which this is a Lewis structure? H H C H- a -H b H Note for advanced students: give the ideal angles, and don't worry about small differences from the ideal groups may have slightly different sizes. a = b = 0 °arrow_forward
- What are the angles a and b in the actual molecule of which this is a Lewis structure? :0: HCOH a Note for advanced students: give the ideal angles, and don't worry about small differences from the ideal that might be caused by the fact that different electron groups may have slightly different sizes. a = 0 b=0° Sarrow_forwardDetermine the structures of the missing organic molecules in the following reaction: + H₂O +H OH O OH +H OH X Note: Molecules that share the same letter have the exact same structure. In the drawing area below, draw the skeletal ("line") structure of the missing organic molecule X. Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forwardIdentify the missing organic reactant in the following reaction: x + x O OH H* + ☑- X H+ O O Х Note: This chemical equation only focuses on the important organic molecules in the reaction. Additional inorganic or small-molecule reactants or products (like H₂O) are not shown. In the drawing area below, draw the skeletal ("line") structure of the missing organic reactant X. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Carrow_forward
- CH3O OH OH O hemiacetal O acetal O neither O 0 O hemiacetal acetal neither OH hemiacetal O acetal O neither CH2 O-CH2-CH3 CH3-C-OH O hemiacetal O acetal CH3-CH2-CH2-0-c-O-CH2-CH2-CH3 O neither HO-CH2 ? 000 Ar Barrow_forwardWhat would be the best choices for the missing reagents 1 and 3 in this synthesis? 1. PPh3 2 2. n-BuLi 3 Draw the missing reagents in the drawing area below. You can draw them in any arrangement you like. • Do not draw the missing reagent 2. If you draw 1 correctly, we'll know what it is. • Note: if one of your reagents needs to contain a halogen, use bromine. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forwardPredict the products of this organic reaction: NaBH3CN + NH2 ? H+ Click and drag to start drawing a structure. ×arrow_forward
- Predict the organic products that form in the reaction below: + OH +H H+ ➤ ☑ X - Y Note: You may assume you have an excess of either reactant if the reaction requires more than one of those molecules to form the products. In the drawing area below, draw the skeletal ("line") structures of the missing organic products X and Y. You may draw the structures in any arrangement that you like, so long as they aren't touching. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Garrow_forwardPredict the organic products that form in the reaction below: OH H+ H+ + ☑ Y Note: You may assume you have an excess of either reactant if the reaction requires more than one of those molecules to form the products. In the drawing area below, draw the skeletal ("line") structures of the missing organic products X and Y. You may draw the structures in any arrangement that you like, so long as they aren't touching. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. ✓ marrow_forwardDetermine the structures of the missing organic molecules in the following reaction: + H₂O +H H+ Y Z ☑ ☑ Note: Molecules that share the same letter have the exact same structure. In the drawing area below, draw the skeletal ("line") structures of the missing organic molecules X, Y, and Z. You may draw the structures in any arrangement that you like, so long as they aren't touching. Molecule X shows up in multiple steps, but you only have to draw its structure once. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. AP +arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





