
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780077687342
Author: Ferdinand P. Beer, E. Russell Johnston Jr., Phillip J. Cornwell, Brian Self
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 14.3, Problem 14.61P
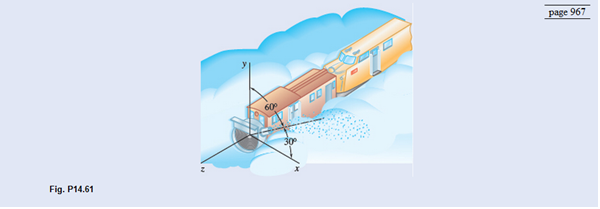
A rotary power plow is used to remove snow from a level section of railroad track. The plow car is placed ahead of an engine that propels it at a constant speed of 20 km/h. The plow car clears 160 Mg of snow per minute, projecting it in the direction shown with a velocity of 12 m/s relative to the plow car. Neglecting friction, determine (a) the force exerted by the engine on the plow car. (2) the lateral force exerted by the track on the plow.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
I tried this problem and don't know what I did wrong or how else I could approach it can you please help me out?
Q3: An engine produce 750 kW power and uses gaseous C12H26 as a fuel
at 25 C; 200% theoretical air is used and air enters at 500 K. The products
of combustion leave at 800 K. The heat loss from the engine is 175 kW.
Determine the fuel consumption for complete combustion.
Qu 5 Determine the carburizing time necessary to achieve a carbon concentration of 0.30 wt% at a position 4 mm into an iron carbon alloy that initially contains 0.10 wt% C. The surface concentration is to be maintained at 0.90 wt% C, and the treatment is to be conducted at 1100°C. Use the data for the diffusion of
carbon into y-iron: Do = 2.3 x10-5 m2/s and Qd = 148,000 J/mol. Express your answer in hours to three significant figures.
show all work step by step problems formula material science
Chapter 14 Solutions
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics
Ch. 14.1 - A 30-g bullet is fired with a horizontal velocity...Ch. 14.1 - Two identical 1350-kg automobiles A and B are at...Ch. 14.1 - An airline employee tosses two suitcases with...Ch. 14.1 - A bullet is fired with a horizontal velocity of...Ch. 14.1 - Two swimmers A and B, of weight 190 lb and 125 lb,...Ch. 14.1 - A 180-lb man and a 120-lb woman stand side by side...Ch. 14.1 - A 40-Mg boxcar A is moving in a railroad...Ch. 14.1 - Two identical cars A and B are at rest on a...Ch. 14.1 - A 20-kg base satellite deploys three...Ch. 14.1 - For the satellite system of Prob. 14.9. assuming...
Ch. 14.1 - A system consists of three identical 19.32-lb...Ch. 14.1 - A system consists of three identical 19.32-lb...Ch. 14.1 - A system consists of three particles A, B, and C....Ch. 14.1 - For the system of particles of Prob. 14.13,...Ch. 14.1 - A 13-kg projectile is passing through the origin O...Ch. 14.1 - A 300-kg space vehicle traveling with a velocity...Ch. 14.1 - A 2-kg model rocket is launched vertically and...Ch. 14.1 - An 18-kg cannonball and a 12-kg cannonball are...Ch. 14.1 - Car A was traveling east at high speed when it...Ch. 14.1 - Knowing that the coordinates of the utility pole...Ch. 14.1 - An expert archer demonstrates his ability by...Ch. 14.1 - Two spheres, each of mass m, can slide freely on a...Ch. 14.1 - In a game of pool, ball A is moving with a...Ch. 14.1 - A 6-kg shell moving with a velocity...Ch. 14.1 - A 6-kg shell moving with a velocity...Ch. 14.1 - In a scattering experiment, an alpha particle A is...Ch. 14.1 - Derive the relation Ho=rmv+HG between the angular...Ch. 14.1 - Show that Eq. (14.23) may be derived directly from...Ch. 14.1 - Consider the frame of reference Ax'y'z' in...Ch. 14.1 - Show that the relation MA=HA where HA is defined...Ch. 14.2 - Determine the energy lost due to friction and the...Ch. 14.2 - Prob. 14.32PCh. 14.2 - In Prob. 14.6. determine the work done by the...Ch. 14.2 - Determine the energy lost as a result of the...Ch. 14.2 - Two automobiles A and B, of mass mA and mB,...Ch. 14.2 - It is assumed that each of the two automobiles...Ch. 14.2 - Solve Sample Prob. 14.5, assuming that cart A is...Ch. 14.2 - Two hemispheres are held together by a cord which...Ch. 14.2 - A 15-lb block B starts from rest and slides on the...Ch. 14.2 - A 40-lb block B is suspended from a 6-ft cord...Ch. 14.2 - In a game of pool, ball A is moving with a...Ch. 14.2 - In a game of pool, ball A is moving with a...Ch. 14.2 - Three spheres, each with a mass of m, can slide...Ch. 14.2 - In a game of pool, ball A is moving with the...Ch. 14.2 - The 2-kg sub-satellite B has an initial velocity...Ch. 14.2 - A 900-lb space vehicle traveling with a velocity...Ch. 14.2 - Four small disks A, B, C, and D can slide freely...Ch. 14.2 - In the scattering experiment of Prob. 14.26, it is...Ch. 14.2 - Three identical small spheres, each of weight 2...Ch. 14.2 - Three small spheres A, B, C, each of mass m, are...Ch. 14.2 - In a game of billiards, ball A is given an initial...Ch. 14.2 - For the game of billiards of Prob. 14.51, it is...Ch. 14.2 - Two small disks A and B of mass 3 kg and 1.5 kg,...Ch. 14.2 - Two small disks A and B of mass 2 kg and 1 kg,...Ch. 14.2 - Three small identical spheres A, B, and C, which...Ch. 14.2 - Three small identical spheres A, B, and C, which...Ch. 14.3 - A stream of water with a density of =1000kg/m3 is...Ch. 14.3 - A jet ski is placed in a channel and is tethered...Ch. 14.3 - The nozzle shown discharges a stream of water at a...Ch. 14.3 - The nozzle shown discharges a stream of water at a...Ch. 14.3 - A rotary power plow is used to remove snow from a...Ch. 14.3 - Tree limbs and branches are being fed at A at the...Ch. 14.3 - Sand falls from three hoppers onto a conveyor belt...Ch. 14.3 - The stream of water shown flows at a rate of 550...Ch. 14.3 - The nozzle shown discharges water at the rate of...Ch. 14.3 - A stream of water flowing at a rate of 1.2 m/min...Ch. 14.3 - A stream of water flowing at a rate of 1.2 m3/min...Ch. 14.3 - Coal is being discharged from a first conveyor...Ch. 14.3 - The total drag due to air friction on a jet...Ch. 14.3 - While cruising in level flight at a speed of 600...Ch. 14.3 - In order to shorten the distance required for...Ch. 14.3 - The helicopter shown can produce a maximum...Ch. 14.3 - Prior to takeoff, the pilot of a 3000-kg...Ch. 14.3 - The jet engine shown scoops in air at A at a rate...Ch. 14.3 - A jet airliner is cruising at a speed of 900 km/h...Ch. 14.3 - A 16-Mg jet airplane maintains a constant speed of...Ch. 14.3 - The propeller of a small airplane has a...Ch. 14.3 - The wind turbine generator shown has an...Ch. 14.3 - A wind turbine generator system having a diameter...Ch. 14.3 - While cruising in level flight at a speed of 570...Ch. 14.3 - In a Pelton-wheel turbine, a stream of water is...Ch. 14.3 - A circular reentrant orifice (also called Borda’s...Ch. 14.3 - A railroad car with length L and mass mg when...Ch. 14.3 - The depth of water flowing in a rectangular...Ch. 14.3 - Determine the rate of flow in the channel of Prob....Ch. 14.3 - A chain of length I and mass m lies in a pile on...Ch. 14.3 - Solve Prob. 14.86, assuming that the chain is...Ch. 14.3 - The ends of a chain lie in piles at A and C. When...Ch. 14.3 - A toy car is propelled by water that squirts from...Ch. 14.3 - A toy car is propelled by water that squirts from...Ch. 14.3 - The main propulsion system of a space shuttle...Ch. 14.3 - The main propulsion system of a space shuttle...Ch. 14.3 - A rocket sled bums fuel at the constant rate of...Ch. 14.3 - A space vehicle describing a circular orbit about...Ch. 14.3 - A 540-kg spacecraft is mounted on top of a rocket...Ch. 14.3 - The rocket used to launch the 540-kg spacecraft of...Ch. 14.3 - The weight of a spacecraft, including fuel, is...Ch. 14.3 - The rocket engines of a spacecraft are fired to...Ch. 14.3 - Determine the distance traveled by the spacecraft...Ch. 14.3 - A rocket weighs 2600 lb. including 2200 lb of...Ch. 14.3 - Determine the altitude reached by the spacecraft...Ch. 14.3 - For the spacecraft and the two-stage launching...Ch. 14.3 - In a jet airplane, the kinetic energy imparted to...Ch. 14.3 - In a rocket, the kinetic energy imparted to the...Ch. 14 - Three identical cars are being unloaded from an...Ch. 14 - A 30-g bullet is fired with a velocity of 480 m/s...Ch. 14 - An 80-Mg railroad engine A coasting at 6.5 km/h...Ch. 14 - In a game of pool, ball A is moving with a...Ch. 14 - Mass C, which has a mass of 4 kg, is suspended...Ch. 14 - A 15-lb block B is at rest and a spring of...Ch. 14 - Car A of mass 1800 kg and car B of mass 1700 kg...Ch. 14 - The nozzle shown discharges a stream of water at...Ch. 14 - An airplane with a weight W and a total wing span...Ch. 14 - The final component of a conveyor system receives...Ch. 14 - A garden sprinkler has four rotating arms, each of...Ch. 14 - A chain of length I and mass m falls through a...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- (Read Question)arrow_forwardIn figure A, the homogeneous rod of constant cross section is attached to unyielding supports. In figure B, a homogeneous bar with a cross-sectional area of 600 mm2 is attached to rigid supports. The bar carries the axial loads P1 = 20 kN and P2 = 60 kN, as shown.1. In figure A, derive the expression that calculates the reaction R1 in terms of P, and the given dimensions.2. In figure B, calculate the reaction (kN) at A.3. In figure B, calculate the maximum axial stress (MPa) in the rod.arrow_forward(Read image)arrow_forward
- (Read Image)arrow_forwardM16x2 grade 8.8 bolts No. 25 C1- Q.2. The figure is a cross section of a grade 25 cast-iron pressure vessel. A total of N, M16x2.0 grade 8.8 bolts are to be used to resist a separating force of 160 kN. (a) Determine ks, km, and C. (b) Find the number of bolts required for a load factor of 2 where the bolts may be reused when the joint 19 mm is taken apart. (c) with the number of bolts obtained in (b), determine the realized load factor for overload, the yielding factor of safety, and the separation factor of safety. 19 mmarrow_forwardProblem4. The thin uniform disk of mass m = 1-kg and radius R = 0.1m spins about the bent shaft OG with the angular speed w2 = 20 rad/s. At the same time, the shaft rotates about the z-axis with the angular speed 001 = 10 rad/s. The angle between the bent portion of the shaft and the z-axis is ẞ = 35°. The mass of the shaft is negligible compared to the mass of the disk. a. Find the angular momentum of the disk with respect to point G, based on the axis orientation as shown. Include an MVD in your solution. b. Find the angular momentum of the disk with respect to point O, based on the axis orientation as shown. (Note: O is NOT the center of fixed-point rotation.) c. Find the kinetic energy of the assembly. z R R 002 2R x Answer: H = -0.046ĵ-0.040 kg-m²/sec Ho=-0.146-0.015 kg-m²/sec T 0.518 N-m =arrow_forward
- Problem 3. The assembly shown consists of a solid sphere of mass m and the uniform slender rod of the same mass, both of which are welded to the shaft. The assembly is rotating with angular velocity w at a particular moment. Find the angular momentum with respect to point O, in terms of the axes shown. Answer: Ñ。 = ½mc²wcosßsinßĵ + (}{mr²w + 2mb²w + ½ mc²wcos²ß) k 3 m r b 2 C لا marrow_forwardOnly question 2arrow_forwardOnly question 1arrow_forward
- Only question 3arrow_forwardI have Euler parameters that describe the orientation of N relative to Q, e = -0.7071*n3, e4 = 0.7071. I have Euler parameters that describe the orientation of U relative to N, e = -1/sqrt(3)*n1, e4 = sqrt(2/3). After using euler parameter rule of successive rotations, I get euler parameters that describe the orientation of U relative to Q, e = -0.4082*n1 - 0.4082*n2 - 0.5774*n3. I need euler parameters that describe the orientation of U relative to Q in vector basis of q instead of n. How do I get that?arrow_forwardDescribe at least 4 processes in engineering where control charts are (or should be) appliedarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
How Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers Work (Engineering); Author: saVRee;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OyQ3SaU4KKU;License: Standard Youtube License