
Concept explainers
The nozzle shown discharges a stream of water at the rate of 200 gal/min. Knowing that at both B and C the stream of water moves with velocity of magnitude 100 ft/s, and neglecting the weight of the vane, determine the force-couple system that must be applied at A to hold the vane in place
The force couple system that must be applied at A to hold the vane in plane.
Answer to Problem 14.112RP
The reaction force at A is
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Rate of discharge of water is
Magnitude of velocity of water is
Concept used:
Write the expression for mass flow rate of water.
Here,
Draw the impulse moment diagram for the vane as shown below:
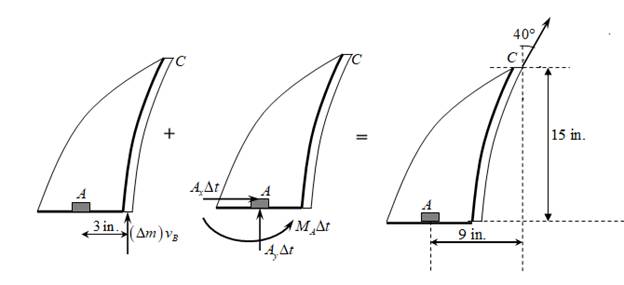
Consider
Simplify the above expression for
Here,
Consider the
Simplify the above expression.
Write the expression for the magnitude of reaction force at
Here,
Write the expression for the direction of reaction at A.
Write the expression for momentum equilibrium at point A.
Simplify the above expression for
Here,
Calculation:
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
The reaction force at A is
Conclusion:
Thus, the reaction force at A is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics
- Qu 5 Determine the carburizing time necessary to achieve a carbon concentration of 0.30 wt% at a position 4 mm into an iron carbon alloy that initially contains 0.10 wt% C. The surface concentration is to be maintained at 0.90 wt% C, and the treatment is to be conducted at 1100°C. Use the data for the diffusion of carbon into y-iron: Do = 2.3 x10-5 m2/s and Qd = 148,000 J/mol. Express your answer in hours to three significant figures. show all work step by step problems formula material sciencearrow_forward(Read Question)arrow_forwardIn figure A, the homogeneous rod of constant cross section is attached to unyielding supports. In figure B, a homogeneous bar with a cross-sectional area of 600 mm2 is attached to rigid supports. The bar carries the axial loads P1 = 20 kN and P2 = 60 kN, as shown.1. In figure A, derive the expression that calculates the reaction R1 in terms of P, and the given dimensions.2. In figure B, calculate the reaction (kN) at A.3. In figure B, calculate the maximum axial stress (MPa) in the rod.arrow_forward
- (Read image)arrow_forward(Read Image)arrow_forwardM16x2 grade 8.8 bolts No. 25 C1- Q.2. The figure is a cross section of a grade 25 cast-iron pressure vessel. A total of N, M16x2.0 grade 8.8 bolts are to be used to resist a separating force of 160 kN. (a) Determine ks, km, and C. (b) Find the number of bolts required for a load factor of 2 where the bolts may be reused when the joint 19 mm is taken apart. (c) with the number of bolts obtained in (b), determine the realized load factor for overload, the yielding factor of safety, and the separation factor of safety. 19 mmarrow_forward
- Problem4. The thin uniform disk of mass m = 1-kg and radius R = 0.1m spins about the bent shaft OG with the angular speed w2 = 20 rad/s. At the same time, the shaft rotates about the z-axis with the angular speed 001 = 10 rad/s. The angle between the bent portion of the shaft and the z-axis is ẞ = 35°. The mass of the shaft is negligible compared to the mass of the disk. a. Find the angular momentum of the disk with respect to point G, based on the axis orientation as shown. Include an MVD in your solution. b. Find the angular momentum of the disk with respect to point O, based on the axis orientation as shown. (Note: O is NOT the center of fixed-point rotation.) c. Find the kinetic energy of the assembly. z R R 002 2R x Answer: H = -0.046ĵ-0.040 kg-m²/sec Ho=-0.146-0.015 kg-m²/sec T 0.518 N-m =arrow_forwardProblem 3. The assembly shown consists of a solid sphere of mass m and the uniform slender rod of the same mass, both of which are welded to the shaft. The assembly is rotating with angular velocity w at a particular moment. Find the angular momentum with respect to point O, in terms of the axes shown. Answer: Ñ。 = ½mc²wcosßsinßĵ + (}{mr²w + 2mb²w + ½ mc²wcos²ß) k 3 m r b 2 C لا marrow_forwardOnly question 2arrow_forward
- Only question 1arrow_forwardOnly question 3arrow_forwardI have Euler parameters that describe the orientation of N relative to Q, e = -0.7071*n3, e4 = 0.7071. I have Euler parameters that describe the orientation of U relative to N, e = -1/sqrt(3)*n1, e4 = sqrt(2/3). After using euler parameter rule of successive rotations, I get euler parameters that describe the orientation of U relative to Q, e = -0.4082*n1 - 0.4082*n2 - 0.5774*n3. I need euler parameters that describe the orientation of U relative to Q in vector basis of q instead of n. How do I get that?arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





