
Concept explainers
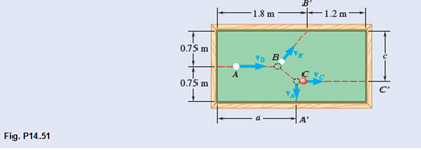
In a game of billiards, ball A is given an initial velocity v0 along the longitudinal axis of the table. It hits ball B and then ball C, which are both at rest. Balls A and C are observed to hit the sides of the table squarely at A' and C'. respectively, and ball B is observed to hit the side obliquely at B'. Knowing that
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 14 Solutions
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics
- Note: Please provide a clear, step-by-step simplified handwritten working out (no explanations!), ensuring it is done without any AI involvement. I require an expert-level answer, and I will assess and rate based on the quality and accuracy of your work and refer to the provided image for more clarity. Make sure to double-check everything for correctness before submitting thanks!. Question: (In the image as provided)arrow_forwardNote: Please provide a clear, step-by-step simplified handwritten working out (no explanations!), ensuring it is done without any AI involvement. I require an expert-level answer, and I will assess and rate based on the quality and accuracy of your work and refer to the provided image for more clarity. Make sure to double-check everything for correctness before submitting thanks!. Question: The rectangular gate shown below is 3 m wide. Compute the force P needed to hold the gate in the position shown.arrow_forwardNote: Please provide a clear, step-by-step simplified handwritten working out (no explanations!), ensuring it is done without any AI involvement. I require an expert-level answer, and I will assess and rate based on the quality and accuracy of your work and refer to the provided image for more clarity. Make sure to double-check everything for correctness before submitting thanks!. Question1: If the following container is 0.6m high, 1.2m wide and half full with water, determine the pressure acting at points A, B, and C if ax=2.6ms^-2.arrow_forward
- Please read the imagearrow_forwardChapter 12 - Lecture Notes.pptx: (MAE 272-01) (SP25) DY... Scoresarrow_forwardConsider a large 6-cm-thick stainless steel plate (k = 15.1 W/m-K) in which heat is generated uniformly at a rate of 5 × 105 W/m³. Both sides of the plate are exposed to an environment at 30°C with a heat transfer coefficient of 60 W/m²K. Determine the value of the highest and lowest temperature. The highest temperature is The lowest temperature is °C. °C.arrow_forwardSketch and explain a PV Diagram and a Temperature Entropy Diagram for a 4 stroke diesel engine please, please explain into detail the difference bewteen the two and referance the a diagram. Please include a sketch or an image of each diagramarrow_forwardDraw left view of the first orthographic projectionarrow_forwardSketch and Describe a timing diagram for a 2 stroke diesel engine emphasis on the 2 stroke as my last answer explained 4 stroke please include a diagram or sketch.arrow_forwardA 4 ft 200 Ib 1000 Ib.ft C 2 ft 350 Ib - за в 2.5 ft 150 Ib 250 Ib 375 300 Ib Replace the force system acting on the frame. shown in the figure by a resultant force (magnitude and direction), and specify where its line of action intersects member (AB), measured from point (A).arrow_forwardA continuous flow calorimeter was used to obtain the calorific value of a sample of fuel and the following data collected: Mass of fuel: 2.25 kgInlet water temperature: 11 ° COutlet water temperature 60 ° CQuantity of water: 360 Liters Calorimeter efficiency: 85%Calculate the calorific value of the sample ( kJ / kg ). ive submitted this question twice and have gotten two way different answers. looking for some help thanksarrow_forward15 kg of steel ball bearings at 100 ° C is immersed in 25 kg of water at 20 ° C . Assuming no loss of heat to or from the container, calculate the final temperature of the water after equilibrium has been attained.Specific heat of steel: 0.4857 kJ / kg / ° KSpecific heat of water: 4.187 kJ / kg / ° Karrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





