
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The reagent needed to convert 2-methylpropene to
Concept Introduction:
A
In a chemical reaction, the substance which is involved in conversion is said to be reactant, whereas, the newly formed substance is called a product. Both reactants and products must be separated by an arrow.
Hydrohalogenation reaction is an addition reaction in which the hydrogen and halogen atoms like Cl, Br are bonded on un-statured carbon atoms of
Answer to Problem 13.67P
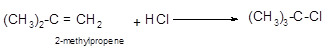
Explanation of Solution
The conversion of 2-methylpropene to
To get the hydrohalogenation product of any alkene, three steps must be followed;
- Locate the position of C=C in the molecule.
- Break the H-Cl bond of the reagent.
- Add one Cl atom to double-bonded C atom to form new C−Cl single bonds in the molecule.
- Add one H atom to another double-bonded C atom to form new C−H single bonds in the molecule.
- The reaction follows the Markovnikov rule which states that the H atom of H-X will bond to that double-bonded C atom which has more number of H atoms.
Hence, the hydrohalogenation of 2-methylpropene can be written as follows
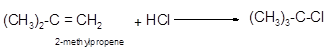
(b)
Interpretation:
The reagent that is needed to convert 2-methylpropene to
Concept Introduction:
A chemical reaction is the symbolic representation of the conversion of substances to new substances.
In a chemical reaction, the substance which is involved in conversion is said to be reactant, whereas, the newly formed substance is called a product. Both reactants and products must be separated by an arrow.
Hydrohalogenation reaction is an addition reaction in which the hydrogen and halogen atoms like Cl, Br are bonded on un-statured carbon atoms of alkene to form alkyl halide.
Answer to Problem 13.67P
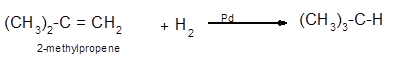
Explanation of Solution
The conversion of 2-methylpropene to
To get the hydrogenated product of any alkene, three steps must be followed;
- Locate the position of C=C in the molecule.
- Break the H−H bond of the reagent.
- Add one H atom to double-bonded C atom to form two new C−H single bonds in the molecule.
Hence the hydrogenation of 2-methylpropene can be written as:
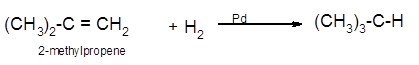
(c)
Interpretation:
The reagent that is needed to convert 2-methylpropene to
Concept Introduction:
A chemical reaction is the symbolic representation of the conversion of substances to new substances.
In a chemical reaction, the substance which is involved in conversion is said to be reactant, whereas, the newly formed substance is called a product. Both reactants and products must be separated by an arrow.
Hydrohalogenation reaction is an addition reaction in which the hydrogen and halogen atoms like Cl, Br are bonded on un-statured carbon atoms of alkene to form alkyl halide.
Answer to Problem 13.67P
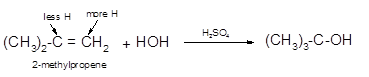
Explanation of Solution
The conversion of 2-methylpropene to
To get the hydration product of any alkene, three steps must be followed;
- Locate the position of C=C in the molecule.
- Break the H-OH bond of the reagent.
- Add the -OH group atom to double-bonded C atom to form new C−OH single bonds in the molecule.
- Add one H atom to another double-bonded C atom to form new C−H single bonds in the molecule.
- The reaction follows the Markovnikov rule which states that the H atom of H-OH will bond to that double-bonded C atom which has more number of H atoms.
Hence, the hydration of 2-methylpropene can be written as:
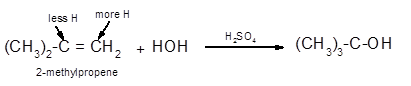
(d)
Interpretation:
The reagent that is needed to convert 2-methylpropene to
Concept Introduction:
A chemical reaction is the symbolic representation of the conversion of substances to new substances.
In a chemical reaction, the substance which is involved in conversion is said to be reactant, whereas, the newly formed substance is called a product. Both reactants and products must be separated by an arrow.
Hydrohalogenation reaction is an addition reaction in which the hydrogen and halogen atoms like Cl, Br are bonded on un-statured carbon atoms of alkene to form alkyl halide.
Answer to Problem 13.67P
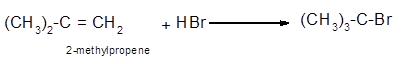
Explanation of Solution
The conversion of 2-methylpropene to
To get the hydrohalogenation product of any alkene, three steps must be followed;
- Locate the position of C=C in the molecule.
- Break the H-Br bond of the reagent.
- Add one Br atom to double-bonded C atom to form new C−Cl single bonds in the molecule.
- Add one H atom to another double-bonded C atom to form new C−H single bonds in the molecule.
- The reaction follows the Markovnikov rule which states that the H atom of H-X will bond to that double-bonded C atom which has more number of H atoms.
Hence, the hydrohalogenation of 2-methylpropene can be written as:
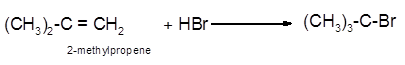
(e)
Interpretation:
The reagent that is needed to convert 2-methylpropene to
Concept Introduction:
A chemical reaction is the symbolic representation of the conversion of substances to new substances.
In a chemical reaction, the substance which is involved in conversion is said to be reactant, whereas, the newly formed substance is called a product. Both reactants and products must be separated by an arrow.
Hydrohalogenation reaction is an addition reaction in which the hydrogen and halogen atoms like Cl, Br are bonded on un-statured carbon atoms of alkene to form alkyl halide.
Answer to Problem 13.67P
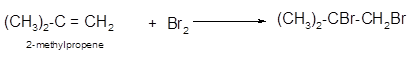
Explanation of Solution
The conversion of 2-methylpropene to
To get the halogenation product of any alkene, three steps must be followed:
- Locate the position of C=C in the molecule.
- Break the Br-Br bond of the reagent.
- Add one Br atom to double-bonded C atom to form two new C−Br single bonds in the molecule.
Hence, the halogenation of 2-methylpropene can be written as:
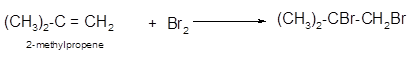
(f)
Interpretation:
The reagent that is needed to convert 2-methylpropene to
Concept Introduction:
A chemical reaction is the symbolic representation of the conversion of substances to new substances.
In a chemical reaction, the substance which is involved in conversion is said to be reactant, whereas, the newly formed substance is called a product. Both reactants and products must be separated by an arrow.
Hydrohalogenation reaction is an addition reaction in which the hydrogen and halogen atoms like Cl, Br are bonded on un-statured carbon atoms of alkene to form alkyl halide.
Answer to Problem 13.67P
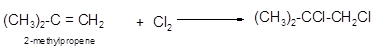
Explanation of Solution
The conversion of 2-methylpropene to
To get the halogenation product of any alkene, three steps must be followed:
- Locate the position of C=C in the molecule.
- Break the Cl-Cl bond of the reagent.
- Add one Cl atom to double-bonded C atom to form two new C−Cl single bonds in the molecule.
Hence the halogenation of 2-methylpropene can be written as follows:
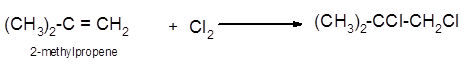
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
General, Organic, & Biological Chemistry
- How to get the predicted product of this reaction belowarrow_forwardPlease help me fill out the chart then using the chart describe the change from cystine to tyrosine and its impact on the protein. Then using the chart describe the change from histidine to aspartic acid.arrow_forwardWrite the Esterification reaction mechanism for acetic acid, and one propanol to make propanol ethanoate (molecule that gives peas its odor in flavor)arrow_forward
 Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
