
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Structure of the molecule B should be converted to a condensed structure and IUPAC name of the molecule should be given.
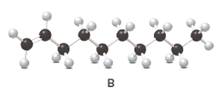
= (
Concept Introduction:
In alkene nomenclature longest C chain will be considered as the parent/ main C chain. At the end of the
Answer to Problem 13.104P
Condensed structure -
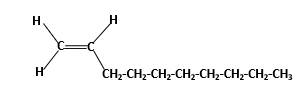
IUPAC name −Decene
Explanation of Solution
In alkenes there is a carbon-carbon double bond and different groups are connected to the two carbons. In most of the alkenes; out of four binding positions of carbon-carbon double bond, two of them are binds with two hydrogen atoms and other two binding positions are binds with two different alkyl groups.In this molecule, carbon atoms are represented in black and hydrogen atoms are represented in white color.Structure of a chemical compound is the arrangement of atoms and bonds in the space.
Condensed structure -
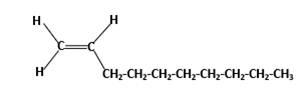
In this molecule, main carbon chain which contains the carbon-carbon double bond is a ten membered chain and there are no substituents in this molecule. According to the numbering of the main chain double bond gets the lowest number and it is number 1.Hence, IUPAC name of the molecule is decene.
(b)
Interpretation:
The resulting product should be identified after reacting
Concept Introduction:
Alkenes are hydrocarbon molecules that consist a carbon-carbon double bond which has the general formula of
Reaction of alkene with
Answer to Problem 13.104P
Explanation of Solution
Unsaturated (
(c)
Interpretation:
The resulting product should be identified after reacting
Concept Introduction:
Alkenes are hydrocarbon molecules that consist a carbon-carbon double bond which has the general formula of
Reaction of alkene with
Hydration reaction of alkenes follows the Markovnikov's rule.
Answer to Problem 13.104P
Explanation of Solution
Unsaturated (
Refer to the below reaction;
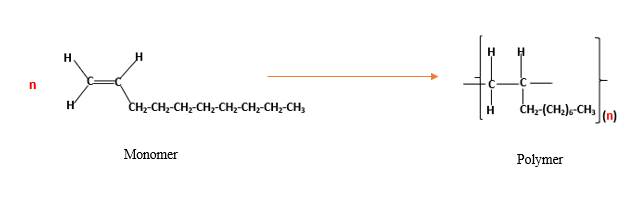
(d)
Interpretation:
The resulting polymer should be identified after
Concept Introduction:
Alkenes are hydrocarbon molecules that contain a carbon-carbon double bond inside a molecule.
Answer to Problem 13.104P
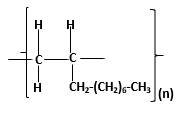
Explanation of Solution
Polymers are high molecular weight macromolecules which formed from covalently bonded monomer molecules. When forming polymers from alkene monomers, the weak bond which is in the carbon-carbon double bond is broken and new strong bond will form to connect the monomer molecules together. Hence; weak bond of the carbon-carbon double bond of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
General, Organic, & Biological Chemistry
- What is the final product when D-galactose reacts with hydroxylamine?arrow_forwardIndicate the formula of the product obtained by reacting methyl 5-chloro-5-oxopentanoate with 1 mole of 4-penten-1-ylmagnesium bromide.arrow_forwardIn the two chair conformations of glucose, the most stable is the one with all the OH groups in the equatorial position. Is this correct?arrow_forward
- please help me with my homeworkarrow_forwardhelparrow_forwardThe temperature on a sample of pure X held at 1.25 atm and -54. °C is increased until the sample boils. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.42 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 2 0 0 200 400 temperature (K) Xarrow_forward
- QUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' STEP 1 by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the photo attached*arrow_forwardpressure (atm) 3 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 0 0 200 temperature (K) 400 аarrow_forwarder your payment details | bar xb Home | bartleby x + aleksogi/x/isl.exe/1o u-lgNskr7j8P3jH-1Qs_pBanHhviTCeeBZbufuBYT0Hz7m7D3ZcW81NC1d8Kzb4srFik1OUFhKMUXzhGpw7k1 O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 1 3- 0- 0 200 Explanation Check temperature (K) 400 X Q Search L G 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved Terms of Use Privacy Cearrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax





