
Concept explainers
What alkyd halide is formed when each

b.
c.
(a)
Interpretation:
The resulting alkyl halide should be identified after reacting following alkene with

Concept Introduction:
Alkenes are hydrocarbon molecules that consist of a carbon-carbon double bond that has the general formula of
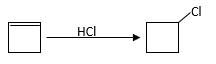
Reaction of an alkene with
Hydro halogenation reaction of alkenes follows Markovnikov's rule.
Answer to Problem 13.61P
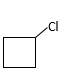
Explanation of Solution
Unsaturated (
Hydro halogenation reaction of alkenes follows Markovnikov's rule. When the addition of
Refer to the below reaction;
(b)
Interpretation:
The resulting alkyl halide should be identified after reacting following alkene with
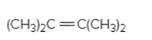
Concept Introduction:
Alkenes are hydrocarbon molecules that consist of a carbon-carbon double bond which has the general formula of
Reaction of an alkene with
Hydro halogenation reaction of alkenes follows Markovnikov's rule.
Answer to Problem 13.61P
Explanation of Solution
Unsaturated (
Hydro halogenation reaction of alkenes follows the Markovnikov's rule. When addition of
Refer to the below reaction;
(c)
Interpretation:
The resulting alkyl halide should be identified after reacting following alkene with
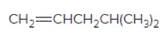
Concept Introduction:
Alkenes are hydrocarbon molecules that consist of a carbon-carbon double bond which has the general formula of
Reaction of an alkene with
Hydro halogenation reaction of alkenes follows the Markovnikov's rule.
Answer to Problem 13.61P
Explanation of Solution
Unsaturated (
Hydro halogenation reaction of alkenes follows the Markovnikov's rule. When the addition of
Refer to the below reaction;
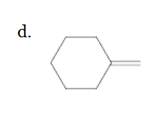
(d)
Interpretation:
The resulting alkyl halide should be identified after reacting following alkene with
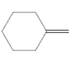
Concept Introduction:
Alkenes are hydrocarbon molecules that consist of a carbon-carbon double bond which has the general formula of
Reaction of an alkene with
Hydro halogenation reaction of alkenes follows the Markovnikov's rule.
Answer to Problem 13.61P
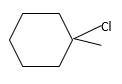
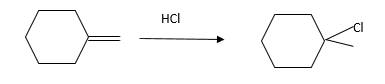
Explanation of Solution
Unsaturated (
Hydro halogenation reaction of alkenes follows the Markovnikov's rule. When
Refer to the below reaction;
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
General, Organic, & Biological Chemistry
- true or false, given that a 20.00 mL sample of NaOH took 24.15 mL of 0.141 M HCI to reach the endpoint in a titration, the concentration of the NaOH is 1.17 M.arrow_forwardin the bromothymol blue experiment, pKa was measured. A closely related compound has a Ka of 2.10 x 10-5. What is the pKa?a) 7.1b) 4.7c) 2.0arrow_forwardcalculate the equilibrium concentration of H2 given that K= 0.017 at a constant temperature for this reaction. The inital concentration of HBr is 0.050 M.2HBr(g) ↔ H2(g) + Br2(g)a) 4.48 x 10-2 M b) 5.17 x 10-3 Mc) 1.03 x 10-2 Md) 1.70 x 10-2 Marrow_forward
- true or falsegiven these two equilibria with their equilibrium constants:H2(g) + CI2(l) ↔ 2HCI(g) K= 0.006 CI2(l) ↔ CI2(g) K= 0.30The equilibrium contstant for the following reaction is 1.8H2(g) + CI2 ↔ 2HCI(g)arrow_forwardI2(g) + CI2(g) ↔ 2ICIK for this reaction is 81.9. Find the equilibrium concentration of I2 if the inital concentration of I2 and CI2 are 0.010 Marrow_forwardtrue or false,the equilibrium constant for this reaction is 0.50.PCI5(g) ↔ PCI3(g) + CI2(g)Based on the above, the equilibrium constant for the following reaction is 0.25.2PCI5(g) ↔. 2PCI3(g) + 2CI2(g)arrow_forward
- true or false, using the following equilibrium, if carbon dioxide is added the equilibrium will shift toward the productsC(s) + CO2(g) ↔ 2CO(g)arrow_forward2S2O2/3- (aq) + I2 (aq) ---> S4O2/6- (aq) +2I- (aq) Experiment I2 (M) S2O3- (M) Initital Rate (M/s) 1 0.01 0.01 0.0004 2 0.01 0.02 0.0004 3 0.02 0.01 0.0008 Calculate the overall order for this reaction using the table data a) 3b) 0c) 2d) 1arrow_forwardthe decomposition of N2O5 is the first order with a half-life of 1.98 minutes. If the inital concentration of N2O5 is 0.200 M, what is the concentration after 6 minutes?a) 0.612 Mb) 0.035 Mc) 0.024 Md) 0.100 Marrow_forward
- 20.00 mL of 0.150 M HCI is titrated with 0.075 M NaOH. What volume of NaOH is needed?a) 50 mLb) 20 mLc) 40 mLd) 26.66 mLarrow_forward20.00 mL of 0.150 M NaOH is titrated with 37.75 mL of HCI. What is the molarity of the HCI?a) 0.150 Mb) 0.079 Mc) 0.025 Md) 0.050 Marrow_forwardin the following reaction, the OH- acts as which of these?NO2- (aq) + H2O (l) ⇌ OH- (aq) + HNO2 (aq)a) not a weak acidb) basec) acidarrow_forward
 Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning





