
For the transistors in the circuit in Figure
(a)
The values of the differential mode voltage gain and the common mode voltage gain for the given transistor circuit.
Answer to Problem 11.93P
The differential-mode voltage gain is
The common-mode voltage gain is
Explanation of Solution
Given:
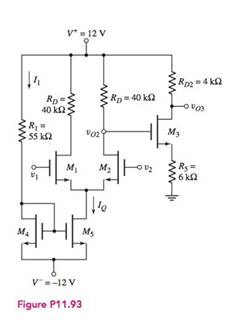
The given circuit is shown below.
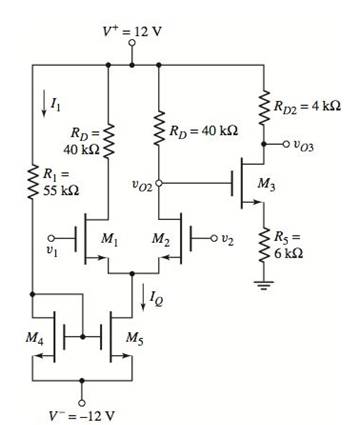
The transistor parameters are:
Calculation:
The small signal model of the given transistor circuit is shown below:
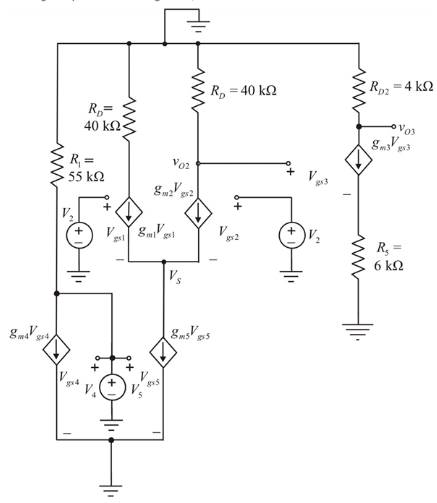
The value of the gate-source voltage of the transistor 4 is calculated as shown below:
The quiescent current is,
The value of the gate-source voltage of the transistor 3 is calculated as shown below:
The transconductance parameters for the differential gain are calculated as shown below:
The differential gain is,
The common mode gain is,
(b)
The values of the output voltage for the given input voltages.
To compare: The result with the ideal case.
Answer to Problem 11.93P
The output voltage is
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given circuit is shown below.
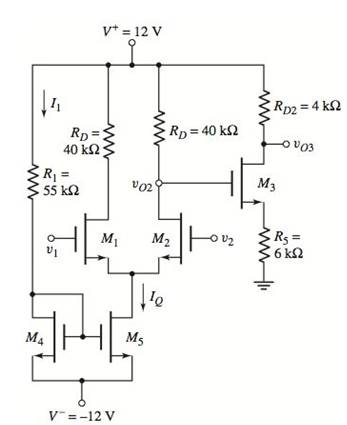
The circuit parameters are:
Calculation:
The output voltage is calculated as shown below:
On comparing the above output voltage with the ideal case,
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
MICROELECT. CIRCUIT ANALYSIS&DESIGN (LL)
- I need an expert mathematical solution. The radiation intensity of an aperture antenna, mounted on an infinite ground plane with perpendicular to the aperture. is rotationally symmetric (not a function of 4), and it is given by U sin (77 sin 0) π sin Find the approximate directivity (dimensionless and in dB) using numerical integration. Use the DIRECTIVITY computer program at the end of this chapter.arrow_forwardDon't use ai to answer I will report you answer.arrow_forwardDon't use ai to answer I will report you answerarrow_forward
- Need handwritten solution not using chatgptarrow_forwardHandwritten Solution pleasearrow_forwardThe E-field pattern of an antenna. independent of , varies as follows: E 0 0° ≤ 0≤ 45° 45°<≤ 90° 90° <8180° (a) What is the directivity of this antenna? Umax 7 why did we use this law Umax = 12 but we divided by 2? In the sent Solution = R 27arrow_forward
- The normalized far-zone field pattern of an antenna is given by (sin cos²) E = 0 00 and 0 ≤ ≤ π/2. 3/22 π elsewhere Find the directivity using (a) the exact expression In the sent soalation Use Prad=2+1 7/2 Pre= 2 + 1 Sco³odo + 5 siño de Where did the 2 Com from?arrow_forwardPen and paper solution please with explaination not using chatgptarrow_forwardhowarrow_forward
- A four pole generator having wave wound armature winding has 51 slots ,each slot containing 20 conductors,what will be the voltage generated in the machine when driven at 1500rpm assuming the flux per pole is 7mWb Don't use Artificial intelligencearrow_forwardNeed Handwritten solution Do not use chatgpt Or AIarrow_forwardI need a detailed solution to a problem. The far-zone electric field intensity (array factor) of an end-fire two-element array antenna, placed along the z-axis and radiating into free-space, is given by E=cos (cos - 1) Find the directivity using (a) Kraus' approximate formula (b) the DIRECTIVITY computer program at the end of this chapter Repeat Problem 2.19 when E = cos -jkr 0505π $[ (cos + 1) (a). Elmax = Cost (case-1)] | max" = 1 at 8-0°. 0.707 Emax = 0.707.(1) = cos [(cose,-1)] (cose-1) = ± 0,= {Cos' (2) = does not exist (105(0)= 90° = rad. Bir Do≈ 4T ar=2() = = Bar 4-1-273 = 1.049 dB T₂ a. Elmax = cos((cose +1)), 0.707 = cos (Close,+1)) = 1 at 6 = π Imax (Cose+1)=== G₁ = cos(-2) does not exist. Girar=2()=π. 4T \cos (0) + 90° + rad Do≈ = +=1.273=1.049dB IT 2arrow_forward
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,





