
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
10th Edition
ISBN: 9780134319650
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 10.6, Problem 10.42P
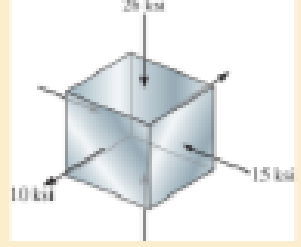
The cube of aluminum is subjected to the three stresses shown. Determine the principal strains. Take Eal = 10(103) ksi and val = 0.33.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
help
any help i dont understand
Battery operated train
Mueh
Groll
CD Af Pair
160,000 kg 0.0005
0.15
19
5m² 1.2kg/m³ 0.98 0.9
Tet neng
0.88
Tesla Prated
Tesla Trated Ywheel ng
Joyle
2
270 kW
440NM
0,45m 20
8.5kg m
Consider a drive cycle of a 500km trip with 3 stops in
the middle. Other than the acceleration and deceleration
associated with the three stops, the tran maintains.
constant cruise speed velocity of 324 km/hr. The
tran will fast charge at each stop for 15 min at a
rate Peharge = 350 kW
Εμ
(MN
15MIN
Stop
w charging
(350kW)
GMIJ
t
6MM
6AW
1) calculate the battery power required to mantain.
constant velocity
of
324km/hr
2) determine the battery energy,
energy required to
constant velocity portion of this drive.
Cover the
3) calculate the battery energy required to accelerate
the train to 324/04/hr.
4) calculate the battery energy that is either fost
in deceleration or recovered due to regenerative
breaking
etc
Chapter 10 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Ch. 10.3 - Prove that the sum of the normal strains in...Ch. 10.3 - The state of strain at the point on the arm has...Ch. 10.3 - The state of strain at the point on the pin leaf...Ch. 10.3 - The state of strain at the point on the pin leaf...Ch. 10.3 - The state of strain at the point on the leaf of...Ch. 10.3 - Use the strain transformation equations and...Ch. 10.3 - Use the strain transformation equations and...Ch. 10.3 - Use the strain transformation equations to...Ch. 10.3 - Use the strain transformation equations to...Ch. 10.3 - Use the strain- transformation equations to...
Ch. 10.3 - Use the strain transformation equations to...Ch. 10.3 - Determine the equivalent state of strain on an...Ch. 10.3 - Determine the equivalent state of strain which...Ch. 10.3 - Use the strain transformation equations to...Ch. 10.3 - Determine the equivalent state of strain, which...Ch. 10.3 - Solve Prob.103 using Mohrs circle. 103. The state...Ch. 10.3 - using Mohrs circle. 103. The state of strain at...Ch. 10.3 - Solve Prob.105 using Mohrs circle. 105. The state...Ch. 10.3 - Solve Prob.108 using Mohrs circle 108. The state...Ch. 10.3 - using Mohrs circle. 106. The state of strain at a...Ch. 10.5 - The strain at point A on the bracket has...Ch. 10.5 - Determine (a) the principal strains at A, (b) the...Ch. 10.5 - Determine (a) the principal strains at A, in the...Ch. 10.5 - The following readings are obtained for each gage:...Ch. 10.5 - The following readings are obtained for each gage:...Ch. 10.5 - The following readings are obtained for each gage:...Ch. 10.5 - The following readings are obtained from each...Ch. 10.6 - For the case of plane stress, show that Hookes law...Ch. 10.6 - to develop the strain tranformation equations....Ch. 10.6 - Determine the modulus of elasticity and Polssons...Ch. 10.6 - If it is subjected to an axial load of 15 N such...Ch. 10.6 - If it has the original dimensions shown, determine...Ch. 10.6 - If it has the original dimensions shown, determine...Ch. 10.6 - A strain gage having a length of 20 mm Is attached...Ch. 10.6 - Determine the bulk modulus for each of the...Ch. 10.6 - The strain gage is placed on the surface of the...Ch. 10.6 - Determine the associated principal stresses at the...Ch. 10.6 - Determine the applied load P. What is the shear...Ch. 10.6 - If a load of P = 3 kip is applied to the A-36...Ch. 10.6 - The cube of aluminum is subjected to the three...Ch. 10.6 - The principal strains at a point on the aluminum...Ch. 10.6 - A uniform edge load of 500 lb/in. and 350 lb/in....Ch. 10.6 - Prob. 10.45PCh. 10.6 - A single strain gage, placed in the vertical plane...Ch. 10.6 - A single strain gage, placed in the vertical plane...Ch. 10.6 - If the material is graphite for which Eg = 800 ksi...Ch. 10.6 - Determine the normal stresses x and y in the plate...Ch. 10.6 - The steel shaft has a radius of 15 mm. Determine...Ch. 10.6 - Prob. 10.51PCh. 10.6 - The A-36 steel pipe is subjected to the axial...Ch. 10.6 - Air is pumped into the steel thin-walled pressure...Ch. 10.6 - Air is pumped into the steel thin-walled pressure...Ch. 10.6 - Prob. 10.55PCh. 10.6 - The thin-walled cylindrical pressure vessel of...Ch. 10.6 - The thin-walled cylindrical pressure vessel of...Ch. 10.6 - Prob. 10.58PCh. 10.7 - A material is subjected to plane stress. Express...Ch. 10.7 - A material is subjected to plane stress. Express...Ch. 10.7 - The yield stress for a zirconium-magnesium alloy...Ch. 10.7 - Solve Prob. 1061 using the maximum distortion...Ch. 10.7 - If a machine part is made of tool L2 steel and a...Ch. 10.7 - Solve Prob.1063 using the maximum distortion...Ch. 10.7 - Prob. 10.65PCh. 10.7 - If a shaft is made of a material for which y = 75...Ch. 10.7 - Solve Prob.1066 using the maximum shear stress...Ch. 10.7 - If the material is machine steel having a yield...Ch. 10.7 - The short concrete cylinder having a diameter of...Ch. 10.7 - Prob. 10.70PCh. 10.7 - The plate is made of Tobin bronze, which yields at...Ch. 10.7 - The plate is made of Tobin bronze, which yields at...Ch. 10.7 - An aluminum alloy is to be used for a solid drive...Ch. 10.7 - If a machine part is made of titanium (TI-6A1-4V)...Ch. 10.7 - The components of plane stress at a critical point...Ch. 10.7 - The components of plane stress at a critical point...Ch. 10.7 - The 304-stainless-steel cylinder has an inner...Ch. 10.7 - The 304-stainless-steel cylinder has an inner...Ch. 10.7 - If the 2-in diameter shaft is made from brittle...Ch. 10.7 - If the 2-in diameter shaft is made from cast iron...Ch. 10.7 - If Y = 50 ksi, determine the factor of safety for...Ch. 10.7 - Prob. 10.82PCh. 10.7 - If the yield stress for steel is Y = 36 ksi,...Ch. 10.7 - Prob. 10.84PCh. 10.7 - The state of stress acting at a critical point on...Ch. 10.7 - The shaft consists of a solid segment AB and a...Ch. 10.7 - The shaft consists of a solid segment AB and a...Ch. 10.7 - Prob. 10.88PCh. 10.7 - If Y = 50 ksi, determine the factor of safety for...Ch. 10.7 - The gas tank is made from A-36 steel and has an...Ch. 10.7 - The internal loadings at a critical section along...Ch. 10.7 - If the material is machine steel having a yield...Ch. 10.7 - If the material is machine steel having a yield...Ch. 10 - In the case of plane stress, where the in-plane...Ch. 10 - The plate is made of material having a modulus of...Ch. 10 - If the material is machine steel having a yield...Ch. 10 - Determine if yielding has occurred on the basis of...Ch. 10 - The 60 strain rosette is mounted on a beam. The...Ch. 10 - Use the strain transformation equations to...Ch. 10 - If the strain gages a and b at points give...Ch. 10 - Use the strain-transformation equations and...Ch. 10 - Use the strain transformation equations to...Ch. 10 - Specify the orientation of the corresponding...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Look at the following description of a problem domain:
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Data Structures (4th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Assume a telephone signal travels through a cable at two-thirds the speed of light. How long does it take the s...
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
What are the design issues for character string types?
Concepts Of Programming Languages
17–1C A high-speed aircraft is cruising in still air. How does the temperature of air at the nose of the aircra...
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
How are relationships between tables expressed in a relational database?
Modern Database Management
Porter’s competitive forces model: The model is used to provide a general view about the firms, the competitors...
Management Information Systems: Managing The Digital Firm (16th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A 22-lb block B rests as shown on a 28-lb bracket A. The coefficients of friction are μs=0.30μs=0.30 and μk=0.25μk=0.25 between block B and bracket A, and there is no friction in the pulley or between the bracket and the horizontal surface. solved in a previous part. max weight of block C if block B is not to slide on bracket A is 5.045 lbs. Please solve for the acceleration of each Blockarrow_forwardTest 1 .DOCX * A File Edit View Tools Help INDUSTRIAL ENGINEERING PROGRAMME IMB 411-INDUSTRIAL LOGISTICS TEST 1- SEPTEMBER 12, 2012 Instructions: Answer all questions. Time allowed is 1.5 hours. Identify your script with your student number ONLY (Do not write your name). 1. Define the following terms (i) Logistics management (ii) Supply chain management (iii) Vertical integration in a supply chain (3 Marks) (3 Marks) (3 Marks) 2. (a) Using examples of your choice, briefly discuss the following levels of customer service (1) Pre-transaction elements (ii) Transaction elements (4 Marks) (4 Marks) (iii) Post-transaction elements (4 Marks) (b) "The challenge facing Dumelang Enterprise (Pty) Ltd is to establish the real profitability of their customers and to develop service strategies that will improve the profitability of all customers". As a logistics consultant, briefly discuss how you can advise Dumelang's customer service management. 3. (a) List the three main forms of inventory in a…arrow_forwardIt is decided to install several single-jet Pelton wheels to produce a total power of 18 MW. The available head is 246 m. The wheel rotational speed is 650 rpm and the speed ratio (❤) = 0.46. The diameter of the nozzle (jet) is limited to be 0.167 m with a Cv of 0.95. The efficiency of each turbine is 87%. Determine: (1) The number of Pelton wheels to be used, and (2) The bucket angle.arrow_forward
- (I) [40 Points] Using centered finite difference approximations as done in class, solve the equation for O: d20 dx² + 0.010+ Q=0 subject to the boundary conditions shown in the stencil below. Do this for two values of Q: (a) Q = 0.3, and (b) Q= √(0.5 + 2x)e-sinx (cos(5x)+x-0.5√1.006-x| + e −43*|1+.001+x* | * sin (1.5 − x) + (cosx+0.001 + ex-1250+ sin (1-0.9x)|) * x - 4.68x4. For Case (a) (that is, Q = 0.3), use the stencil in Fig. 1. For Case (b), calculate with both the stencils in Fig. 1 and Fig 2. For all the three cases, show a table as well as a plot of O versus x. Discuss your results. Use MATLAB and hand in the MATLAB codes. 1 0=0 x=0 2 3 4 0=1 x=1 Fig 1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 0=0 x=0 0=1 x=1 Fig 2arrow_forwardFig 2 (II) [60 Points] Using centered finite difference approximation as done in class, solve the equation: 020 020 + მx2 მy2 +0.0150+Q=0 subject to the boundary conditions shown in the stencils below. Do this for two values of Q: (a) Q = 0.3, and (b) Q = 10.5x² + 1.26 * 1.5 x 0.002 0.008. For Case (a) (that is, Q = 0.3) use Fig 3. For Case (b), use both Fig. 3 and Fig 4. For all the three cases, show a table as well as the contour plots of versus (x, y), and the (x, y) heat flux values at all the nodes on the boundaries x = 1 and y = 1. Discuss your results. Use MATLAB and hand in the MATLAB codes. (Note that the domain is (x, y)e[0,1] x [0,1].) 0=0 0=0 4 8 12 16 10 Ꮎ0 15 25 9 14 19 24 3 11 15 0=0 8-0 0=0 3 8 13 18 23 2 6 сл 5 0=0 10 14 6 12 17 22 1 6 11 16 21 13 e=0 Fig 3 Fig 4 Textbook: Numerical Methods for Engineers, Steven C. Chapra and Raymond P. Canale, McGraw-Hill, Eighth Edition (2021).arrow_forwardShip construction question. Sketch and describe the forward arrangements of a ship. Include componets of the structure and a explanation of each part/ term. Ive attached a general fore end arrangement. Simplfy construction and give a brief describion of the terms.arrow_forward
- Problem 1 Consider R has a functional relationship with variables in the form R = K xq xx using show that n ✓ - (OR 1.) = i=1 2 Их Ux2 Ихэ 2 (177)² = ² (1)² + b² (12)² + c² (1)² 2 UR R x2 x3arrow_forward4. Figure 3 shows a crank loaded by a force F = 1000 N and Mx = 40 Nm. a. Draw a free-body diagram of arm 2 showing the values of all forces, moments, and torques that act due to force F. Label the directions of the coordinate axes on this diagram. b. Draw a free-body diagram of arm 2 showing the values of all forces, moments, and torques that act due to moment Mr. Label the directions of the coordinate axes on this diagram. Draw a free body diagram of the wall plane showing all the forces, torques, and moments acting there. d. Locate a stress element on the top surface of the shaft at A and calculate all the stress components that act upon this element. e. Determine the principal stresses and maximum shear stresses at this point at A.arrow_forward3. Given a heat treated 6061 aluminum, solid, elliptical column with 200 mm length, 200 N concentric load, and a safety factor of 1.2, design a suitable column if its boundary conditions are fixed-free and the ratio of major to minor axis is 2.5:1. (Use AISC recommended values and round the ellipse dimensions so that both axes are whole millimeters in the correct 2.5:1 ratio.)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Lec21, Part 5, Strain transformation; Author: Mechanics of Materials (Libre);https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sgJvz5j_ubM;License: Standard Youtube License