
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
10th Edition
ISBN: 9780134319650
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 10.7, Problem 10.83P
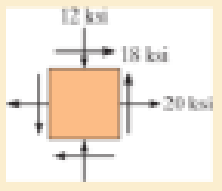
If the yield stress for steel is σY = 36 ksi, determine if yielding occurs using the maximum distortion energy theory.
10−83. Solve Prob.10−82 using the maximum shear stress theory.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
6-13. A smooth tube in the form of a circle of radius r rotates in its vertical plane with a
constant angular velocity w. The position of a particle of mass m that slides inside
the tube is given by the relative coordinate p. Find the differential equation for .
e
О
E
g
ω
Figure P6-13
Problem 2
Consider the power drawn by a resistance load in a DC circuit. The power is calculated as P = VI or P = 1²R. It is
given that the normalized uncertainty or % percentage uncertainty in measurements of I, R, and V are the same.
Find the uncertainty in P using the two different expressions for power. Is the uncertainty using the two methods
the same? If not, WHY, explain?
A piston–cylinder device contains 3 kg of nitrogen initially at 100 kPa and 25°C. Nitrogen is now compressed slowly in a polytropic process during which PV1.3 = constant until the volume is reduced by one-half. Determine the work done and the heat transfer for this process. The gas constant of N2 is R = 0.2968 kPa·m3/kg·K. The cv value of N2 at the anticipated average temperature of 350 K is 0.744 kJ/kg·K (Table A-2b).
The work done for this process is kJ.
The heat transfer for this process is kJ.
Chapter 10 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Ch. 10.3 - Prove that the sum of the normal strains in...Ch. 10.3 - The state of strain at the point on the arm has...Ch. 10.3 - The state of strain at the point on the pin leaf...Ch. 10.3 - The state of strain at the point on the pin leaf...Ch. 10.3 - The state of strain at the point on the leaf of...Ch. 10.3 - Use the strain transformation equations and...Ch. 10.3 - Use the strain transformation equations and...Ch. 10.3 - Use the strain transformation equations to...Ch. 10.3 - Use the strain transformation equations to...Ch. 10.3 - Use the strain- transformation equations to...
Ch. 10.3 - Use the strain transformation equations to...Ch. 10.3 - Determine the equivalent state of strain on an...Ch. 10.3 - Determine the equivalent state of strain which...Ch. 10.3 - Use the strain transformation equations to...Ch. 10.3 - Determine the equivalent state of strain, which...Ch. 10.3 - Solve Prob.103 using Mohrs circle. 103. The state...Ch. 10.3 - using Mohrs circle. 103. The state of strain at...Ch. 10.3 - Solve Prob.105 using Mohrs circle. 105. The state...Ch. 10.3 - Solve Prob.108 using Mohrs circle 108. The state...Ch. 10.3 - using Mohrs circle. 106. The state of strain at a...Ch. 10.5 - The strain at point A on the bracket has...Ch. 10.5 - Determine (a) the principal strains at A, (b) the...Ch. 10.5 - Determine (a) the principal strains at A, in the...Ch. 10.5 - The following readings are obtained for each gage:...Ch. 10.5 - The following readings are obtained for each gage:...Ch. 10.5 - The following readings are obtained for each gage:...Ch. 10.5 - The following readings are obtained from each...Ch. 10.6 - For the case of plane stress, show that Hookes law...Ch. 10.6 - to develop the strain tranformation equations....Ch. 10.6 - Determine the modulus of elasticity and Polssons...Ch. 10.6 - If it is subjected to an axial load of 15 N such...Ch. 10.6 - If it has the original dimensions shown, determine...Ch. 10.6 - If it has the original dimensions shown, determine...Ch. 10.6 - A strain gage having a length of 20 mm Is attached...Ch. 10.6 - Determine the bulk modulus for each of the...Ch. 10.6 - The strain gage is placed on the surface of the...Ch. 10.6 - Determine the associated principal stresses at the...Ch. 10.6 - Determine the applied load P. What is the shear...Ch. 10.6 - If a load of P = 3 kip is applied to the A-36...Ch. 10.6 - The cube of aluminum is subjected to the three...Ch. 10.6 - The principal strains at a point on the aluminum...Ch. 10.6 - A uniform edge load of 500 lb/in. and 350 lb/in....Ch. 10.6 - Prob. 10.45PCh. 10.6 - A single strain gage, placed in the vertical plane...Ch. 10.6 - A single strain gage, placed in the vertical plane...Ch. 10.6 - If the material is graphite for which Eg = 800 ksi...Ch. 10.6 - Determine the normal stresses x and y in the plate...Ch. 10.6 - The steel shaft has a radius of 15 mm. Determine...Ch. 10.6 - Prob. 10.51PCh. 10.6 - The A-36 steel pipe is subjected to the axial...Ch. 10.6 - Air is pumped into the steel thin-walled pressure...Ch. 10.6 - Air is pumped into the steel thin-walled pressure...Ch. 10.6 - Prob. 10.55PCh. 10.6 - The thin-walled cylindrical pressure vessel of...Ch. 10.6 - The thin-walled cylindrical pressure vessel of...Ch. 10.6 - Prob. 10.58PCh. 10.7 - A material is subjected to plane stress. Express...Ch. 10.7 - A material is subjected to plane stress. Express...Ch. 10.7 - The yield stress for a zirconium-magnesium alloy...Ch. 10.7 - Solve Prob. 1061 using the maximum distortion...Ch. 10.7 - If a machine part is made of tool L2 steel and a...Ch. 10.7 - Solve Prob.1063 using the maximum distortion...Ch. 10.7 - Prob. 10.65PCh. 10.7 - If a shaft is made of a material for which y = 75...Ch. 10.7 - Solve Prob.1066 using the maximum shear stress...Ch. 10.7 - If the material is machine steel having a yield...Ch. 10.7 - The short concrete cylinder having a diameter of...Ch. 10.7 - Prob. 10.70PCh. 10.7 - The plate is made of Tobin bronze, which yields at...Ch. 10.7 - The plate is made of Tobin bronze, which yields at...Ch. 10.7 - An aluminum alloy is to be used for a solid drive...Ch. 10.7 - If a machine part is made of titanium (TI-6A1-4V)...Ch. 10.7 - The components of plane stress at a critical point...Ch. 10.7 - The components of plane stress at a critical point...Ch. 10.7 - The 304-stainless-steel cylinder has an inner...Ch. 10.7 - The 304-stainless-steel cylinder has an inner...Ch. 10.7 - If the 2-in diameter shaft is made from brittle...Ch. 10.7 - If the 2-in diameter shaft is made from cast iron...Ch. 10.7 - If Y = 50 ksi, determine the factor of safety for...Ch. 10.7 - Prob. 10.82PCh. 10.7 - If the yield stress for steel is Y = 36 ksi,...Ch. 10.7 - Prob. 10.84PCh. 10.7 - The state of stress acting at a critical point on...Ch. 10.7 - The shaft consists of a solid segment AB and a...Ch. 10.7 - The shaft consists of a solid segment AB and a...Ch. 10.7 - Prob. 10.88PCh. 10.7 - If Y = 50 ksi, determine the factor of safety for...Ch. 10.7 - The gas tank is made from A-36 steel and has an...Ch. 10.7 - The internal loadings at a critical section along...Ch. 10.7 - If the material is machine steel having a yield...Ch. 10.7 - If the material is machine steel having a yield...Ch. 10 - In the case of plane stress, where the in-plane...Ch. 10 - The plate is made of material having a modulus of...Ch. 10 - If the material is machine steel having a yield...Ch. 10 - Determine if yielding has occurred on the basis of...Ch. 10 - The 60 strain rosette is mounted on a beam. The...Ch. 10 - Use the strain transformation equations to...Ch. 10 - If the strain gages a and b at points give...Ch. 10 - Use the strain-transformation equations and...Ch. 10 - Use the strain transformation equations to...Ch. 10 - Specify the orientation of the corresponding...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- I tried solving this one but I have no idea where I went wrong can you please help me out with this?arrow_forwardDuring a picnic on a hot summer day, all the cold drinks disappear quickly, and the only available drinks are those at the ambient temperature of 85°F. In an effort to cool a 12- fluid-oz drink in a can, a person grabs the can and starts shaking it in the iced water of the chest at 32°F. Using the properties of water for the drink, determine the mass of ice that will melt by the time the canned drink cools to 37°F. The density and specific heat of water at the average temperature of (85+37)/2 = 61ºF are ρ = 62.3 lbm/ft3 and cp = 1.0 Btu/lbmºF (Table A-3E). The heat of fusion of water is 143.5 Btu/lbm. The mass of ice that will melt by the time the canned drink cools to 37°F is lbm.arrow_forwardSteam enters a nozzle at 400°C and 800 kPa with a velocity of 10 m/s and leaves at 375°C and 400 kPa while losing heat at a rate of 26.5 kW. For an inlet area of 800 cm2, determine the velocity and the volume flow rate of the steam at the nozzle exit. Use steam tables. At the left side of the lines, 800 kilo Pascal, 400 degree Centigrade, 10 meters per second are shown. At the right side of the lines, 400 kilo Pascal, 375 degree Centigrade are shown. The velocity of the steam at the nozzle exit is m/s. The volume flow rate of the steam at the nozzle exit is m3/s.arrow_forward
- A saturated liquid–vapor mixture of water, called wet steam, in a steam line at 1450 kPa is throttled to 50 kPa and 100°C. What is the quality in the steam line? Use data from the steam tables. Above the right side of the tube, 50 kilos 100 degree Centigrade indicated. The quality in the steam line is .arrow_forwardI tried this problems a couple of ways but I don't know what I'm doing wrong can you help me please?arrow_forwardRefrigerant-134a enters a compressor at 180 kPa as a saturated vapor with a flow rate of 0.35 m3/min and leaves at 900 kPa. The power supplied to the refrigerant during the compression process is 2.35 kW. What is the temperature of R-134a at the exit of the compressor? The temperature of R-134a at the exit of the compressor is °C.arrow_forward
- Air enters the compressor of a gas-turbine plant at ambient conditions of 100 kPa and 25°C with a low velocity and exits at 1 MPa and 347°C with a velocity of 90 m/s. The compressor is cooled at a rate of 1500 kJ/min, and the power input to the compressor is 250 kW. Determine the mass flow rate of air through the compressor. The inlet and exit enthalpies of air are 298.2 kJ/kg and 628.07 kJ/kg. The mass flow rate of air is kg/s.arrow_forwardConsider a 1000-W iron whose base plate is made of 0.5-cm-thick aluminum alloy 2024-T6 (ρ = 2770 kg/m3 and cp = 875 J/kg·°C). The base plate has a surface area of 0.03 m2. Initially, the iron is in thermal equilibrium with the ambient air at 22°C. Assuming 90 percent of the heat generated in the resistance wires is transferred to the plate, determine the minimum time needed for the plate temperature to reach 240°C. The minimum time needed for the plate temperature to reach 240°C is s.arrow_forwardA desktop computer is to be cooled by a fan whose flow rate is 0.34 m3/min. Determine the mass flow rate of air through the fan at an elevation of 3400 m where the air density is 0.7 kg/m3. Also, if the average velocity of air is not to exceed 123 m/min, determine the diameter of the casing of the fan. The mass flow rate of air through the fan is kg/min. The diameter of the casing of the fan is cm.arrow_forward
- The diffuser in a jet engine is designed to decrease the kinetic energy of the air entering the engine compressor without any work or heat interactions. Calculate the velocity at the exit of a diffuser when air at 100 kPa and 30°C enters it with a velocity of 359 m/s and the exit state is 200 kPa and 90°C. The specific heat of air at the average temperature of 60°C = 333 K is cp = 1.007 kJ/kg·K. The velocity at the exit is m/sarrow_forwardA piston–cylinder device contains 3 kg of nitrogen initially at 100 kPa and 25°C. Nitrogen is now compressed slowly in a polytropic process during which PV1.3 = constant until the volume is reduced by one-half. Determine the work done and the heat transfer for this process. The gas constant of N2 is R = 0.2968 kPa·m3/kg·K. The cv value of N2 at the anticipated average temperature of 350 K is 0.744 kJ/kg·K (Table A-2b). The work done for this process is kJ. The heat transfer for this process is kJ.arrow_forwardA 4-m × 5-m × 6-m room is to be heated by a baseboard resistance heater. It is desired that the resistance heater be able to raise the air temperature in the room from 5 to 25°C within 10 min. Assuming no heat losses from the room and an atmospheric pressure of 100 kPa, determine the required power of the resistance heater. Assume constant specific heats at room temperature. The properties of air are R = 0.287 kJ/kg·K and cv = 0.718 kJ/kg·K (Table A-2a). The required power of the resistance heater is kW.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Understanding Failure Theories (Tresca, von Mises etc...); Author: The Efficient Engineer;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xkbQnBAOFEg;License: Standard youtube license