
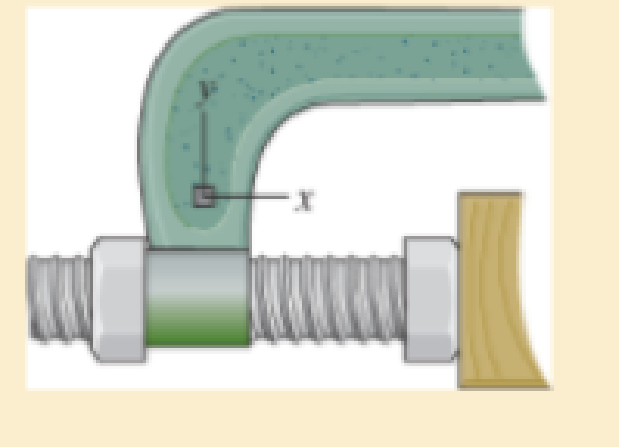
The state of strain at the point on the arm has components of εx = 200 (10−6), εy = −300 (10−6), and γxy = 400(10−6). Use the strain transformation equations to determine the equivalent in-plane strains on an element oriented at an angle of 30° counterclockwise from the original position, Sketch the deformed element due to these strains within the x–y plane.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 10 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Automotive Technology: Principles, Diagnosis, And Service (6th Edition) (halderman Automotive Series)
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Data Structures (4th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
Fluid Mechanics: Fundamentals and Applications
Vector Mechanics For Engineers
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
- My ID# 016948724 please find the forces for Fx=0: fy=0: fz=0: please help me to solve this problem step by steparrow_forwardMy ID# 016948724 please solve the proble step by step find the forces fx=o: fy=0; fz=0; and find shear moment and the bending moment diagran please draw the diagram for the shear and bending momentarrow_forwardMy ID#016948724. Please help me to find the moment of inertia lx ly are a please show to solve step by stepsarrow_forward
- My ID# 016948724arrow_forwardPlease do not use any AI tools to solve this question. I need a fully manual, step-by-step solution with clear explanations, as if it were done by a human tutor. No AI-generated responses, please.arrow_forwardPlease do not use any AI tools to solve this question. I need a fully manual, step-by-step solution with clear explanations, as if it were done by a human tutor. No AI-generated responses, please.arrow_forward
- Please do not use any AI tools to solve this question. I need a fully manual, step-by-step solution with clear explanations, as if it were done by a human tutor. No AI-generated responses, please.arrow_forward[Q2]: The cost information supplied by the cost accountant is as follows:Sales 20,00 units, $ 10 per unitCalculate the (a/ newsale guantity and (b) new selling price to earn the sameVariable cost $ 6 per unit, Fixed Cost $ 30,000, Profit $ 50,000profit ifi) Variable cost increases by $ 2 per unitil) Fixed cost increase by $ 10,000Ili) Variable cost increase by $ 1 per unit and fixed cost reduces by $ 10,000arrow_forwardcan you please help me perform Visual Inspection and Fractography of the attatched image: Preliminary examination to identify the fracture origin, suspected fatigue striation, and corrosion evidences.arrow_forward
 Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L


