
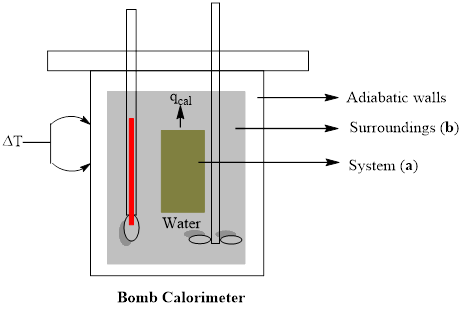
A bomb calorimeter is a study metal vessel in which samples can be ignited and the amount of heat given off can be measured as the heat warms up surrounding water. Draw a rough sketch of such an experimental setup and label (a) the system and (b) the surroundings.
Interpretation:
A rough sketch of experimental setup of bomb calorimeter is to be drawn with labeling of (a) system and (b) surroundings
Concept introduction:
Calorimeter is an instrument which is used to measure the heat of the chemical reactions, physical changes and heat capacity. There are different types of calorimeter such as 1) differential scanning calorimeter 2) isothermal calorimeter 3) titration calorimeter 4) accelerated rate calorimeter. The main components of calorimeter consist of a thermometer attached to a metal container with water suspended above a combustion chamber. This device is used in various fields to study thermodynamics, chemistry and biochemistry.
Answer to Problem 1.1E
Explanation of Solution
A bomb calorimeter is a kind of constant-volume calorimeter, which is used to measure the heat of combustion of a particular reaction. The four important components of bomb calorimeter are as follows; 1) a bomb (vessel) having the combustible material. It must be a strong and thick-walled vessel which is made up of high-quality metal and should have a provision to open for inserting the sample, to remove the products of combustion and to clean the apparatus. 2) a bucket (container) with a measured quantity of water to hold the bomb. Besides, it should be fitted with a probe to read the temperature and a mechanical stirrer to promote rapid thermal equilibrium with no excessive heat in the form of mechanical energy. These buckets are made with a highly polished exterior finish to reduce the absorption and emission of heat as radiation. 3) An insulating jacket to protect the container from transient thermal changes during the combustion process
The enthalpy change per mole of a substance A in a reaction between A and B is measured by adding the substances separately into the calorimeter and calculating the initial and final temperatures of the system. On multiplying the temperature change by the mass and specific heat capacities of the substances, we can get the value of energy which is given off during the reaction. When we divide the energy change by moles of A involved in the reaction, we can obtain the enthalpy change of reaction.
A rough sketch of experimental setup of bomb calorimeter is drawn with labeling of (a) system and (b) surroundings.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
Physical Chemistry
- 1. Identify the following alkenes as E or Z NH₂ Br 2. Draw the structures based on the IUPAC names (3R,4R)-3-bromo-4-fluoro- 1-hexene (Z)-4-bromo-2-iodo-3-ethyl- 3-heptene تر 3. For the following, predict all possible elimination product(s) and circle the major product. HO H₂SO4 Heat 80 F4 OH H2SO4 Heat 어요 F5 F6 1 A DII 4 F7 F8 F9 % & 5 6 7 * ∞ 8 BAB 3 E R T Y U 9 F D G H J K O A F11 F10arrow_forwardDraw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. ○ O 1. H₂O, pyridine 2. neutralizing work-up a N W X 人 Parrow_forward✓ Check the box under each molecule that has a total of five ẞ hydrogens. If none of the molecules fit this description, check the box underneath the table. tab OH CI 0 Br xx Br None of these molecules have a total of five ẞ hydrogens. esc Explanation Check caps lock shift 1 fn control 02 F2 W Q A N #3 S 80 F3 E $ t 01 205 % 5 F5 & 7 © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibility FT * 8 R T Y U כ F6 9 FIG F11 F D G H J K L C X V B < N M H option command P H + F12 commandarrow_forward
- Draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts and the carboxylic acid side product. O 1. CHзMgBr (excess) 2. H₂O ✓ W X 人arrow_forwardIf cyclopentyl acetaldehyde reacts with NaOH, state the product (formula).arrow_forwardDraw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. N S S HgCl2, H2SO4 く 8 W X Parrow_forward
- tab esc く Drawing the After running various experiments, you determine that the mechanism for the following reaction occurs in a step-wise fashion. Br + OH + Using this information, draw the correct mechanism in the space below. 1 Explanation Check F2 F1 @2 Q W A os lock control option T S # 3 80 F3 Br $ 4 0105 % OH2 + Br Add/Remove step X C F5 F6 6 R E T Y 29 & 7 F D G H Click and drag to start drawing a structure. © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Ce A F7 DII F8 C Ո 8 * 9 4 F10 F C J K L C V Z X B N M H command P ge Coarrow_forwardIndicate compound A that must react with ethylbenzene to obtain 4-ethylbenzene-1-sulfonic acid. 3-bromo-4-ethylbenzene-1-sulfonic acid.arrow_forwardPart 1 of 2 Draw the structure of A, the minor E1 product of the reaction. esc I Skip Part Check H₂O, D 2 A + Click and drag to start drawing a structure. -0- F1 F2 1 2 # 3 Q A 80 F3 W E S D F4 $ 4 % 5 F5 ㅇ F6 R T Y F G X 5 & 7 + Save 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. DII F7 F8 H * C 80 J Z X C V B N 4 F9 6arrow_forward
- File Preview The following is a total synthesis of the pheromone of the western pine beetle. Such syntheses are interesting both because of the organic chemistry, and because of the possibility of using species specific insecticides, rather than broad band insecticides. Provide the reagents for each step. There is some chemistry from our most recent chapter in this synthesis, but other steps are review from earlier chapters. (8 points) COOEt COOEt A C COOEt COOEt COOH B OH OTS CN D E See the last homework set F for assistance on this one. H+, H₂O G OH OH The last step is just nucleophilic addition reactions, taking the ketone to an acetal, intramolecularly. But it is hard to visualize the three dimensional shape as it occurs. Frontalin, pheromone of the western pine beetlearrow_forwardFor the reaction below: 1. Draw all reasonable elimination products to the right of the arrow. 2. In the box below the reaction, redraw any product you expect to be a major product. C Major Product: Check + ◎ + X ง © Cl I F2 80 F3 I σ F4 I F5 NaOH Click and drawing F6 A 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights E F7 F8 $ # % & 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Q W E R T Y U A S D F G H Jarrow_forwardCan I please get help with this graph. If you can show exactly where it needs to pass through.arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 World of ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780618562763Author:Steven S. ZumdahlPublisher:Houghton Mifflin College Div
World of ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780618562763Author:Steven S. ZumdahlPublisher:Houghton Mifflin College Div Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning





