
Concept explainers
Size and Life
Physicists look for simple models and general principles that underlie and explain diverse physical phenomena. In the first 13 chapters of this textbook, you’ve seen that just a handful of general principles and laws can be used to solve a wide range of problems. Can this approach have any relevance to a subject like biology? It may seem surprising, but there are general 'laws of biology“’ that apply, with quantitative accuracy, to organisms as diverse as elephants and mice.
Let’s look at an example. An elephant uses more metabolic power than a mouse. This is not surprising, as an elephant is much bigger. But recasting the data shows an interesting trend. When we looked at the energy required to raise the temperature of different substances, we considered specific heat. The “specific” meant that we considered the heat required for 1 kilogram. For animals, rather than metabolic rate, we can look at the specific metabolic rate, the metabolic power used per kilogram of tissue. If we factor out the mass difference between a mouse and an elephant, are their specific metabolic powers the same?
In fact, the specific metabolic rate varies quite a bit among mammals, as the graph of specific metabolic rate versus mass shows. But there is an interesting trend: All of the data points lie on a single smooth curve. In other words, there really is a biological law we can use to predict a mammal’s metabolic rate knowing only its mass M. In particular, the specific metabolic rate is proportional to M –0.25. Because a 4000 kg elephant is 160,000 times more massive than a 25 g mouse, the mouse’s specific metabolic power is (160,000)0.25 = 20 times that of the elephant. A law that shows how a property scales with the size of a system is called a scaling law.
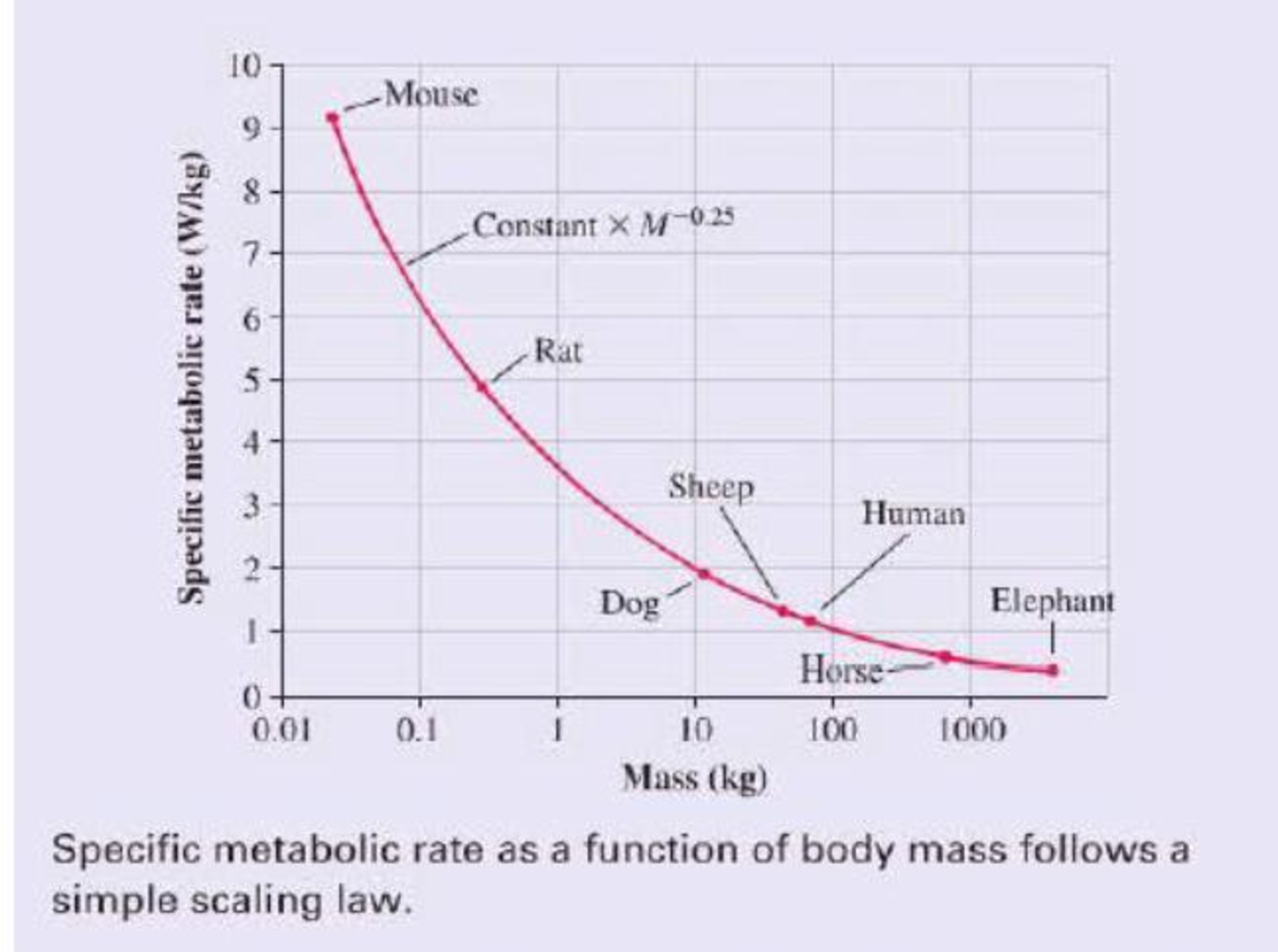
A similar scaling law holds for birds, reptiles, and even bacteria. Why should a single simple relationship hold true for organisms that range in size from a single cell to a 100 ton blue whale? Interestingly, no one knows for sure. It is a matter of current research to find out just what this and other scaling laws tell us about the nature of life.
Perhaps the metabolic-power scaling law is a result of
If heat dissipation were the only factor limiting metabolism, we can show that the specific metabolic rate should scale as M–0.33quite different from the M–0.25 scaling observed. Clearly, another factor is at work. Exactly what underlies the M–0.25 scaling is still a matter of debate, but some recent analysis suggests the scaling is due to limitations not of heat transfer but of fluid flow. Cells in mice, elephants, and all mammals receive nutrients and oxygen for metabolism from the bloodstream. Because the minimum size of a capillary is about the same for all mammals, the structure of the circulatory system must vary from animal to animal. The human aorta has a diameter of about 1 inch; in a mouse, the diameter is approximately l/20th of this. Thus a mouse has fewer levels of branching to smaller and smaller blood vessels as we move from the aorta to the capillaries. The smaller blood vessels in mice mean that viscosity is more of a factor throughout the circulatory system. The circulatory system of a mouse is quite different from that of ail elephant.
A model of specific metabolic rate based on blood-flow limitations predicts a M–0.25 law, exactly as observed. The model also makes other testable predictions. For example, the model predicts that the smallest possible mammal should have a body mass of about 1 gram—exactly the size of the smallest shrew. Even smaller animals have different types of circulatory' systems; in the smallest animals, nutrient transport is by diffusion alone. But the model can be extended to predict that the specific metabolic rate for these animals will follow a scaling law similar to that for mammals, exactly as observed. It is too soon to know if this model will ultimately prove to be correct, but it’s indisputable that there are large-scale regularities in biology that follow mathematical relationships based on the laws of physics.
The following questions are related to the passage "Size and Life" on the previous page.
A typical timber wolf has a mass of 40 kg, a typical jackrabbit a mass of 2.5 kg. Given the scaling law presented in the passage, we’d expect the wolf to use ________ times more energy than a jackrabbit in the course of a day.
- A. 2
- B. 4
- C. 8
- D. 16
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter P Solutions
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
- Race car driver is cruising down the street at a constant speed of 28.9 m/s (~65 mph; he has a “lead” foot) when the traffic light in front of him turns red. a) If the driver’s reaction time is 160 ms, how far does he and his car travel down the road from the instant he sees the light change to the instant he begins to slow down? b) If the driver’s combined reaction and movement time is 750 ms, how far do he and his car travel down the road from the instant he sees the light change to the instant he slams on her brakes and car begins to slow down? c) If the driver’s average rate of acceleration is -9.5 m/s2 as he slows down, how long does it take him to come to a stop (use information about his speed of 28.9 m/s but do NOT use his reaction and movement time in this computation)? Please answer parts a-c. Show all work. For each question draw a diagram to show the vector/s. Show all the step and provide units in the answers. Provide answer to 2 decimal places unless stated otherwise.arrow_forwardBelow you will find 100 m split times for the American and France men’s 4x100 meter free style relay race during the 2008 Beijing Summer Olympics). Answer questions a-d. a) What was the total race time for each team, in seconds? b) Which team won the race? What was the difference in the teams’ times? c) What was the average speed for each team for the whole race? (provide answer to 3 decimal places). d) Calculate the average speed for each swimmer and report the results in a table like the one above. Remember to show the calculation steps. (provide answer to 3 decimal places). PLEASE SHOW ALL WORK AND STEPS.arrow_forwardNeed complete solution Pleasearrow_forward
- Below you will find 100 m split times for the American and France men’s 4x100 meter free style relay race during the 2008 Beijing Summer Olympics). Fill out the chart below. Calculate average speed per split (m/s). Show all work.arrow_forwardThe magnitude of vector →A i s 261. m and points in the direction 349.° counterclockwise from the positive x-axis. Calculate the x-component of this vector . Calculate the y-component of this vector.arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- 4.4 A man is dragging a trunk up the loading ramp of a mover's truck. The ramp has a slope angle of 20.0°, and the man pulls upward with a force F whose direction makes an angle of 30.0° 75.0° with the ramp (Fig. E4.4). (a) How large a force F is necessary for the component Fx parallel to the ramp to be 90.0 N? (b) How large will the component Fy perpendicular to the ramp be then? Figure E4.4 30.0 20.0°arrow_forward1. * A projectile is shot from a launcher at an angle e, with an initial velocity magnitude v., from a point even with a tabletop. The projectile lands on the tabletop a horizontal distance R (the "range") away from where it left the launcher. Set this up as a formal problem, and solve for vo (i.e., determine an expression for Vo in terms of only R, 0., and g). Your final equation will be called Equation 1.arrow_forward2. A projectile is shot from a launcher at an angle 0,, with an initial velocity magnitude vo, from a point even with a tabletop. The projectile hits an apple atop a child's noggin (see Figure 1). The apple is a height y above the tabletop, and a horizontal distance x from the launcher. Set this up as a formal problem, and solve for x. That is, determine an expression for x in terms of only v₁, o,y and g. Actually, this is quite a long expression. So, if you want, you can determine an expression for x in terms of v., 0., and time t, and determine another expression for timet (in terms of v., 0., y and g) that you will solve and then substitute the value of t into the expression for x. Your final equation(s) will be called Equation 3 (and Equation 4).arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College





