
Concept explainers
a.
To complete the table and form a graph
a.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The charity walk is 25.5km long.
J’s speed is, constant through-out the race, at 4.25km per hour.
Concept Used:
Equation making and solving
Graph:
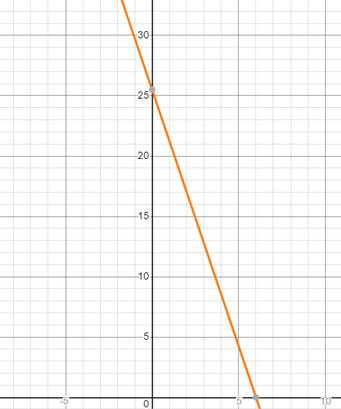
Calculation:
Let, the number of hours be “x”
Therefore, the equation will be,
Where, x is the time
y is the distance.
Hence, the table is,
| x | y=25.5-4.25x | y | (x,y) |
| 1 | 25.5-(4.25x1) | 21.25 | (1, 21.25) |
| 2 | 25.5-(4.25x2) | 17 | (2, 17) |
| 3 | 25.5-(4.25x3) | 12.75 | (3, 12.75) |
b.
To evaluate x and y- intercept.
b.
Answer to Problem 3.2.1P
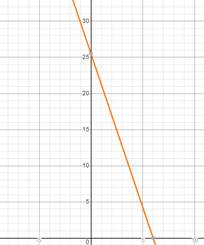
x-intercept shows the total time she took and the y-intercept shows the total distance.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The equation is 1y
Concept Used:
Graph evaluation
Calculation:
The x-intercept is the point where the line touches the x-axis. In this situation it shows the total time J takes to complete the race.
The y- intercept is the point where the line touches the y-axis. In this situation it shows the total distance J has to travel.
Conclusion:
x-intercept shows the total time she took and the y-intercept shows the total distance.
c.
To calculate the time it will take her, if she has walked 17km
c.
Answer to Problem 3.2.1P
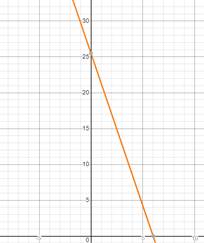
It will take her 4 hours more to complete the race.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Concept Used:
Graph reading.
Calculation:
Concluding from the graph, the point where J has completed 17km, that is, y is 17, is
Therefore, Time she took to reach 17km is,
Time she will take to complete the race now= total time- time at 17km
Substituting the values,
On solving,
Therefore, it will take her 4 hours more to complete the race.
Conclusion:
It will take her 4 hours more to complete the race.
d.
To evaluate the given situation
d.
Answer to Problem 3.2.1P
This new equation cannot give the solution
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The equation is
Replacing the constant with 8.5
Concept Used:
Equation evaluation
Graph:
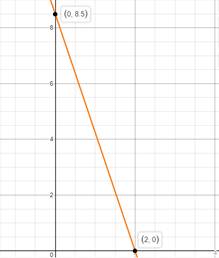
Calculation:
Substituting the new constant in the equation,
Forming the graph of this equation,
Concluding from the graph,
Total distance she has to travel is 8.5km
And time taken is 2hours.
Therefore, using this equation Reza would have not found the solution.
Conclusion:
This new equation cannot give the solution
Chapter ISG Solutions
Algebra 1, Homework Practice Workbook (MERRILL ALGEBRA 1)
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
Elementary Statistics (13th Edition)
University Calculus: Early Transcendentals (4th Edition)
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
Basic Business Statistics, Student Value Edition
- Please use the infinite series formula and specify how you did each step. Thank you.arrow_forward8) Solve the given system using the Gaussian Elimination process. 2x8y = 3 (-6x+24y = −6arrow_forward7) Solve the given system using the Gaussian Elimination process. (5x-4y = 34 (2x - 2y = 14arrow_forward
- 33 (a) (b) Let A(t) = = et 0 0 0 cos(t) sin(t) 0-sin(t) cos(t)) For any fixed tЄR, find det(A(t)). Show that the matrix A(t) is invertible for any tЄ R, and find the inverse (A(t))¹.arrow_forwardUse the infinite geometric sum to convert .258 (the 58 is recurring, so there is a bar over it) to a ratio of two integers. Please go over the full problem, specifying how you found r. Thank you.arrow_forwardH.w: Find the Eigen vectors for the largest Eigen value of the system X1+ +2x3=0 3x1-2x2+x3=0 4x1+ +3x3=0arrow_forward
- need help with 5 and 6 pleasearrow_forward1) Given matrix A below, answer the following questions: a) What is the order of the matrix? b) What is the element a13? c) What is the element a₁₁? 4 -1arrow_forward[25 points] Given the vector let v = ER² and the collection of vectors ε = E-{)·()}-{☹) (9)} = {(A)·(9)}· B: = and C = · {(6)·(})}· answer the following question. (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) verify Verify is a basis for R² and find the coordinate [] of under ε. Verify B is a basis for R2 and find the coordinate []B of ʊ Verify C is a basis for R2 and find the coordinate []c of under ε. under ε. Find the change-of-basis matrix [I]+B from basis B to basis ε, and EE+BUB Find the change-of-basis matrix [I]B+ε from basis Ɛ to basis B, and verify [U]B= [] B+EVEarrow_forward
- Explain the following terms | (a) linear span (b) dimension of vector space (c) linearly independent (d) linearly dependent (e) rank of matrix Aarrow_forward3. Let u = 3/5 √ = and = -4/5 -() Define V span{ū, }. (a) (b) (c) Show that {u, } is orthonormal and forms a basis for V. Explicitly compute Projy w. Explicitly give a non-zero vector in V+.arrow_forwardIs 1.1 0.65 -3.4 0.23 0.4 -0.44 a basis for R3? You must explain your answer 0arrow_forward
 Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning
Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press
Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





