
a)
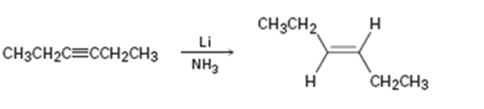
Interpretation:
Whether the mechanism of the reaction given is polar, radical or both to be identified.
Concept introduction:
A polar mechanism involves the formation of carbocation or carbanion as intermediates. A radical mechanism involves the free radicals as intermediates.
To identify:
Whether the mechanism of the reaction given is polar, radical or both.
b)
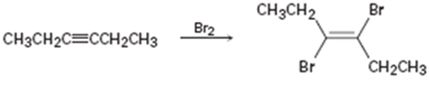
Interpretation:
Whether the mechanism of the reaction given is polar, radical or both to be identified.
Concept introduction:
A polar mechanism involves the formation of carbocation or carbanion as intermediates. A radical mechanism involves the free radicals as intermediates.
To identify:
Whether the mechanism of the reaction given is polar, radical or both.
c)
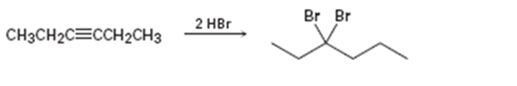
Interpretation:
Whether the mechanism of the reaction given is polar, radical or both to be identified.
Concept introduction:
A polar mechanism involves the formation of carbocation or carbanion as intermediates. A radical mechanism involves the free radicals as intermediates.
To identify:
Whether the mechanism of the reaction given is polar, radical or both.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 9 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- What is the relationship between A and B? H3C A Br Cl H3C B Br relationship (check all that apply) O same molecule O enantiomer O diastereomer structural isomer O stereoisomer isomer O need more information to decide O same molecule ☐ enantiomer Br Br Br CH3 Br CI CH3 O diastereomer ☐ structural isomer ☐ stereoisomer isomer O need more information to decide O same molecule O enantiomer Odiastereomer structural isomer O stereoisomer ☐ isomer O need more information to decidearrow_forwardb. Please complete the zig-zag conformation of the compound (3R,4S)-3,4-dichloro-2,5-dimethylhexane by writing the respective atoms in the boxes. 4arrow_forwardc. Serricornin, the female-produced sex pheromone of the cigarette beetle, has the following structure. OH What is the maximum number of possible stereoisomers? Is this structure a meso compound? d. Please consider the natural product alkaloids shown below. Are these two structures enantiomers, diastereomers or conformers? H HO H H HN HO HN R R с R=H cinchonidine R=ET cinchonine Harrow_forward
- Nail polish remover containing acetone was spilled in a room 5.23 m × 3.28 m × 2.76 m. Measurements indicated that 2,250 mg of acetone evaporated. Calculate the acetone concentration in micrograms per cubic meter.arrow_forwardPlease help me answer number 1. 1. If your graphs revealed a mathematical relationship between specific heat and atomic mass, write down an equation for the relationship. I also don't understand, is the equation from the line regression the one that I'm suppose use to show the relationship? If so could you work it all the way out?arrow_forwardDescribe the principle of resonance and give a set of Lewis Structures to illustrate your explanation.arrow_forward
- Don't used hand raitingarrow_forwardIt is not unexpected that the methoxyl substituent on a cyclohexane ring prefers to adopt the equatorial conformation. OMe H A G₂ = +0.6 kcal/mol OMe What is unexpected is that the closely related 2-methoxytetrahydropyran prefers the axial conformation: H H OMe OMe A Gp=-0.6 kcal/mol Methoxy: CH3O group Please be specific and clearly write the reason why this is observed. This effect that provides stabilization of the axial OCH 3 group in this molecule is called the anomeric effect. [Recall in the way of example, the staggered conformer of ethane is more stable than eclipsed owing to bonding MO interacting with anti-bonding MO...]arrow_forward206 Pb 82 Express your answers as integers. Enter your answers separated by a comma. ▸ View Available Hint(s) VAΣ ΜΕ ΑΣΦ Np, N₁ = 82,126 Submit Previous Answers ? protons, neutronsarrow_forward
- Please draw the inverted chair forms of the products for the two equilibrium reactions shown below. Circle the equilibrium reaction that would have a AG = 0, i.e., the relative energy of the reactant (to the left of the equilibrium arrows) equals the relative energy of the product? [No requirement to show or do calculations.] CH3 CH3 HH CH3 1 -CH3arrow_forward5. Please consider the Newman projection of tartaric acid drawn below as an eclipsed conformer (1). Please draw the most stable conformer and two intermediate energy conformers noting that staggered conformers are lower in energy than eclipsed forms even if the staggered conformers have gauche relationships between groups. [Draw the substituents H and OH on the front carbons and H, OH and CO₂H on the back carbons based on staggered forms. -CO₂H is larger than -OH.] OH COH ICOOH COOH COOH 1 2 COOH COOH 3 4 Staggered Staggered Staggered (most stable) Indicate the number of each conformer above (1, 2, 3 and 4) that corresponds to the relative energies below. Ref=0 Rotation 6. (60 points) a. Are compounds 1 and 2 below enantiomers, diastereomers or identical? OH OH HO HO LOH HO HO OH 2 OH OH b. Please complete the zig-zag conformation of the compound (3R,4S)-3,4-dichloro-2,5-dimethylhexane by writing the respective atoms in the boxes. 3.arrow_forwardThe plutonium isotope with 144 neutrons Enter the chemical symbol of the isotope.arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning




